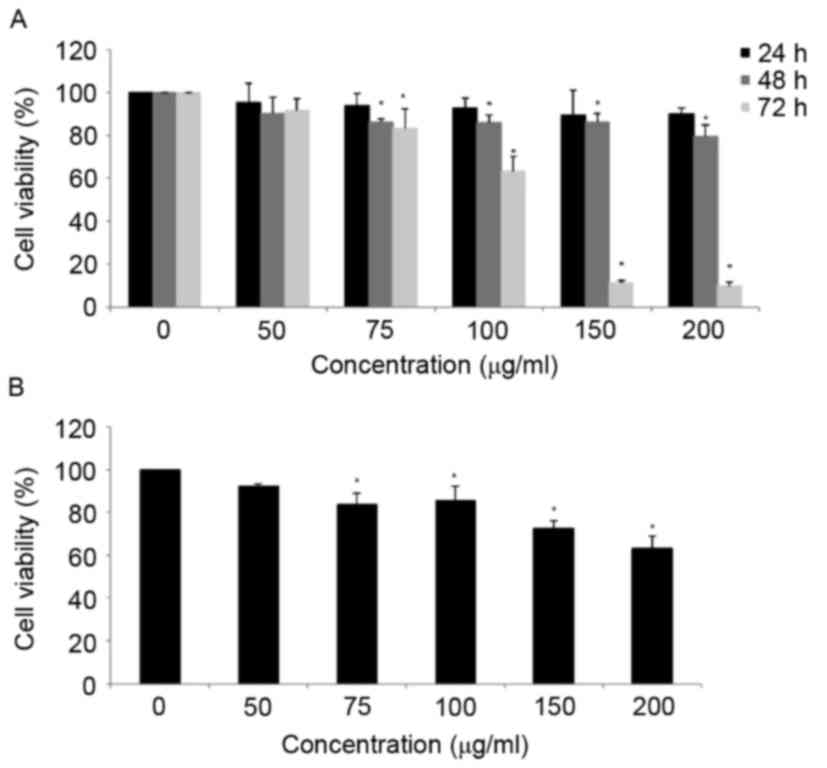
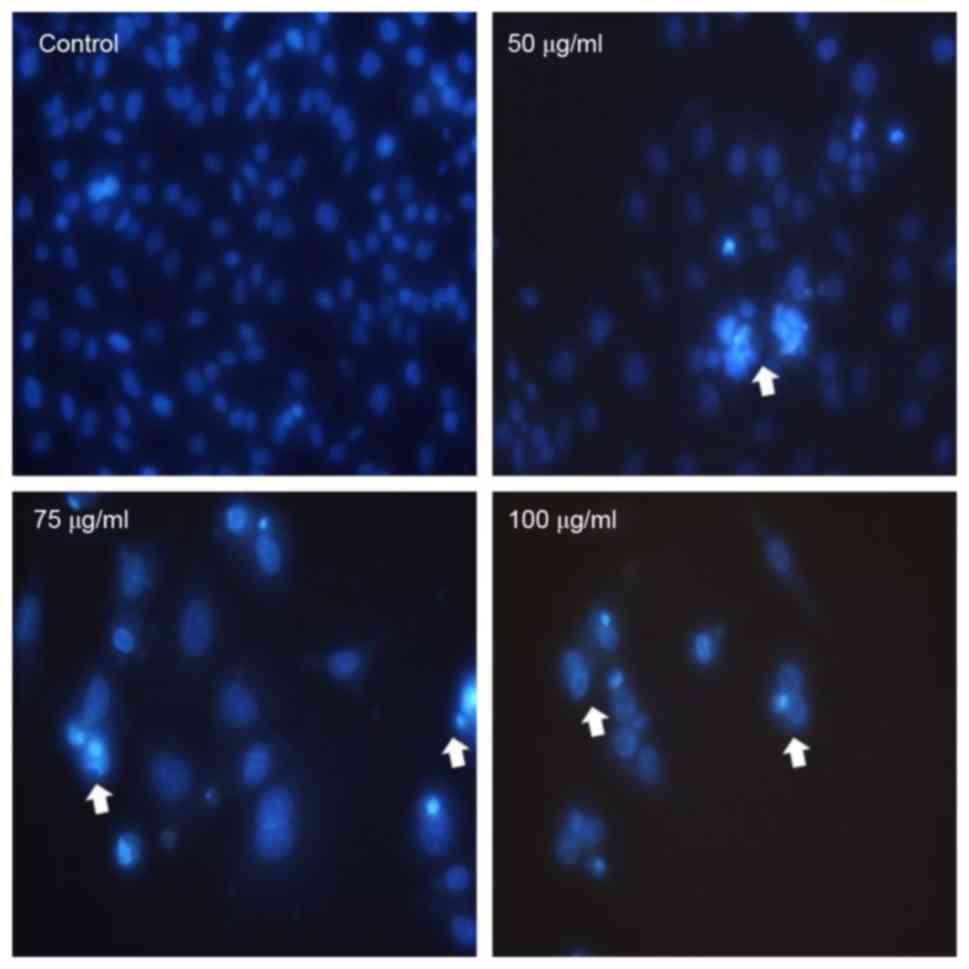
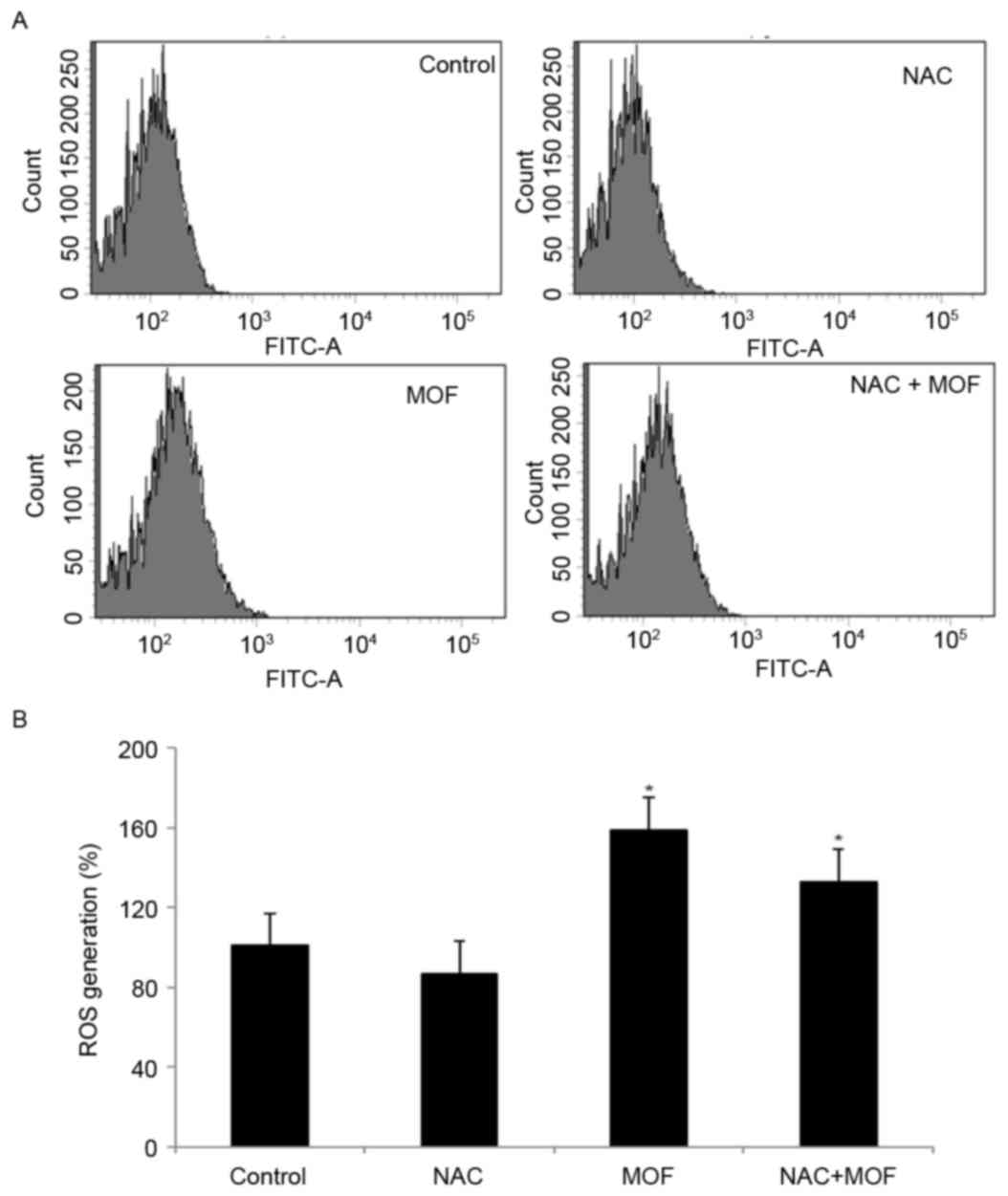
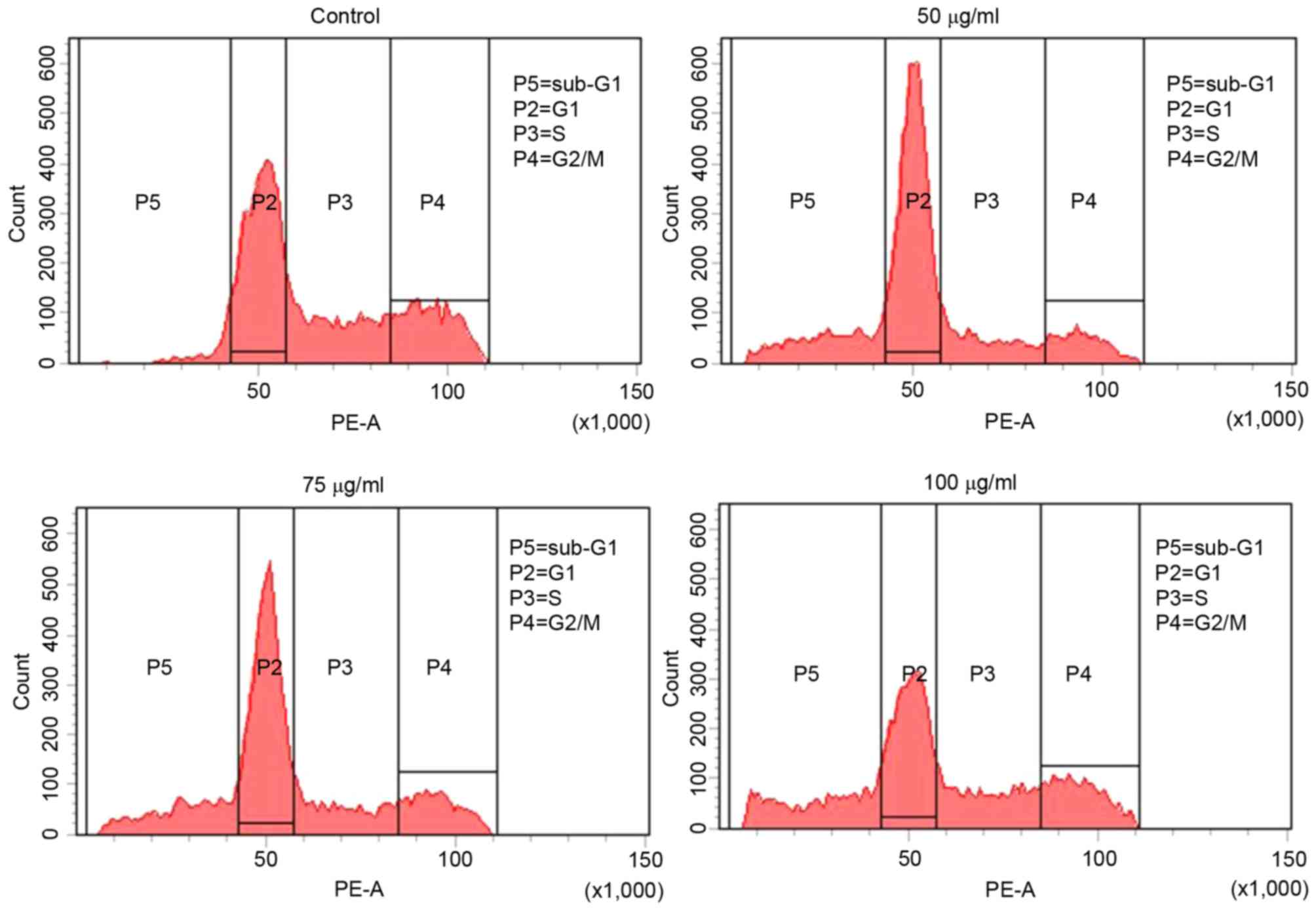
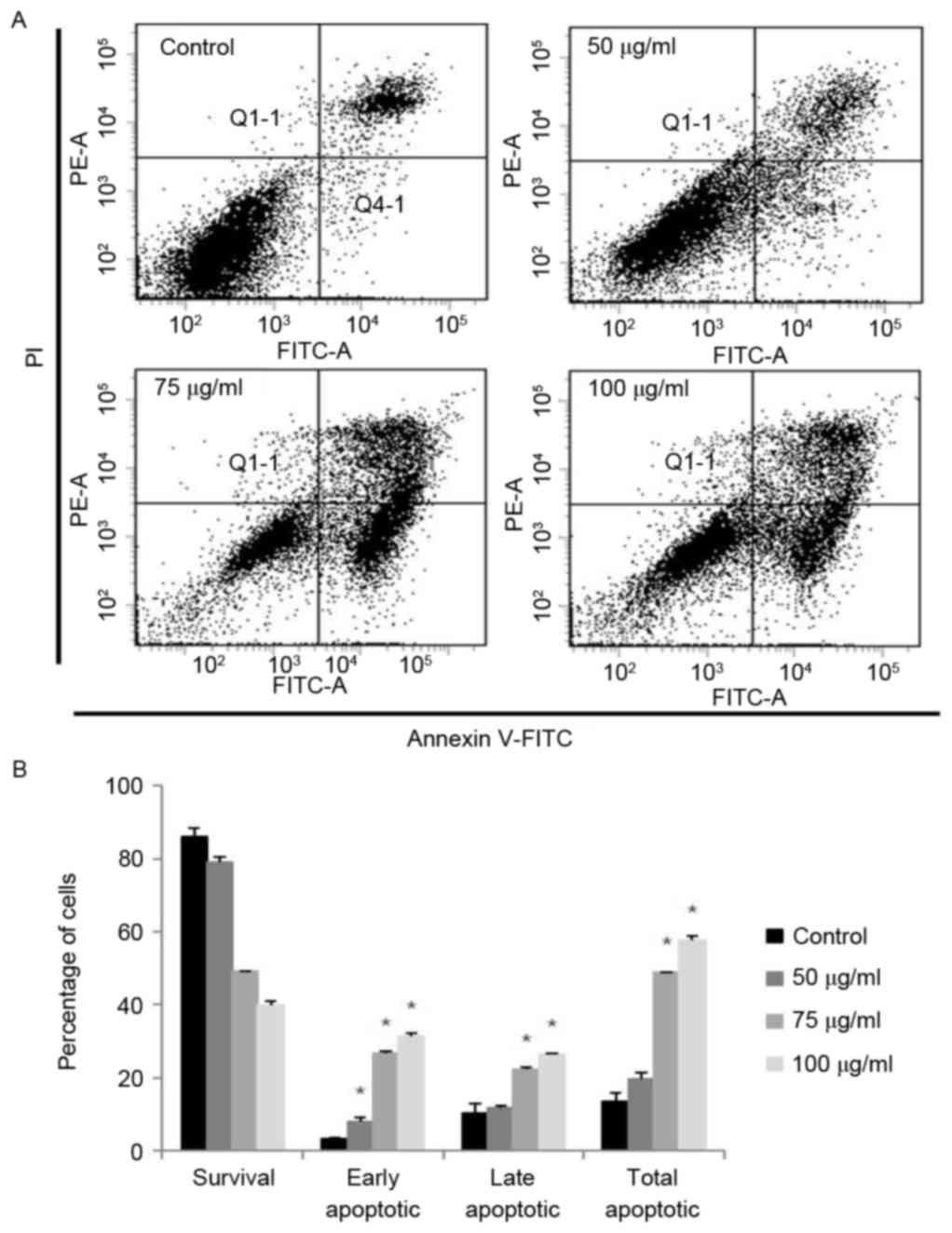
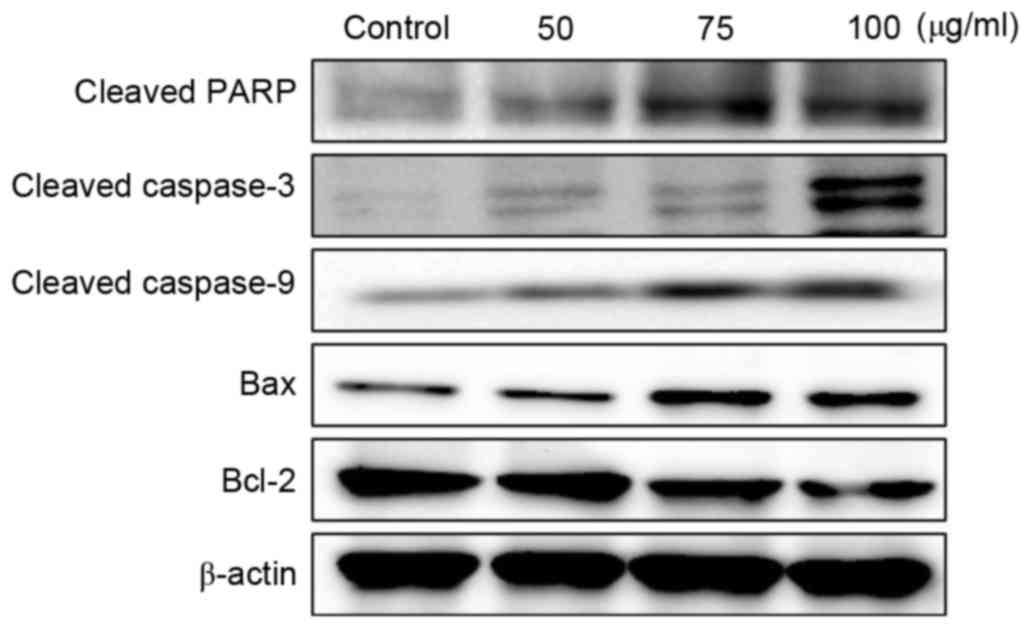
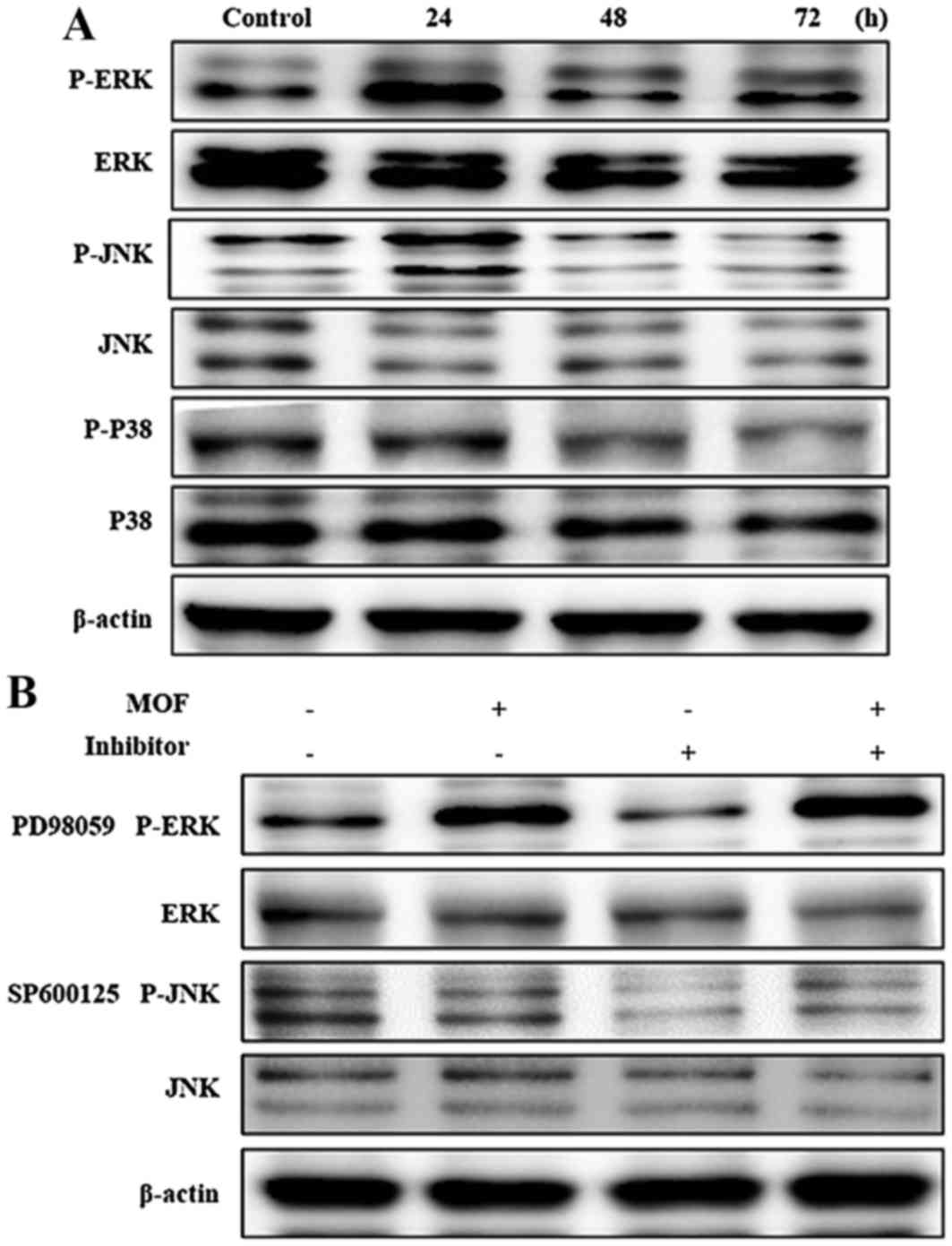
|
1
|
Singh S, Zafar A, Khan S and Naseem I:
Towards therapeutic advances in melanoma management: An overview.
Life Sci. Feb 23–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shayanfar N, Bahari L, Safaie-Naraghi Z,
Kamyab K, Gheytanchi E and Rezaei N: Negative HER2/neu
amplification using immunohistochemistry and chromogenic in situ
hybridization techniques in skin melanoma cases. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:421–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Read RL, Pasquali S, Haydu L, Thompson JF,
Stretch JR, Saw RP, Quinn MJ, Shannon K and Spillane AJ: Quality
assurance in melanoma surgery: The evolving experience at a large
tertiary referral centre. Eur J Surg Oncol. 41:830–836. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Markovic SN, Erickson LA, Rao RD, Weenig
RH, Pockaj BA, Bardia A, Vachon CM, Schild SE, McWilliams RR, Hand
JL, et al: Melanoma melanoma in the 21st century, part 2: Staging,
prognosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 82:pp. 490–513. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics for Hispanics/Latinos. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:283–298.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anwar F, Latif S, Ashraf M and Gilani AH:
Moringa oleifera A food plant with multiple medicinal uses.
Phytother Res. 21:17–25. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leone A, Fiorillo G, Criscuoli F,
Ravasenghi S, Santagostini L, Fico G, Spadafranca A, Battezzati A,
Schiraldi A, Pozzi F, et al: Nutritional characterization and
phenolic profiling of Moringa oleifera leaves grown in chad,
sahrawi refugee camps, and haiti. Int J Mol Sci. 16:18923–18937.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bharali R, Tabassum J and Azad MR:
Chemomodulatory effect of Moringa oleifera, Lam, on hepatic
carcinogen metabolising enzymes, antioxidant parameters and skin
papillomagenesis in mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 4:131–139.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Siddhuraju P and Becker K: Antioxidant
properties of various solvent extracts of total phenolic
constituents from three different agroclimatic origins of drumstick
tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves. J Agric Food Chem.
51:2144–2155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim DH, Park KW, Chae IG, Kundu J, Kim EH,
Kundu JK and Chun KS: Carnosic acid inhibits STAT3 signaling and
induces apoptosis through generation of ROS in human colon cancer
HCT116 cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:1096–1110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clarke PG and Clarke S: Historic
apoptosis. Nature. 378:2301995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stadtman ER: Protein oxidation in aging
and age-related diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 928:22–38. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sauer H, Wartenberg M and Hescheler J:
Reactive oxygen species as intracellular messengers during cell
growth and differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 11:173–186. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kuo PL, Chen CY and Hsu YL:
Isoobtusilactone A induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through
reactive oxygen species/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:7406–7420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Burris HA III: Overcoming acquired
resistance to anticancer therapy: Focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:829–842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alcazar O, Achberger S, Aldrich W, Hu Z,
Negrotto S, Saunthararajah Y and Triozzi P: Epigenetic regulation
by decitabine of melanoma differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Int
J Cancer. 131:18–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Triozzi PL, Aldrich W, Achberger S,
Ponnazhagan S, Alcazar O and Saunthararajah Y: Differential effects
of low-dose decitabine on immune effector and suppressor responses
in melanoma-bearing mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 61:1441–1450.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazder AF,
Minnan JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based
semiautomated colorimetric assay: Assessment of chemosensitivity
testing. Cancer Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lizard G, Fournel S, Genestier L, Dgedin
N, Chaput C, Flacher M, Mutin M, Panaye G and Revillard JP:
Kinetics of plasma membrane and mitochondrial alterations in cells
undergoing apoptosis. Cytometry. 21:275–283. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cathcart R, Schwiers E and Ames BN:
Detection of picomole levels of hydroperoxides using a fluorescent
dichlorofluorescein assay. Anal Biochem. 134:111–116. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC,
Grignani F and Riccardi C: A rapid and simple method for measuring
thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow
cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 139:271–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ryu MJ and Chung HS: [10]-Gingerol induces
mitochondrial apoptosis through activation of MAPK pathway in
HCT116 human colon cancer cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
51:92–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stadheim TA and Kucera GI: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK) is
required for mitoxantrone- and anisomycin-induced apoptosis in
HL-60 cells. Leuk Res. 26:55–65. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Erdei E and Torres SM: A new understanding
in the epidemiology of melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
10:1811–1823. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Diffey B: Climate change, ozone depletion
and the impact on ultraviolet exposure of human skin. Phys Med
Biol. 49:R1–R11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jerant AF, Johnson JT, Sheridan CD and
Caffrey TJ: Early detection and treatment of skin cancer. Am Fam
Physician. 62:357–368. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lopez RF, Lange N, Guy R and Bentley MV:
Photodynamic therapy of skin cancer: Controlled drug delivery of
5-ALA and its esters. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 56:77–94. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rebecca HSU, Sharon M, Arbainsyah A and de
Witte L: Moringa oleifera: Medicinal and Socio-Economic
UsesInternational Course on Economic Botany. National Herbarium
Leiden; The Netherlands: pp. 2–6. 2006
|
|
29
|
Guevara AP, Vargas C, Sakurai H, Fujiwara
Y, Hashimoto K, Maoka T, Kozuka M, Ito Y, Tokuda H and Nishino H:
An antitumor promoter from Moringa oleifera Lam. Mutat Res.
440:181–188. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mahajan SG and Mehta AA: Effect of Moringa
oleifera Lam. seed extract on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation
in guinea pigs. Inhal Toxicol. 20:897–909. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rhee SG: Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary
evil for cell signaling. Science. 312:1882–1883. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ozben T: Oxidative stress and apoptosis:
Impact on cancer therapy. J Pharm Sci. 96:2181–2196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCubrey JA, Lahair MM and Franklin RA:
Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase
signaling pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 8:1775–1789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hanawa N, Shinohara M, Saberi B, Gaarde
WA, Han D and Kaplowitz N: Role of JNK translocation to
mitochondria leading to inhibition of mitochondria bioenergetics in
acetaminophen-induced liver injury. J Biol Chem. 283:13565–13577.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dérijard B, Hibi M, Wu IH, Barrett T, Su
B, Deng T, Karin M and Davis RJ: JNK1: A protein kinase stimulated
by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun
activation domain. Cell. 76:10251994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kyriakis JM, Banerjee P, Nikolakaki E, Dai
T, Rubie EA, Ahmad MF, Avruch J and Woodgett JR: The
stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature.
369:156–160. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers J, Dickens M,
Han J, Ulevitch R and Davis RJ: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and
environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J
Biol Chem. 270:7420–7426. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ichijo H: From receptors to
stress-activated MAP kinases. Oncogene. 18:6087–6093. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Strasser A, O'Connor L and Dixit VM:
Apoptosis signaling. Ann Rev Biochem. 69:217–245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pathak S, Sharma CH, Jayaram HN and Singh
N: Apoptotic signaling induced by benzamideriboside: An in vitro
study. Mol Cell Biochem. 328:67–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gschwind M and Huber G: Apoptotic cell
death induced by beta-amyloid 1–42 peptide is cell type dependent.
J Neurochem. 65:292–300. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kiechle FL and Zhang X: Apoptosis:
Biochemical aspects and clinical implications. Clin Chim Acta.
326:27–45. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Brenner D and Mak TW: Mitochondrial cell
death effectors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:871–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cain K, Bratton SB and Cohen GM: The
Apaf-1 apoptosome: A large caspase-activating complex. Biochimie.
84:203–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bold RJ, Termuhlen PM and McConkey DJ:
Apoptosis, cancer and cancer therapy. Surg Oncol. 6:133–142. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shamas-Din A, Bindner S, Zhu W, Zaltsman
Y, Campbell C, Gross A, Leber B, Andrews DW and Fradin C: tBid
undergoes multiple conformational changes at the membrane required
for Bax activation. J Biol Chem. 288:22111–22127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Alves NL, van Lier RA and Eldering E:
Withdrawal symptoms on display: Bcl-2 members under investigation.
Trends Immunol. 28:26–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nagappan A, Park KI, Park HS, Kim JA, Hong
GE, Kang SR, Lee H, Kim EH, Lee WS, Won CK and Kim GS: Vitamin C
induces apoptosis in AGS cells by down-regulation of 14–3-3σ via a
mitochondrial dependent pathway. Food Chem. 135:1920–1928. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Guon TE and Chug HS: Hyperoside and rutin
of nelumbo nucifera induce mitochondrial apoptosis through a
caspase-dependent mechanism in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 11:2463–2470. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim KN, Ham YM, Moon JY, Kim MJ, Jung YH,
Jeon YJ, Lee NH, Kang N, Yang HM, Kim D and Hyun CG: Acanthoic acid
induces cell apoptosis through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway
in HL-60 human promyelocytic leukaemia. Food Chem. 135:2112–2117.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|