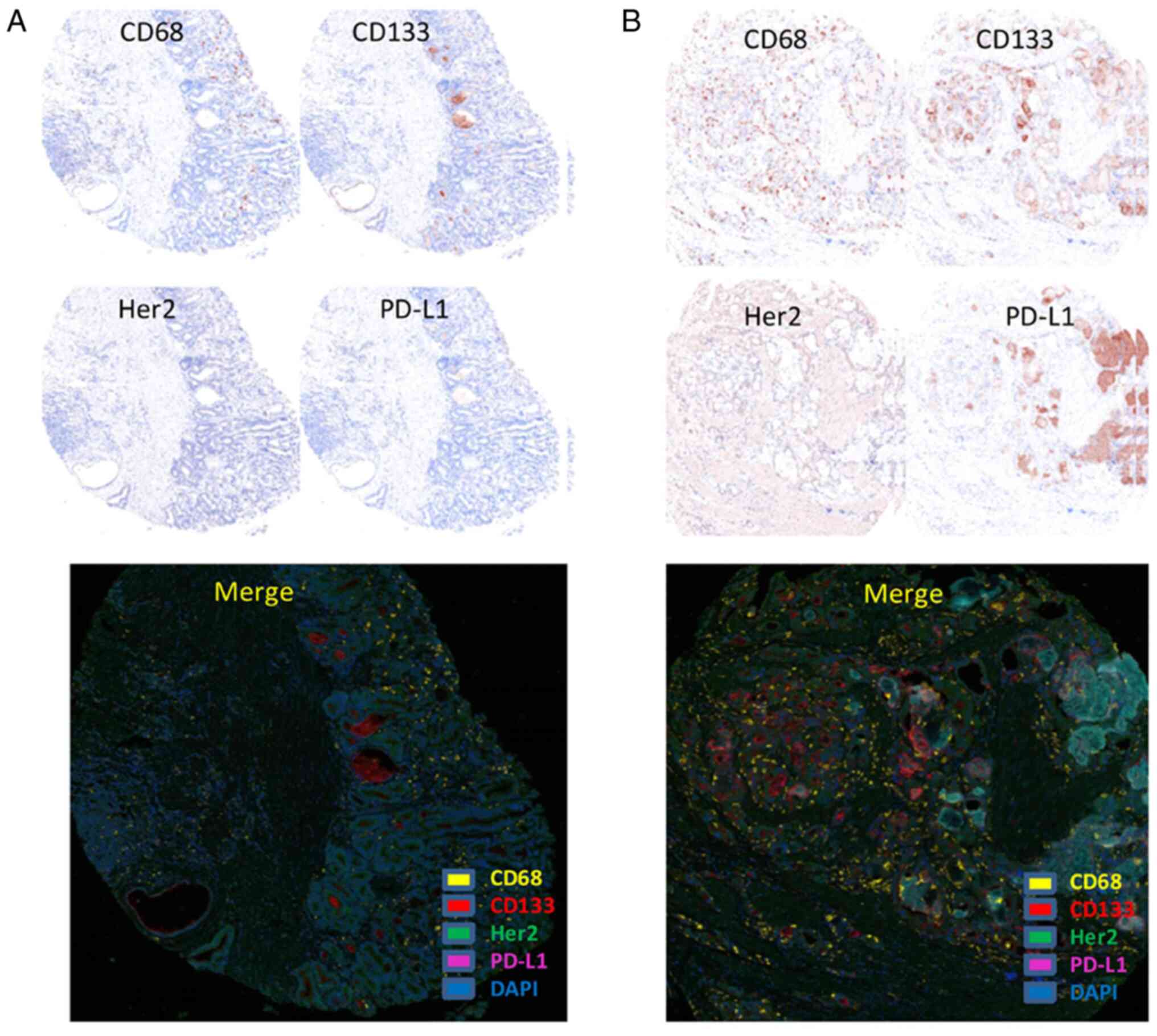
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie W, Yang T, Zuo J, Ma Z, Yu W, Hu Z and
Song Z: Chinese and global burdens of gastrointestinal cancers from
1990 to 2019. Front Public Health. 10:9412842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iwasaki A, Shinozaki-Ushiku A, Kunita A,
Yamazawa S, Sato Y, Yamashita H, Fukayama M, Seto Y and Ushiku T:
Human leukocyte antigen class I deficiency in gastric carcinoma: An
adaptive immune evasion strategy most common in microsatellite
instable tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 45:1213–1220. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qing Y, Li Q, Ren T, Xia W, Peng Y, Liu
GL, Luo H, Yang YX, Dai XY, Zhou SF and Wang D: Upregulation of
PD-L1 and APE1 is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis
of gastric cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:901–909. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y,
Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, Fukumoto Y, Osaki T, Ashida K and Fujiwara
Y: Highly activated PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in gastric cancer with PD-L1
expression. Anticancer Res. 38:107–112. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang M, Dong Y, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhao S,
Xuan Q, Wang Y and Zhang Q: The clinicopathological and prognostic
significance of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis
of 10 studies with 1,901 patients. Sci Rep. 6:379332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pereira MA, Ramos MFKP, Dias AR, Ribeiro
R, Cardili L, Zilberstein B, Cecconello I, Ribeiro U Jr, de Mello
ES and de Castria TB: Scoring systems for PD-L1 expression and
their prognostic impact in patients with resectable gastric cancer.
Virchows Arch. 478:1039–1048. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rha SY, Ku GY, Kim HS, Chung HC, Amlashi
FG, Maru DM, Fein CA, Tang LH, Zhou W, Wu T, et al: PD-L1
expression and overall survival in Asian and western patients with
gastric cancer. Future Oncol. 18:2623–2634. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Böger C, Behrens HM, Mathiak M, Krüger S,
Kalthoff H and Röcken C: PD-L1 is an independent prognostic
predictor in gastric cancer of western patients. Oncotarget.
7:24269–24283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang F, Zhang J, Zhao L, Zhai M, Zhang T
and Yu D: A PD-L1 negative advanced gastric cancer patient with a
long response to PD-1 blockade after failure of systematic
treatment: A case report. Front Immunol. 12:7592502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ribeiro HSC, Menezes JN, da Costa WL Jr, F
de Jesus VH, Diniz AL, Godoy AL, de Farias IC, Torres SM, Neotti T,
Mello CAL, et al: PD-L1 expression in gastric and gastroesophageal
junction cancer patients treated with perioperative chemotherapy. J
Surg Oncol. 126:150–160. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu Y, Cao D, Qu L, Cao X, Jia Z, Zhao T,
Wang Q and Jiang J: PD-1 and PD-L1 co-expression predicts favorable
prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 8:64066–64082. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ju X, Shen R, Huang P, Zhai J, Qian X,
Wang Q and Chen M: Predictive relevance of PD-L1 expression with
pre-existing TILs in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 8:99372–99381.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park IH, Kong SY, Ro JY, Kwon Y, Kang JH,
Mo HJ, Jung SY, Lee S, Lee KS, Kang HS, et al: Prognostic
implications of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in association with
programmed death ligand 1 expression in early-stage breast cancer.
Clin Breast Cancer. 16:51–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Q, Lou W, Di W and Wu X: Prognostic
value of tumor PD-L1 expression combined with CD8+ tumor
infiltrating lymphocytes in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Int
Immunopharmacol. 52:7–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chakrabarti J, Koh V, Steele N, Hawkins J,
Ito Y, Merchant JL, Wang J, Helmrath MA, Ahmad SA, So JBY, et al:
Disruption of Her2-induced PD-L1 inhibits tumor cell immune evasion
in patient-derived gastric cancer organoids. Cancers (Basel).
13:61582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
China Medical Biotechnology Association
Biobank (Trial), . Chin Med Biotechnol. 6:71–79. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Zou Y, Zhang J, Zhang L and Yan X:
Interferon-induced protein 16 expression in colorectal cancer and
its correlation with proliferation and immune signature markers.
Onco Lett. 22:6872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Taube JM, Akturk G, Angelo M, Engle EL,
Gnjatic S, Greenbaum S, Greenwald NF, Hedvat CV, Hollmann TJ, Juco
J, et al: The society for immunotherapy of cancer statement on best
practices for multiplex immunohistochemistry (IHC) and
immunofluorescence (IF) staining and validation. J Immunother
Cancer. 8:e0001552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG and
Xu N: Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1
ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical
significance. Acta Histochem. 108:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hassen G, Kasar A, Jain N, Berry S, Dave
J, Zouetr M, Priyanka Ganapathiraju VLN, Kurapati T, Oshai S, Saad
M, et al: Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) positivity and factors
associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer: An
umbrella meta-analysis. Cureus. 14:e238452022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen L, Wang L, Li X, Zhang G, Li Z and
Wang Y: Clinic-pathological characteristics and prognostic value of
PD-L1 and HER2 in gastric cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 40:405–413. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amatatsu M, Arigami T, Uenosono Y,
Yanagita S, Uchikado Y, Kijima Y, Kurahara H, Kita Y, Mori S,
Sasaki K, et al: Programmed death-ligand 1 is a promising blood
marker for predicting tumor progression and prognosis in patients
with gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:814–820. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He PX, Ma ZL, Han H, Zhang XY, Niu SH, Du
LN, Zheng YC and Liu HM: Expression of programmed death ligand 1
(PD-L1) is associated with metastasis and differentiation in
gastric cancer. Life Sci. 242:1172472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng D, Li M, Zhou R, Zhang J, Sun H, Shi
M, Bin J, Liao Y, Rao J and Liao W: Tumor microenvironment
characterization in gastric cancer identifies prognostic and
immunotherapeutically relevant gene signatures. Cancer Immunol Res.
7:737–750. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamashita K, Iwatsuki M, Harada K, Eto K,
Hiyoshi Y, Ishimoto T, Nagai Y, Iwagami S, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N,
et al: Prognostic impacts of the combined positive score and the
tumor proportion score for programmed death ligand-1 expression by
double immunohistochemical staining in patients with advanced
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 23:95–104. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fong C and Chau I: HER2 inhibition in
gastric cancer-novel therapeutic approaches for an established
target. Cancers (Basel). 14:38242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oki E, Okano S, Saeki H, Umemoto Y,
Teraishi K, Nakaji Y, Ando K, Zaitsu Y, Yamashita N, Sugiyama M, et
al: Protein expression of programmed death 1 ligand 1 and HER2 in
gastric carcinoma. Oncology. 93:387–394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Attia S, Abd El Hafez A, Abdel-Aziz A,
Elmetwaly S and Mokhtar N: Prognostic value of PD-L1
immunohistochemical marker in gastric carcinoma and its correlation
with HER2 status. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 23:1466–1444. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pous A, Notario L, Hierro C, Layos L and
Bugés C: HER2-positive gastric cancer: The role of immunotherapy
and novel therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 24:114032023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoon SO, Shin S, Lee HJ, Chun HK and Chung
AS: Isoginkgetin inhibits tumor cell invasion by regulating
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2666–2675. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fink MY and Chipuk JE: Survival of
HER2-positive breast cancer cells: Receptor signaling to apoptotic
control centers. Genes Cancer. 4:187–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang X, Zhou J, Giobbie-Hurder A, Wargo J
and Hodi FS: The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to
BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK
and PI3K inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 19:598–609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen J, Jiang CC, Jin L and Zhang XD:
Regulation of PD-L1: A novel role of pro-survival signalling in
cancer. Ann Oncol. 27:409–416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D, Chen X, Du Y, Li X, Ying L, Lu Y,
Shen B, Gao X, Yi X, Xia X, et al: Associations of HER2 mutation
with immune-related features and immunotherapy outcomes in solid
tumors. Front Immunol. 13:7999882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen XY, Thike AA, Md Nasir ND, Koh VCY,
Bay BH and Tan PH: Higher density of stromal M2 macrophages in
breast ductal carcinoma in situ predicts recurrence. Virchows Arch.
476:825–833. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Zugazagoitia J, Ahmed FS, Henick
BS, Gettinger SN, Herbst RS, Schalper KA and Rimm DL: Immune Cell
PD-L1 colocalizes with macrophages and is associated with outcome
in PD-1 pathway blockade therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 26:970–977.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang ZQ, Milne K, Derocher H, Webb JR,
Nelson BH and Watson PH: PD-L1 and intratumoral immune response in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:51641–51651. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang C, Chan YT, Yuen MF
and Feng Y: Lysyl oxidase-like 4 fosters an immunosuppressive
microenvironment during hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology.
73:2326–2341. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kawai O, Ishii G, Kubota K, Murata Y,
Naito Y, Mizuno T, Aokage K, Saijo N, Nishiwaki Y, Gemma A, et al:
Predominant infiltration of macrophages and CD8(+) T Cells in
cancer nests is a significant predictor of survival in stage IV
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 113:1387–1395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ohno S, Inagawa H, Dhar DK, Fujii T, Ueda
S, Tachibana M, Suzuki N, Inoue M, Soma G and Nagasue N: The degree
of macrophage infiltration into the cancer cell nest is a
significant predictor of survival in gastric cancer patients.
Anticancer Res. 23:5015–5022. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Medrek C, Pontén F, Jirström K and
Leandersson K: The presence of tumor associated macrophages in
tumor stroma as a prognostic marker for breast cancer patients. BMC
Cancer. 12:3062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Attia S, Atwan N, Arafa M and Shahin RA:
Expression of CD133 as a cancer stem cell marker in invasive
gastric carcinoma. Pathologica. 111:18–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang Y, He Y, Li H, Li HN, Zhang L, Hu W,
Sun YM, Chen FL and Jin XM: Expressions of putative cancer stem
cell markers ABCB1, ABCG2, and CD133 are correlated with the degree
of differentiation of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 15:440–450.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu Y, Yu J, Wang S, Lu R, Wu J and Jiang
B: Overexpression of CD133 enhances chemoresistance to
5-fluorouracil by activating the PI3K/Akt/p70S6K pathway in gastric
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 32:2437–2444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen XL, Chen XZ, Wang YG, He D, Lu ZH,
Liu K, Zhang WH, Wang W, Li CC, Xue L, et al: Clinical significance
of putative markers of cancer stem cells in gastric cancer: A
retrospective cohort study. Oncotarget. 7:62049–62069. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Razmi M, Ghods R, Vafaei S, Sahlolbei M,
Saeednejad Zanjani L and Madjd Z: Clinical and prognostic
significances of cancer stem cell markers in gastric cancer
patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int.
21:1392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yiming L, Yunshan G, Bo M, Yu Z, Tao W,
Gengfang L, Dexian F, Shiqian C, Jianli J, Juan T and Zhinan C:
CD133 overexpression correlates with clinicopathological features
of gastric cancer patients and its impact on survival: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:42019–42027. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hashimoto K, Aoyagi K, Isobe T, Kouhuji K
and Shirouzu K: Expression of CD133 in the cytoplasm is associated
with cancer progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
Gastric Cancer. 17:97–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ishigami S, Ueno S, Arigami T, Uchikado Y,
Setoyama T, Arima H, Kita Y, Kurahara H, Okumura H, Matsumoto M, et
al: Prognostic impact of CD133 expression in gastric carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 30:2453–2457. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao P, Li Y and Lu Y: Aberrant expression
of CD133 protein correlates with Ki-67 expression and is a
prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer.
10:2182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sasaki A, Kamiyama T, Yokoo H, Nakanishi
K, Kubota K, Haga H, Matsushita M, Ozaki M, Matsuno Y and Todo S:
Cytoplasmic expression of CD133 is an important risk factor for
overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
24:537–546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jao SW, Chen SF, Lin YS, Chang YC, Lee TY,
Wu CC, Jin JS and Nieh S: Cytoplasmic CD133 expression is a
reliable prognostic indicator of tumor regression after neoadjuvant
concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 19:3432–3440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|