|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R
and Saborowski A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 400:1345–1362.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega
J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V,
Salem R, et al: BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and
treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 76:681–693.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, Roberts LR,
Schwartz M, Chen PJ, Kudo M, Johnson P, Wagner S, Orsini LS and
Sherman M: Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management
from diagnosis to death: The BRIDGE study. Liver Int. 35:2155–2166.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Benson AB, D'Angelica MI, Abbott DE, Anaya
DA, Anders R, Are C, Bachini M, Borad M, Brown D, Burgoyne A, et
al: Hepatobiliary cancers, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice
guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 19:541–565. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang C, Zhang H, Zhang L, Zhu AX, Bernards
R, Qin W and Wang C: Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
20:203–222. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singal AG, Llovet JM, Yarchoan M, Mehta N,
Heimbach JK, Dawson LA, Jou JH, Kulik LM, Agopian VG, Marrero JA,
et al: AASLD practice guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 78:1922–1965.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta
G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, Girardi L, Cillo U, Burra P, Giacomin A and
Farinati F: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): The role of angiogenesis and
invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:914–921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiong XX, Qiu XY, Hu DX and Chen XQ:
Advances in hypoxia-mediated mechanisms in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Pharmacol. 92:246–255. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shimose S, Kawaguchi T, Tanaka M, Iwamoto
H, Miyazaki K, Moriyama E, Suzuki H, Niizeki T, Shirono T, Nakano
M, et al: Lenvatinib prolongs the progression-free survival time of
patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
refractory to transarterial chemoembolization: A multicenter cohort
study using data mining analysis. Oncol Lett. 20:2257–2265. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding X, Sun W, Li W, Shen Y, Guo X, Teng
Y, Liu X, Zheng L, Li W and Chen J: Transarterial chemoembolization
plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus
sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with
portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study. Cancer.
127:3782–3793. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JN, Li JJ, Yan S, Zhang GN and Yi PS:
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib versus
transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 13:10747932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Long J, Chen B and Liu Z: Comparative
efficacy and safety of molecular targeted agents combined with
transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma: A network meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
13:11794312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
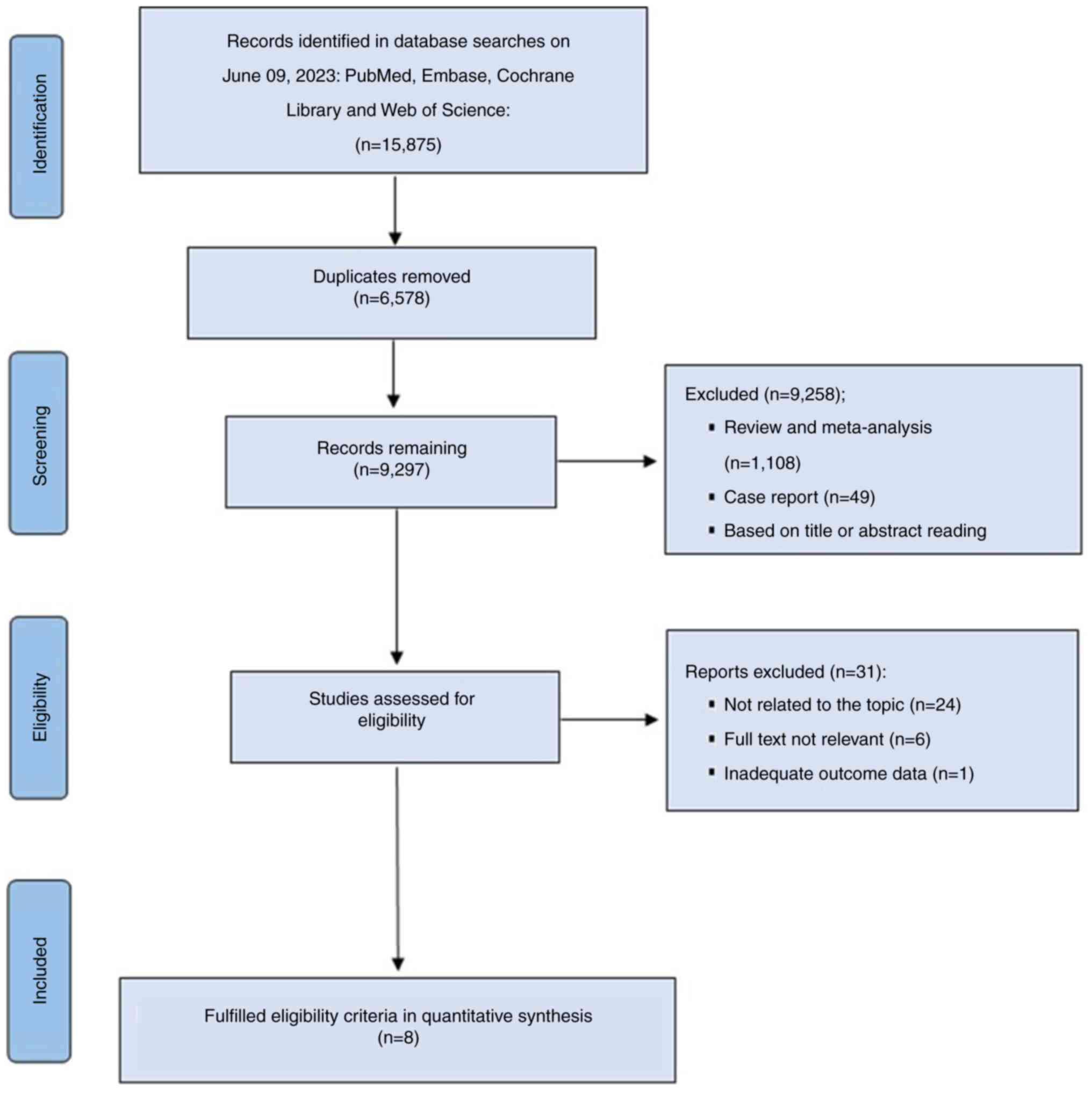
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA, et
al: The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343:d59282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lencioni R and Llovet JM: Modified RECIST
(mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
30:52–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kudo M, Imanaka K, Chida N, Nakachi K, Tak
WY, Takayama T, Yoon JH, Hori T, Kumada H, Hayashi N, et al: Phase
III study of sorafenib after transarterial chemoembolisation in
Japanese and Korean patients with unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 47:2117–2127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lencioni R, Llovet JM, Han G, Tak WY, Yang
J, Guglielmi A, Paik SW, Reig M, Kim DY, Chau GY, et al: Sorafenib
or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for
intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J Hepatol. 64:1090–1098.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meyer T, Fox R, Ma YT, Ross PJ, James MW,
Sturgess R, Stubbs C, Stocken DD, Wall L, Watkinson A, et al:
Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolisation in
patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (TACE 2): A
randomised placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:565–575. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park JW, Kim YJ, Kim DY, Bae SH, Paik SW,
Lee YJ, Kim HY, Lee HC, Han SY, Cheong JY, et al: Sorafenib with or
without concurrent transarterial chemoembolization in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The phase III STAH trial. J
Hepatol. 70:684–691. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Ikeda M, Torimura T,
Tanabe N, Aikata H, Izumi N, Yamasaki T, Nojiri S, Hino K, et al:
Final results of TACTICS: A randomized, prospective trial comparing
transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib to transarterial
chemoembolization alone in patients with unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 11:354–367. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng Z, Fan W, Zhu B, Wang G, Sun J, Xiao
C, Huang F, Tang R, Cheng Y, Huang Z, et al: Lenvatinib combined
with transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III, randomized clinical
trial (LAUNCH). J Clin Oncol. 41:117–127. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan D, Liu H, Ma X, Qu P, Cao M, Qin X,
Tang J, Pan R, Huang Q and Han Z: Safety and efficacy of TACE +
lenvatinib in treating advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis.
32:222–229. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xue M, Wu Y, Zhu B, Zou X, Fan W and Li J:
Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads plus lenvatinib versus
sorafenib, a propensity score matching retrospective study. Am J
Cancer Res. 11:6107–6118. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Wu Y, Zheng T, Chen X, Chen G,
Chen H, Guo X, Zheng S, Xie X and Zhang B: Efficacy of
transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted
agents for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network
meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 14:37102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu L, Lin J, Shi X and Wang A: Efficacy of
transarterial therapy combined with first-line tyrosine kinase
inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network
meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 21:2082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang JX, Chen YX, Zhou CG, Liu J, Liu S,
Shi HB and Zu QQ: Transarterial chemoembolization combined with
lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization combined with
sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparative
retrospective study. Hepatol Res. 52:794–803. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang B, Jie L, Yang T, Chen M, Gao Y,
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wu H and Liao Z: TACE plus lenvatinib versus TACE
plus sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with
portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective cohort study. Front
Oncol. 11:8215992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
An J, Han S, Kim HI and Shim JH: Ranking
of transarterial and targeted therapies for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma in the era of immuno-oncology: A network meta-analysis of
randomized sorafenib-controlled trials. Hepatol Commun.
6:2886–2900. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo J, Gao B, Lin Z, Fan H, Ma W, Yu D,
Yang Q, Tian J, Yang X and Li B: Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 12:10107262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mou L, Tian X, Zhou B, Zhan Y, Chen J, Lu
Y, Deng J, Deng Y, Wu Z, Li Q, et al: Improving outcomes of
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: New data
and ongoing trials. Front Oncol. 11:7527252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang L and Fu L: Mechanisms of resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:390–401.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schicho A, Hellerbrand C, Krüger K, Beyer
LP, Wohlgemuth W, Niessen C, Hohenstein E, Stroszczynski C, Pereira
PL and Wiggermann P: Impact of different embolic agents for
transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) procedures on systemic
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels. J Clin Transl
Hepatol. 4:288–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Petrillo M, Patella F, Pesapane F, Suter
MB, Ierardi AM, Angileri SA, Floridi C, de Filippo M and
Carrafiello G: Hypoxia and tumor angiogenesis in the era of
hepatocellular carcinoma transarterial loco-regional treatments.
Future Oncol. 14:2957–2967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dufour JF, Hoppe H, Heim MH, Helbling B,
Maurhofer O, Szucs-Farkas Z, Kickuth R, Borner M, Candinas D and
Saar B: Continuous administration of sorafenib in combination with
transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma: Results of a phase I study. Oncologist. 15:1198–1204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JW, Koh YH, Kim HB, Kim HY, An S,
Choi JI, Woo SM and Nam BH: Phase II study of concurrent
transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:1336–1342.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Okamoto K, Ikemori-Kawada M, Jestel A, von
König K, Funahashi Y, Matsushima T, Tsuruoka A, Inoue A and Matsui
J: Distinct binding mode of multikinase inhibitor lenvatinib
revealed by biochemical characterization. ACS Med Chem Lett.
6:89–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matsuki M, Hoshi T, Yamamoto Y,
Ikemori-Kawada M, Minoshima Y, Funahashi Y and Matsui J: Lenvatinib
inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling
pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models. Cancer Med.
7:2641–2653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamamoto Y, Matsui J, Matsushima T,
Obaishi H, Miyazaki K, Nakamura K, Tohyama O, Semba T, Yamaguchi A,
Hoshi SS, et al: Lenvatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor targeting
VEGFR/FGFR, shows broad antitumor activity in human tumor xenograft
models associated with microvessel density and pericyte coverage.
Vasc Cell. 6:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hoshi T, Watanabe Miyano S, Watanabe H,
Sonobe RMK, Seki Y, Ohta E, Nomoto K, Matsui J and Funahashi Y:
Lenvatinib induces death of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
harboring an activated FGF signaling pathway through inhibition of
FGFR-MAPK cascades. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:1–7. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He X, Hikiba Y, Suzuki Y, Nakamori Y,
Kanemaru Y, Sugimori M, Sato T, Nozaki A, Chuma M and Maeda S: EGFR
inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 12:80072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Romei C, Ciampi R and Elisei R: A
comprehensive overview of the role of the RET proto-oncogene in
thyroid carcinoma. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:192–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu J, Wei S, Yang L, Yu J, Yan D and Yi
P: Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus
lenvatinib with or without programmed death-1 inhibitors in the
treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:14451–14461.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|