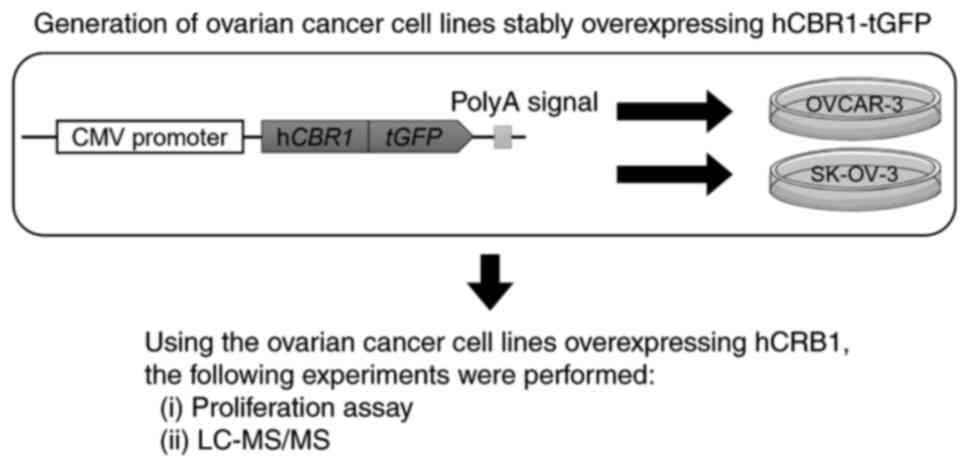
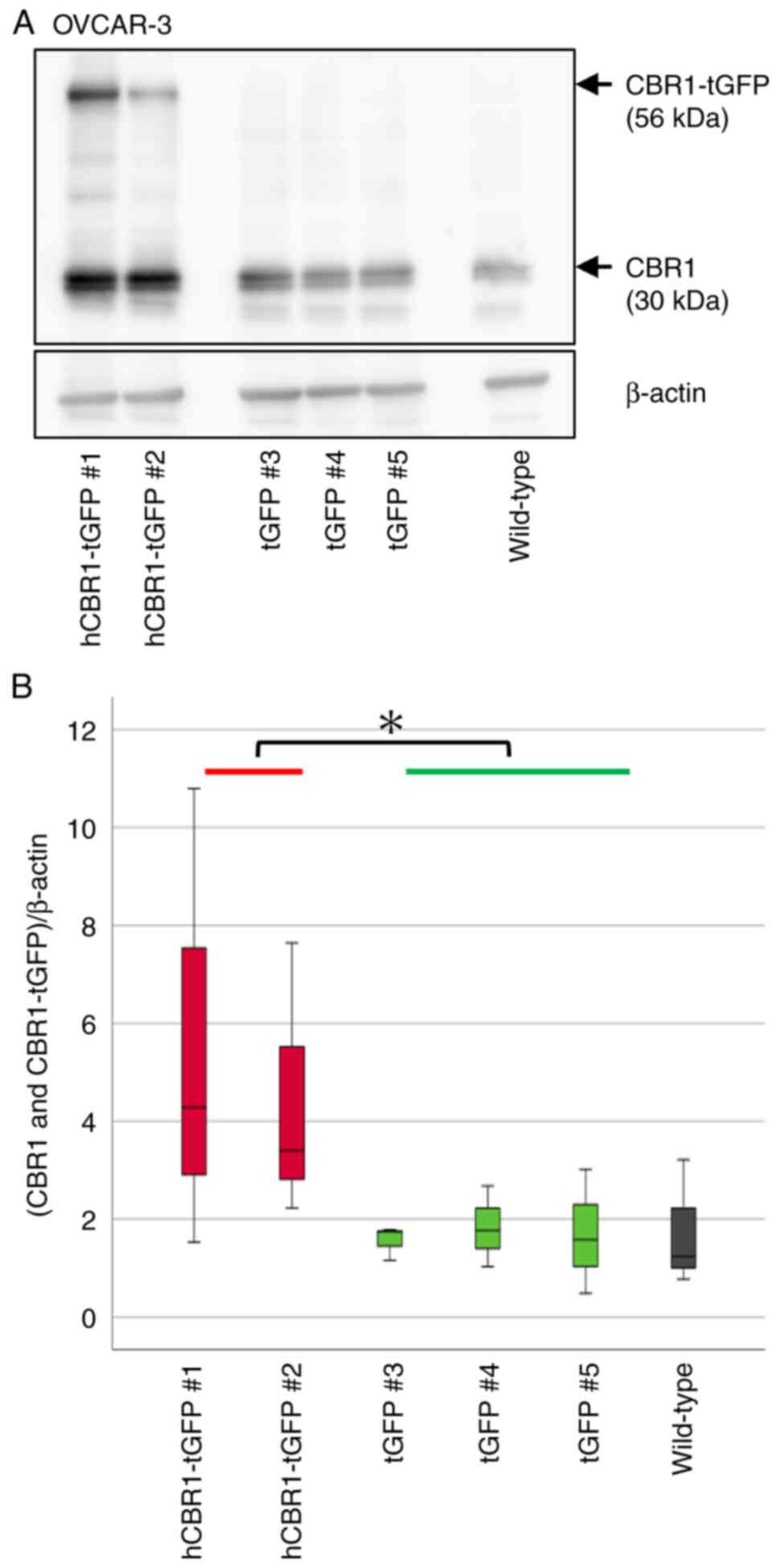
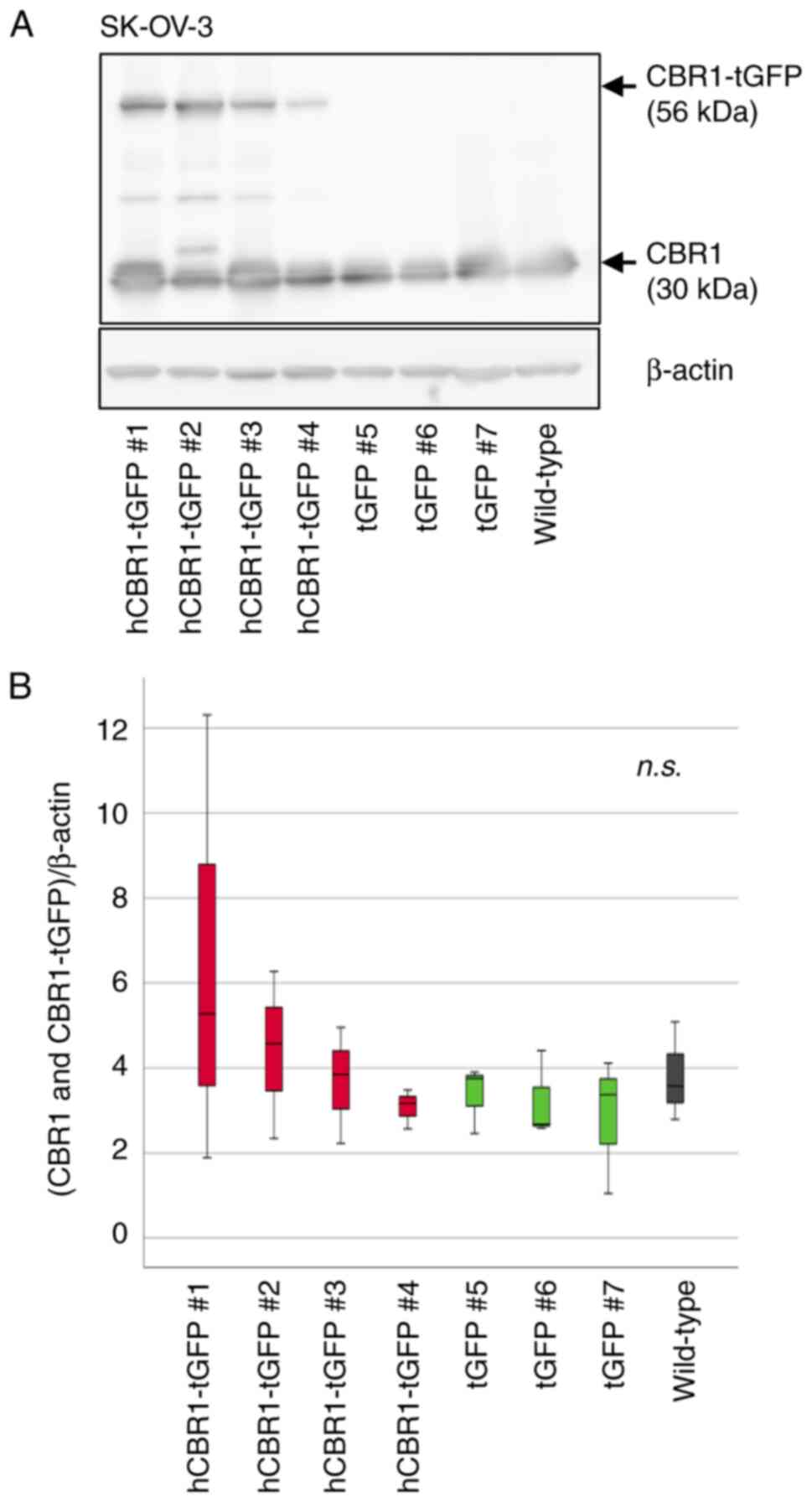
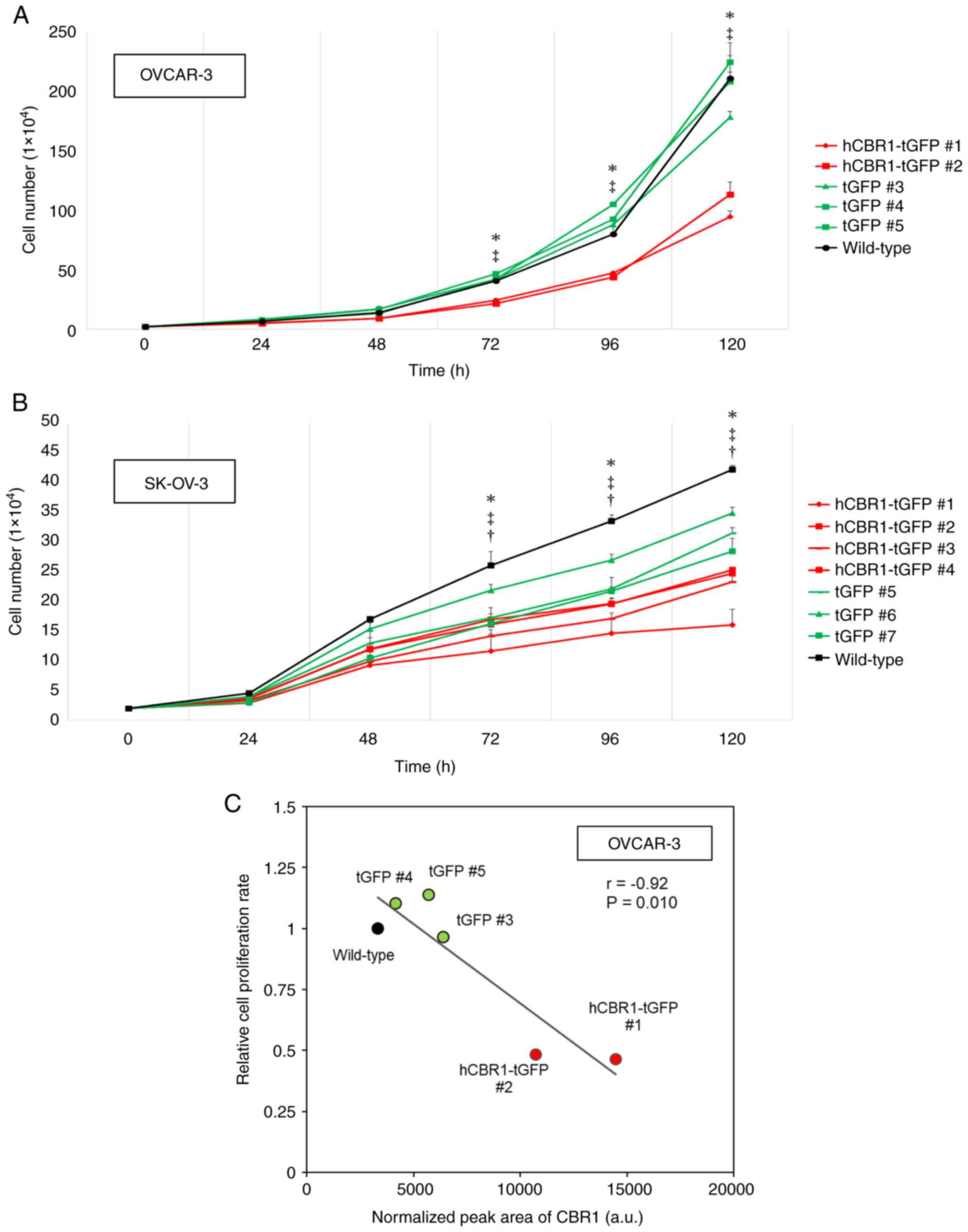
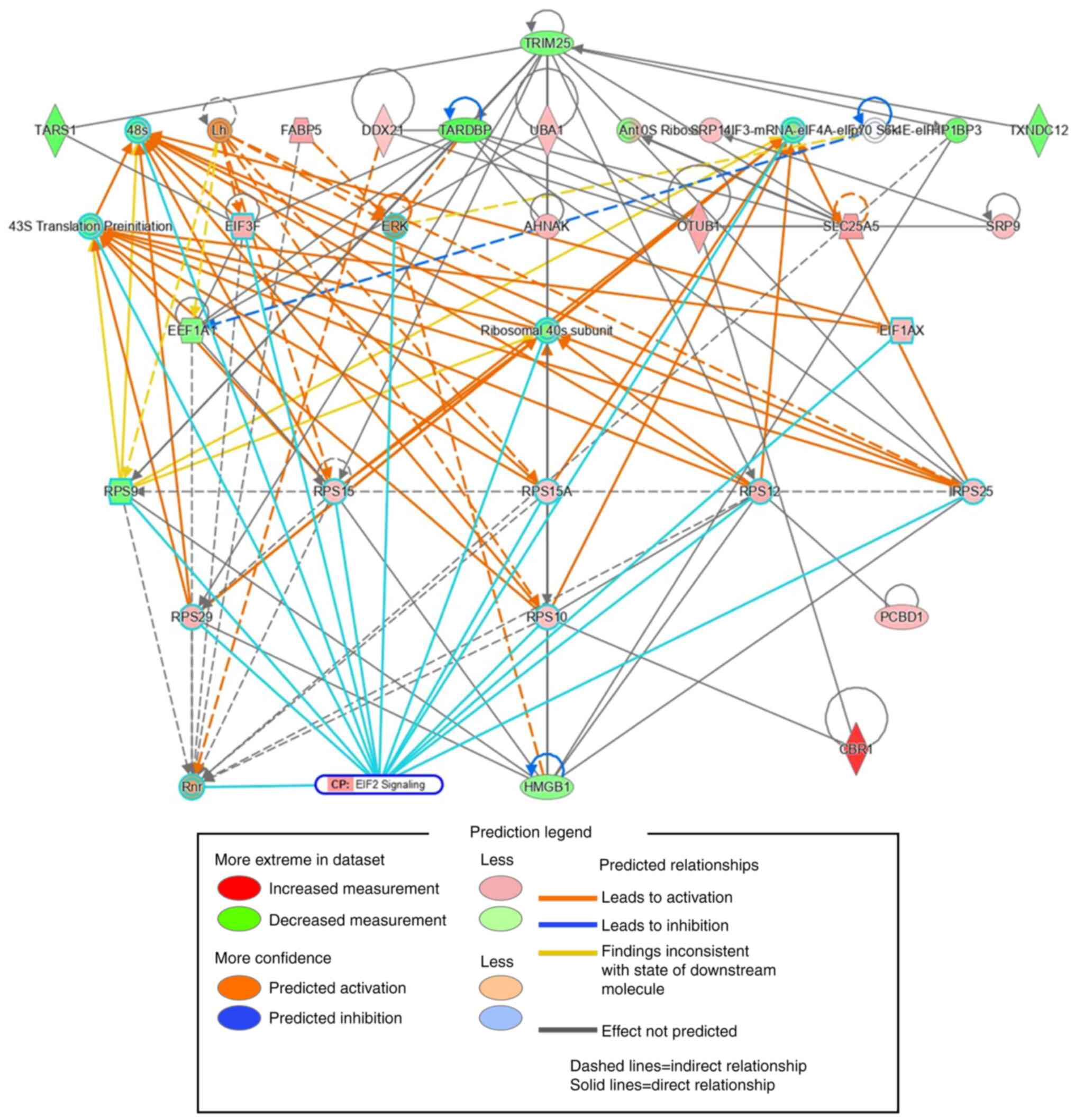
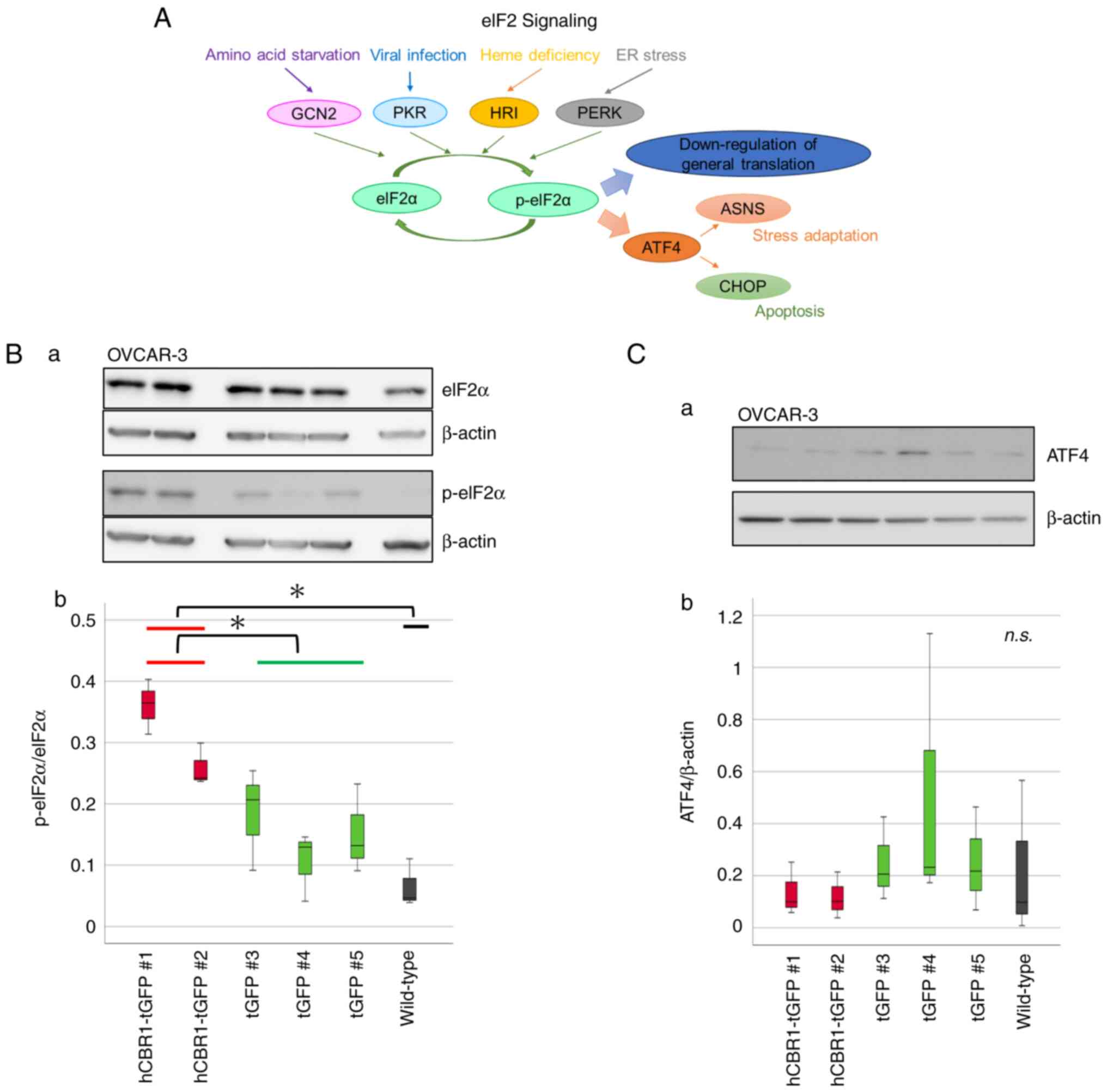
|
1
|
Mindnich RD and Penning TM: Aldo-keto
reductase (AKR) superfamily: Genomics and annotation. Hum Genomics.
3:362–370. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P,
Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S,
Danielsson A, Edlund K, et al: Analysis of the human
tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of
transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:397–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wermuth B, Bohren KM, Heinemann G, von
Wartburg JP and Gabbay KH: Human carbonyl reductase. Nucleotide
sequence analysis of a cDNA and amino acid sequence of the encoded
protein. J Biol Chem. 263:16185–16188. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Umemoto M, Yokoyama Y, Sato S, Tsuchida S,
Al-Mulla F and Saito Y: Carbonyl reductase as a significant
predictor of survival and lymph node metastasis in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 85:1032–1036. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Osawa Y, Yokoyama Y, Shigeto T, Futagami M
and Mizunuma H: Decreased expression of carbonyl reductase 1
promotes ovarian cancer growth and proliferation. Int J Oncol.
46:1252–1258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miura R, Yokoyama Y, Shigeto T, Futagami M
and Mizunuma H: Inhibitory effect of carbonyl reductase 1 on
ovarian cancer growth via tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling.
Int J Oncol. 47:2173–2180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nishimoto Y, Murakami A, Sato S, Kajimura
T, Nakashima K, Yakabe K, Sueoka K and Sugino N: Decreased carbonyl
reductase 1 expression promotes tumor growth via epithelial
mesenchymal transition in uterine cervical squamous cell
carcinomas. Reprod Med Biol. 17:173–181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kajimura T, Sato S, Murakami A,
Hayashi-Okada M, Nakashima K, Sueoka K and Sugino N: Overexpression
of carbonyl reductase 1 inhibits malignant behaviors and epithelial
mesenchymal transition by suppressing TGF-β signaling in uterine
leiomyosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett. 18:1503–1512. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takenaka K, Ogawa E, Oyanagi H, Wada H and
Tanaka F: Carbonyl reductase expression and its clinical
significance in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 14:1972–1975. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Graves PR and Haystead TA: Molecular
biologist's guide to proteomics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 66:39–63.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chandramouli K and Qian PY: Proteomics:
Challenges, techniques and possibilities to overcome biological
sample complexity. Hum Genomics Proteomics. 8:2392042009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang D, Eraslan B, Wieland T, Hallström B,
Hopf T, Zolg DP, Zecha J, Asplund A, Li LH, Meng C, et al: A deep
proteome and transcriptome abundance atlas of 29 healthy human
tissues. Mol Syst Biol. 15:e85032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Martínez-Rodríguez F, Limones-González JE,
Mendoza-Almanza B, Esparza-Ibarra EL, Gallegos-Flores PI,
Ayala-Luján JL, Godina-González S, Salinas E and Mendoza-Almanza G:
Understanding cervical cancer through proteomics. Cells.
10:18542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shigeto T, Yokoyama Y, Xin B and Mizunuma
H: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and γ ligands
inhibit the growth of human ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 18:833–840.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wakui M, Yokoyama Y, Wang H, Shigeto T,
Futagami M and Mizunuma H: Efficacy of a methyl ester of
5-aminolevulinic acid in photodynamic therapy for ovarian cancers.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1143–1150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cebulla J, Huuse EM, Pettersen K, van der
Veen A, Kim E, Andersen S, Prestvik WS, Bofin AM, Pathak AP,
Bjørkøy G, et al: MRI reveals the in vivo cellular and vascular
response to BEZ235 in ovarian cancer xenografts with different
PI3-kinase pathway activity. Br J Cancer. 112:504–513. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zalewski M, Kulbacka J, Saczko J,
Drag-Zalesinska M and Choromanska A: Valspodar-modulated
chemotherapy in human ovarian cancer cells SK-OV-3 and MDAH-2774.
Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 19:234–241. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu T, Tang J, Shrestha B, Heath BR, Hong
L, Lei YL, Ljungman M and Neamati N: Up-regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor antisense as a novel approach to treat
ovarian cancer. Theranostics. 10:6959–6976. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohgane K and Yoshioka H: Quantification of
gel bands by an image J Macro, Band/Peak Quantification Tool v1.
Protocols.io. 2019.doi:/10.17504/protocols.io.7vghn3w.
|
|
20
|
Yokoyama M, Fujita T, Kadonosawa Y, Tatara
Y, Motooka D, Ikawa M, Fujii H and Yokoayama Y: Development of
transgenic mice overexpressing mouse carbonyl reductase 1. Mol Biol
Rep. 50:531–540. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Costantini LM, Fossati M, Francolini M and
Snapp EL: Assessing the tendency of fluorescent proteins to
oligomerize under physiologic conditions. Traffic. 13:643–649.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Boye E and Grallert B: eIF2α
phosphorylation and the regulation of translation. Curr Genet.
66:293–297. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Johnston GC, Pringle JR and Hartwell LH:
Coordination of growth with cell division in the yeast
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 105:79–98. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kovalski JR, Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D and Ruggero
D: Protein synthesis control in cancer: selectivity and therapeutic
targeting. EMBO J. 41:e1098232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clemens MJ and Bommer UA: Translational
control: The cancer connection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 31:1–23.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hinnebusch AG: Molecular mechanism of
scanning and start codon selection in eukaryotes. Microbiol Mol
Biol Rev. 75:434–467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia-a key regulatory factor
in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hinnebusch AG: The scanning mechanism of
eukaryotic translation initiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 83:779–812.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gandin V, Masvidal L, Cargnello M, Gyenis
L, McLaughlan S, Cai Y, Tenkerian C, Morita M, Balanathan P,
Jean-Jean O, et al: mTORC1 and CK2 coordinate ternary and eIF4F
complex assembly. Nat Commun. 7:111272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wengrod J, Wang D, Weiss S, Zhong H, Osman
I and Gardner LB: Phosphorylation of eIF2α triggered by mTORC1
inhibition and PP6C activation is required for autophagy and is
aberrant in PP6C-mutated melanoma. Sci Signal. 8:ra272015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|