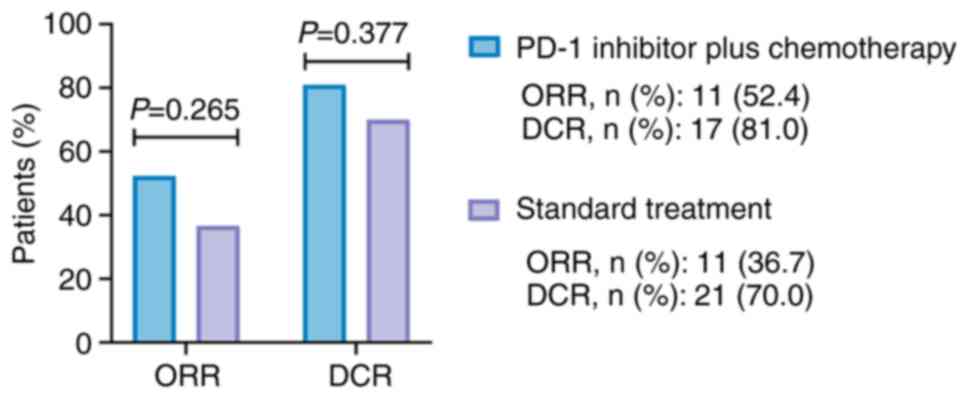
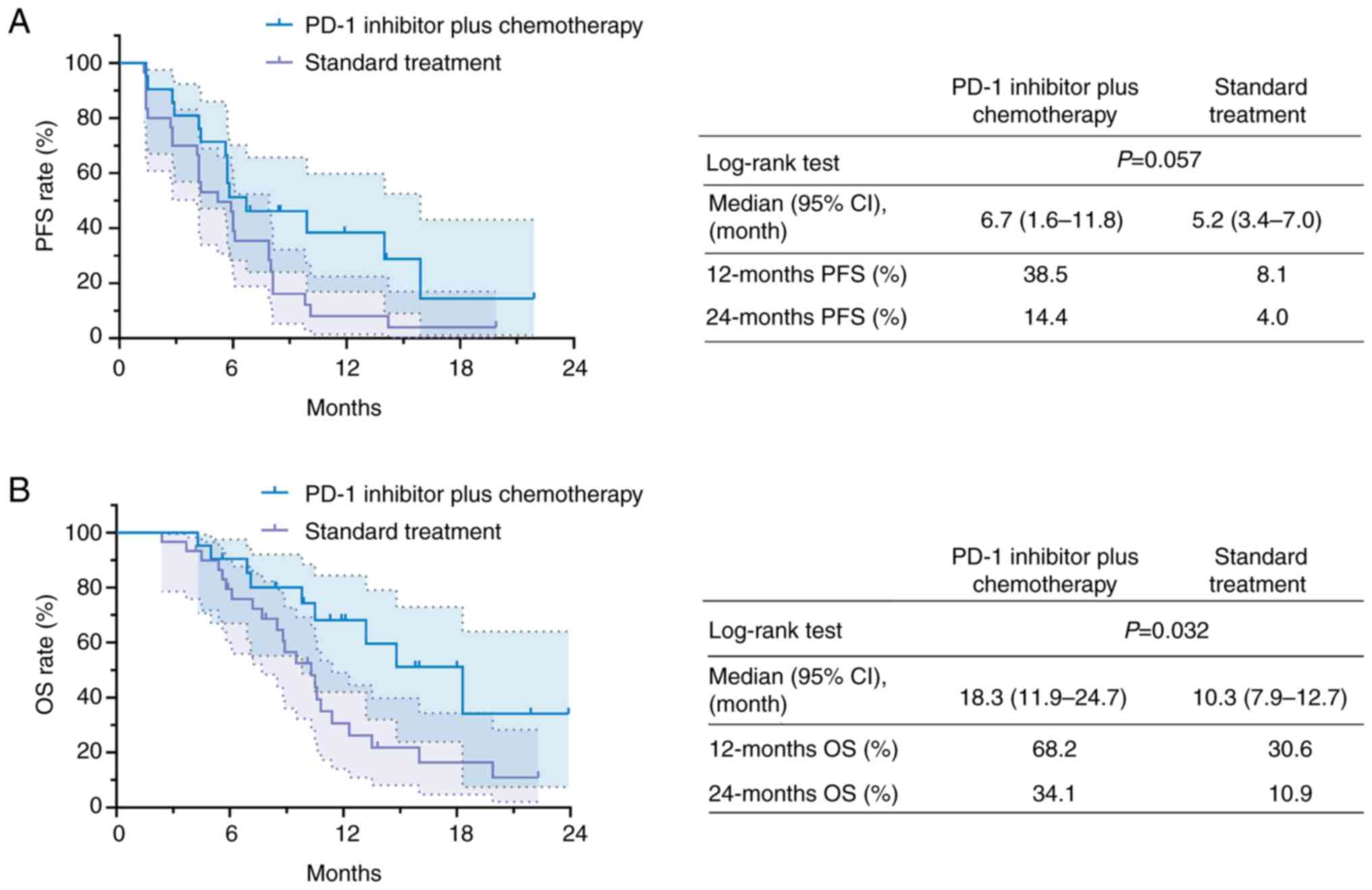
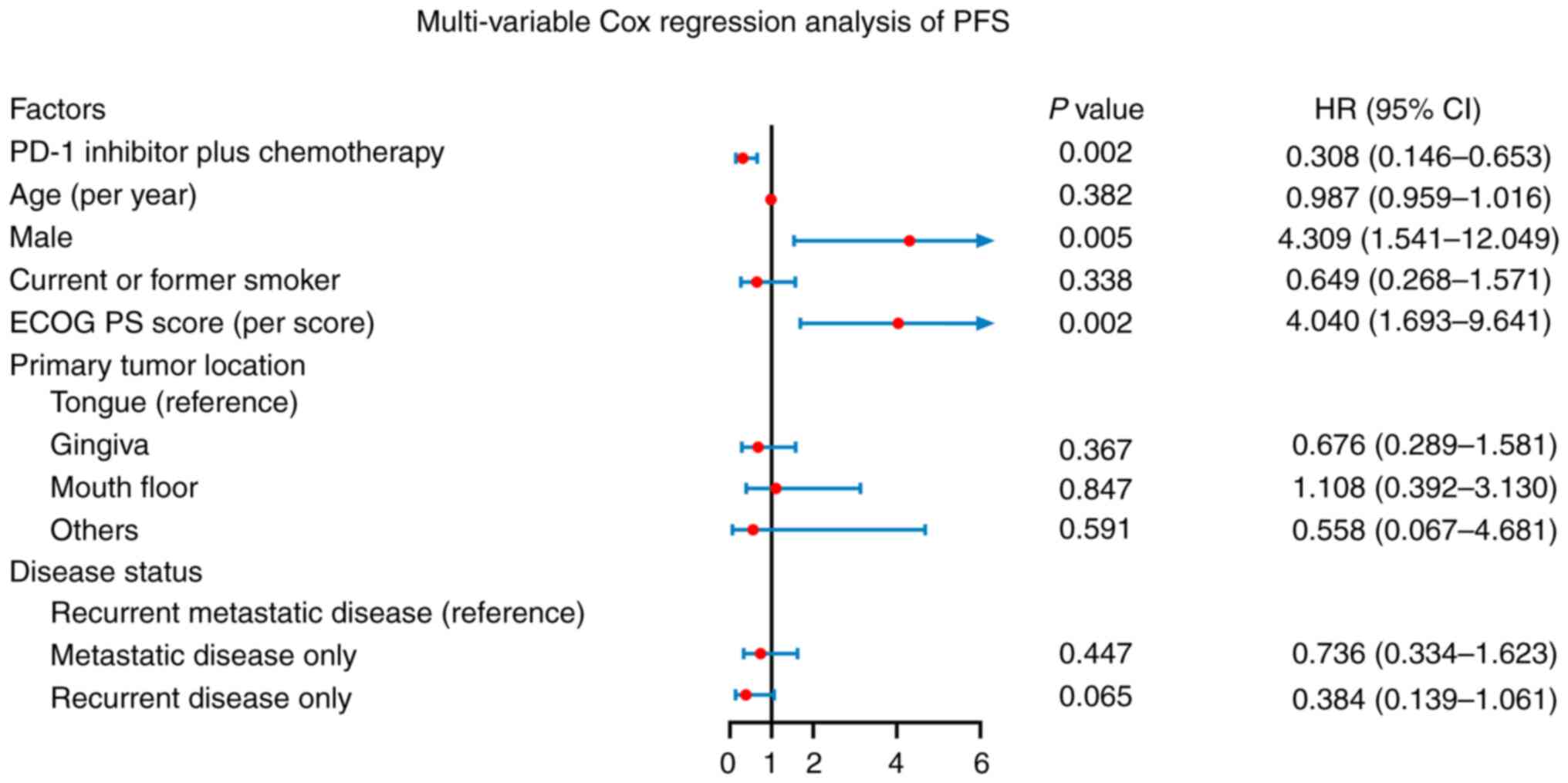
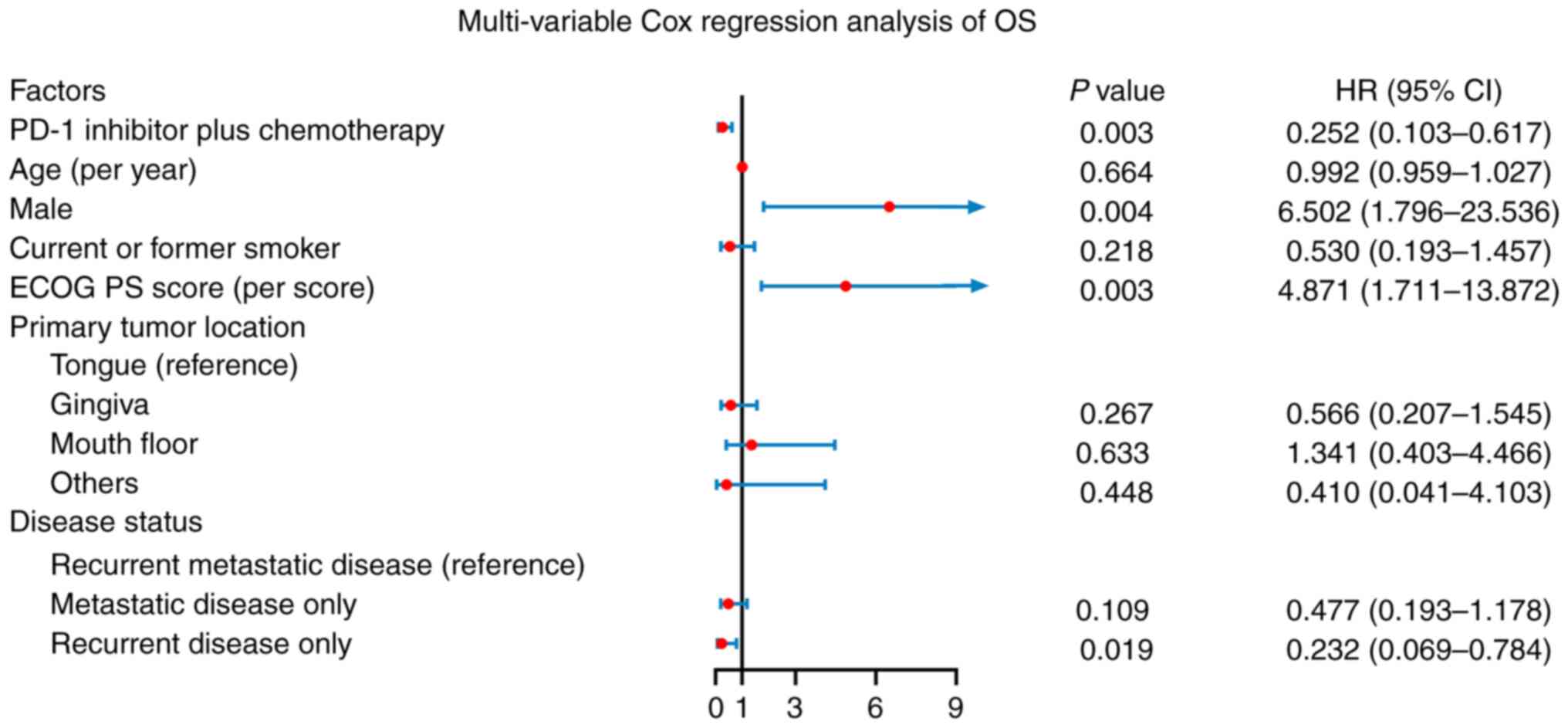
|
1
|
Xie L and Shang ZJ: Oral cancer incidence,
mortality, and mortality-to-incidence ratio are associated with
human development index in China, 1990-2019. Biomed Res Int.
2022:64578402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rivera C: Essentials of oral cancer. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:11884–11894. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sarode G, Maniyar N, Sarode SC, Jafer M,
Patil S and Awan KH: Epidemiologic aspects of oral cancer. Dis Mon.
66:1009882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chamoli A, Gosavi AS, Shirwadkar UP,
Wangdale KV, Behera SK, Kurrey NK, Kalia K and Mandoli A: Overview
of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Risk factors, mechanisms,
and diagnostics. Oral Oncol. 121:1054512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chow LQM: Head and neck cancer. N Engl J
Med. 382:60–72. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui
VWY, Bauman JE and Grandis JR: Head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chinese society of clinical oncology
(CSCO) diagnosis and treatment guidelines for head and neck cancer
2018 (english version). Chin J Cancer Res. 31:84–98. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bagchi S, Yuan R and Engleman EG: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: Clinical impact
and mechanisms of response and resistance. Annu Rev Pathol.
16:223–249. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y,
Wu W, Han L and Wang S: The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of
immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol.
13:9644422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, He Z, Tao Y, Yang X, Ge S, Xu H,
Shang W and Song K: Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab
monotherapy for recurrent/unresectable/metastatic oral squamous
cell carcinoma: A single-center study in China. J Oncol.
2022:72839462022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamakawa N, Umeda M, Yoshii Y, Mitsudo K,
Noguchi M, Kusukawa J, Katakura A, Nakayama H, Sasaki M, Noguchi T,
et al: Multicenter retrospective study of nivolumab for
recurrent/metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis.
30:247–258. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ju WT, Xia RH, Zhu DW, Dou SJ, Zhu GP,
Dong MJ, Wang LZ, Sun Q, Zhao TC, Zhou ZH, et al: A pilot study of
neoadjuvant combination of anti-PD-1 camrelizumab and VEGFR2
inhibitor apatinib for locally advanced resectable oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 13:53782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ferris RL, Haddad R, Even C, Tahara M,
Dvorkin M, Ciuleanu TE, Clement PM, Mesia R, Kutukova S, Zholudeva
L, et al: Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in patients with
recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
EAGLE, a randomized, open-label phase III study. Ann Oncol.
31:942–950. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsieh RW, Borson S, Tsagianni A and
Zandberg DP: Immunotherapy in recurrent/metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Front Oncol. 11:7056142021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Upadhaya S, Neftelino ST, Hodge JP, Oliva
C, Campbell JR and Yu JX: Combinations take centre stage in
PD1/PDL1 inhibitor clinical trials. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
20:168–169. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meric-Bernstam F, Larkin J, Tabernero J
and Bonini C: Enhancing anti-tumour efficacy with immunotherapy
combinations. Lancet. 397:1010–1022. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oliva M, Spreafico A, Taberna M, Alemany
L, Coburn B, Mesia R and Siu LL: Immune biomarkers of response to
immune-checkpoint inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 30:57–67. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R,
Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, Psyrri A, Basté N, Neupane
P, Bratland Å, et al: Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy
versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 394:1915–1928. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li L, Chen L, Yan L, Guo Y, Li F, Fan M,
Lan M, Lai X, Zhou J, Huang Y, et al: Initial analysis of the
synergy of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitor and concurrent
chemoradiotherapy treatment for recurrent/metastatic head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma patients. Radiat Oncol. 18:1092023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, Takata
T and Slootweg PJ: WHO classification of head and neck tumours.
IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 203–260. 2017
|
|
22
|
Cho JH, Sorensen SF, Choi YL, Feng Y, Kim
TE, Choi H, Georgsen JB, Dolled-Filhart M, Emancipator K, Meldgaard
P, et al: Programmed death ligand 1 expression in paired non-small
cell lung cancer tumor samples. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:e473–e479.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kulangara K, Zhang N, Corigliano E,
Guerrero L, Waldroup S, Jaiswal D, Ms MJ, Shah S, Hanks D, Wang J,
et al: Clinical utility of the combined positive score for
programmed death ligand-1 expression and the approval of
pembrolizumab for treatment of gastric cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
143:330–337. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schwartz LH, Litière S, de Vries E, Ford
R, Gwyther S, Mandrekar S, Shankar L, Bogaerts J, Chen A, Dancey J,
et al: RECIST 1.1-update and clarification: From the RECIST
committee. Eur J Cancer. 62:132–137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Freites-Martinez A, Santana N,
Arias-Santiago S and Viera A: Using the common terminology criteria
for adverse events (CTCAE-version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of
adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl
Ed). 112:90–92. 2021.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J,
Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington K, Kasper S, Vokes EE,
Even C, et al: Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 375:1856–1867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Sousa LG and Ferrarotto R:
Pembrolizumab in the first-line treatment of advanced head and neck
cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 21:1321–1331. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cohen EEW, Soulieres D, Le Tourneau C,
Dinis J, Licitra L, Ahn MJ, Soria A, Machiels JP, Mach N, Mehra R,
et al: Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab
for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma
(KEYNOTE-040): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet.
393:156–167. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xue Y, Gao S, Gou J, Yin T, He H, Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Tang X and Wu R: Platinum-based chemotherapy in
combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: Preclinical and clinical
studies and mechanism of action. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
18:187–203. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saleh K, Khalifeh-Saleh N, Kourie HR, Nasr
F and Chahine G: Do immune checkpoint inhibitors increase
sensitivity to salvage chemotherapy? Immunotherapy. 10:163–165.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Melo-Alvim C, Neves ME, Santos JL,
Abrunhosa-Branquinho AN, Barroso T, Costa L and Ribeiro L:
Radiotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy-current practice and
future perspectives for recurrent/metastatic oral cavity squamous
cell carcinoma. Diagnostics (Basel). 13:992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wakabayashi G, Lee YC, Luh F, Kuo CN,
Chang WC and Yen Y: Development and clinical applications of cancer
immunotherapy against PD-1 signaling pathway. J Biomed Sci.
26:962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J,
Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington KJ, Kasper S, Vokes EE,
Even C, et al: Nivolumab vs investigator's choice in recurrent or
metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: 2-year
long-term survival update of checkMate 141 with analyses by tumor
PD-L1 expression. Oral Oncol. 81:45–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang Q, Xu P, Cao F, Wu D and Liu X: PD-1
Inhibitors combined with paclitaxel (albumin-bound) and cisplatin
for larynx preservation in locally advanced laryngeal and
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:4161–4168. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cohen EEW, Bell RB, Bifulco CB, Burtness
B, Gillison ML, Harrington KJ, Le QT, Lee NY, Leidner R, Lewis RL,
et al: The society for immunotherapy of cancer consensus statement
on immunotherapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck (HNSCC). J Immunother Cancer. 7:1842019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oh LJ, Asher R, Veness M, Smee R,
Goldstein D, Gopalakrishna Iyer N, Balasubramanian D, Low TH, Palme
CE, Gupta R and Clark J: Effect of age and gender in non-smokers
with oral squamous cell carcinoma: Multi-institutional study. Oral
Oncol. 116:1052102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hato SV, Khong A, de Vries IJ and
Lesterhuis WJ: Molecular pathways: The immunogenic effects of
platinum-based chemotherapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2831–2837.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pontes F, Garcia AR, Domingues I, João
Sousa M, Felix R, Amorim C, Salgueiro F, Mariano M and Teixeira M:
Survival predictors and outcomes of patients with recurrent and/or
metastatic head and neck cancer treated with chemotherapy plus
cetuximab as first-line therapy: A real-world retrospective study.
Cancer Treat Res Commun. 27:1003752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|