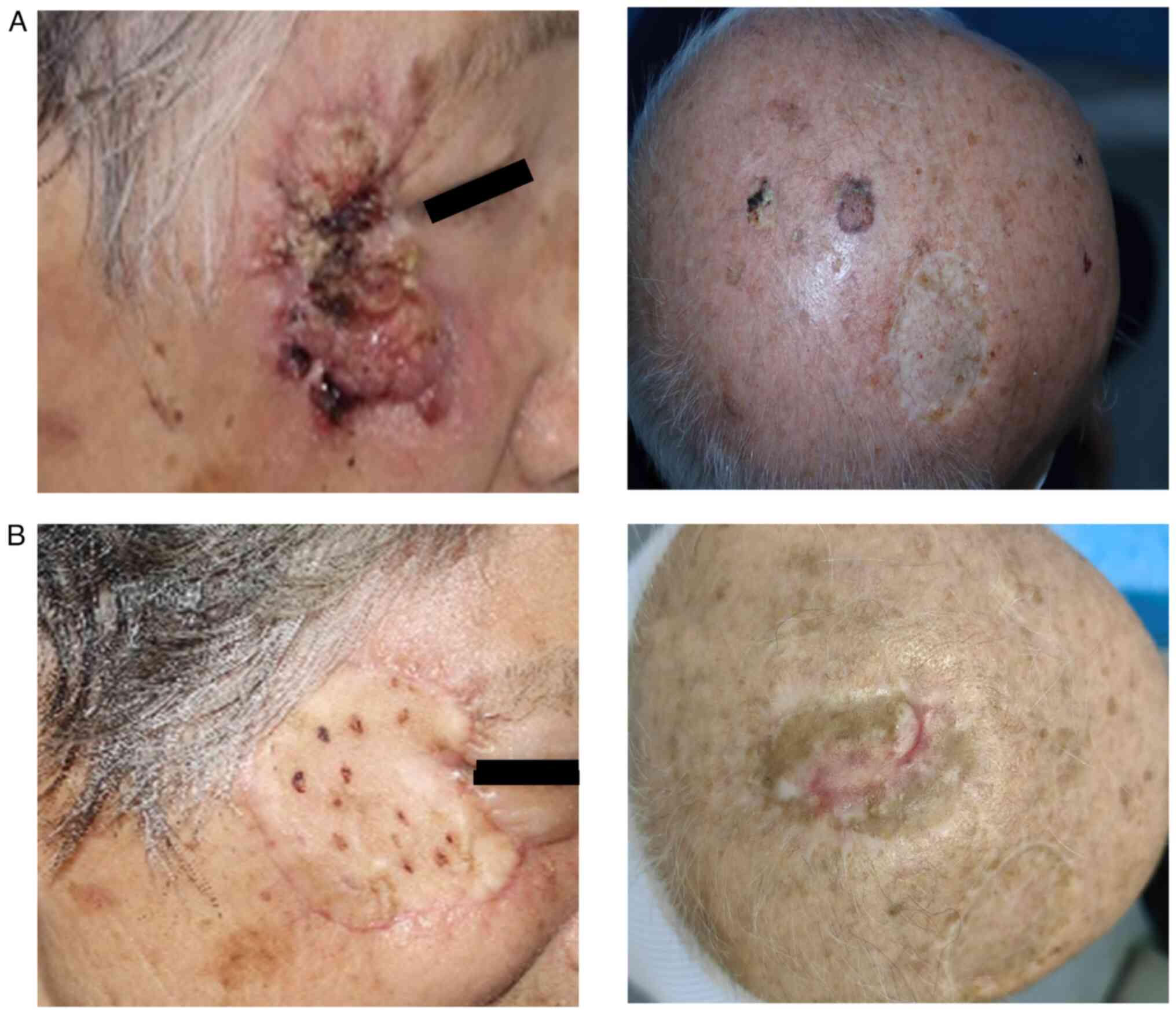
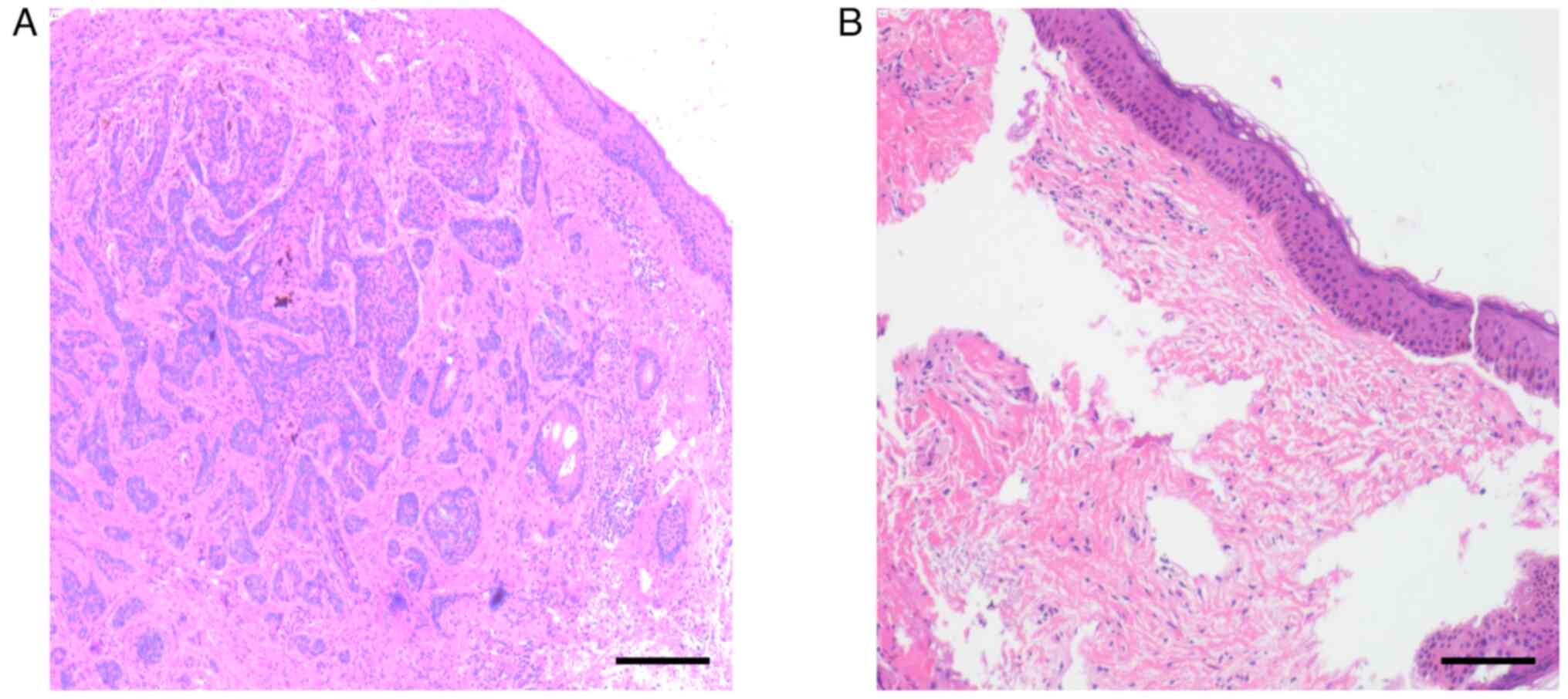
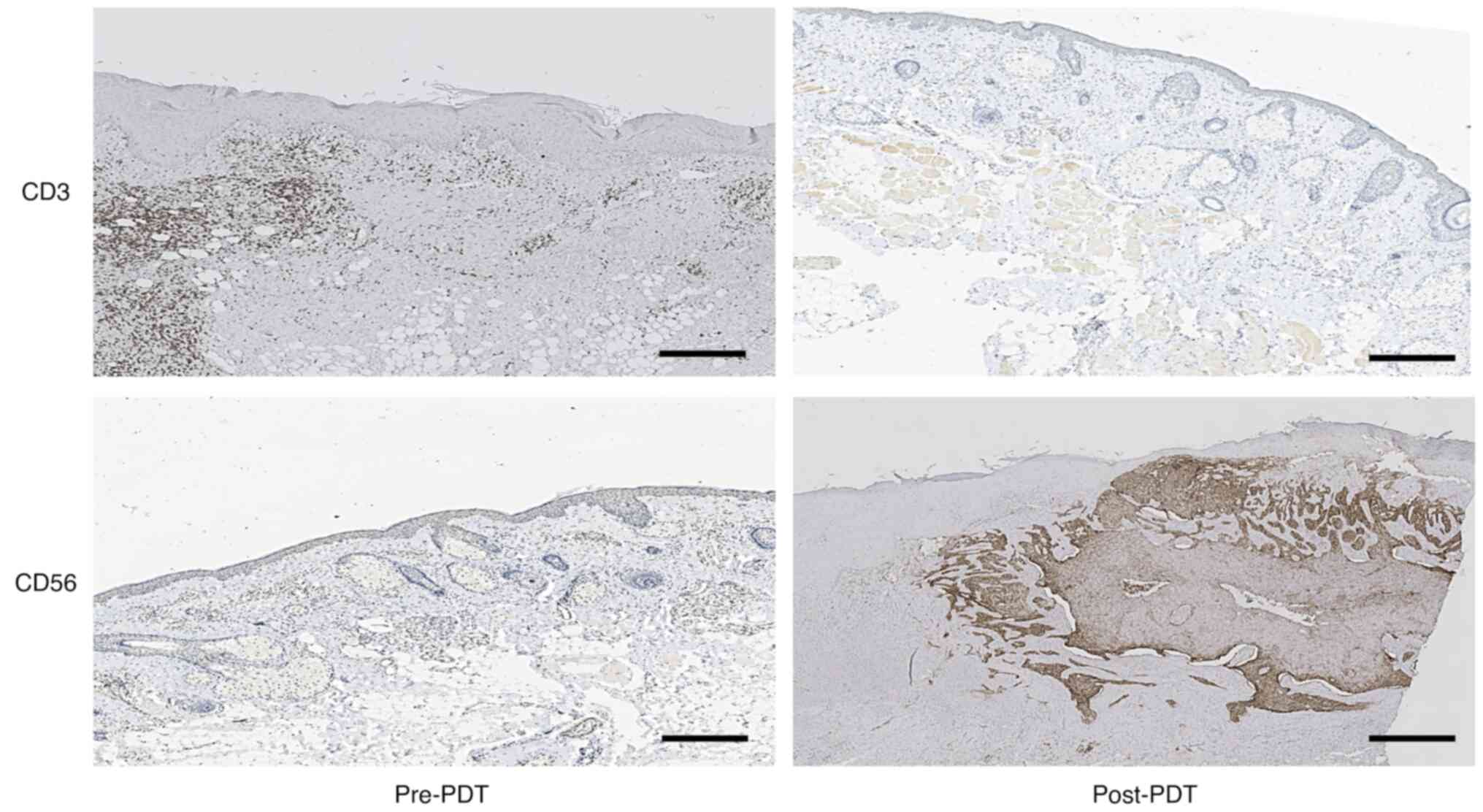
|
1
|
Gallego-Rentero M, Gutiérrez-Pérez M,
Fernández-Guarino M, Mascaraque M, Portillo-Esnaola M, Gilaberte Y,
Carrasco E and Juarranz Á: TGFβ1 secreted by cancer-associated
fibroblasts as an inductor of resistance to photodynamic therapy in
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancers (Basel). 13:56132021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hao Y, Chen Y, He X, Yang F, Han R, Yang
C, Li W and Qian Z: Near-infrared responsive 5-fluorouracil and
indocyanine green loaded MPEG-PCL nanoparticle integrated with
dissolvable microneedle for skin cancer therapy. Bioact Mater.
5:542–552. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Que SKT, Zwald FO and Schmults CD:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Incidence, risk factors,
diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 78:237–247. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martincorena I, Roshan A, Gerstung M,
Ellis P, van Loo P, McLaren S, Wedge DC, Fullam A, Alexandrov LB,
Tubio JM, et al: Tumor evolution. High burden and pervasive
positive selection of somatic mutations in normal human skin.
Science. 348:880–886. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Skulsky SL, O'Sullivan B, McArdle O,
Leader M, Roche M, Conlon PJ and O'Neill JP: Review of high-risk
features of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and discrepancies
between the American Joint Committee on Cancer and NCCN Clinical
Practice Guidelines In Oncology. Head Neck. 39:578–594. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Work Group and Invited Reviewers, . Kim
JYS, Kozlow JH, Mittal B, Moyer J, Olenecki T and Rodgers P:
Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell
carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 78:560–578. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiang F, Lucas R, Hales S and Neale R:
Incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer in relation to ambient UV
radiation in white populations, 1978–2012: Empirical relationships.
JAMA Dermatol. 150:1063–1071. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marsidi N, Ottevanger R, Bouwes Bavinck
JN, Krekel-Taminiau NMA, Goeman JJ and Genders RE: Risk factors for
incomplete excision of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A large
cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 36:1229–1234. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Curiel-Lewandrowski C, Myrdal CN, Saboda
K, Hu C, Arzberger E, Pellacani G, Legat FJ, Ulrich M, Hochfellner
P, Oliviero MC, et al: In Vivo reflectance confocal microscopy as a
response monitoring tool for actinic keratoses undergoing
cryotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:54882021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Keyal U, Bhatta AK, Zhang G and Wang XL:
Present and future perspectives of photodynamic therapy for
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 80:765–773.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang XL, Wang HW, Guo MX and Xu SZ: T
reatment of skin cancer and pre-cancer using topical ALA-PDT -a
single hospital experience. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther.
5:127–133. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Jaworski S, Biniecka P, Bugajska Ż,
Daniluk K, Dyjak S, Strojny B, Kutwin M, Wierzbicki M, Grodzik M
and Chwalibog A: Analysis of the cytotoxicity of hierarchical
nanoporous graphenic carbon against human glioblastoma grade IV
cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:3839–3849. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wilson C, Zhang X, Buckley C, Heathcote
HR, Lee MD and McCarron JG: Increased vascular contractility in
hypertension results from impaired endothelial calcium signaling.
Hypertension. 74:1200–1214. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Castano AP, Mroz P and Hamblin MR:
Photodynamic therapy and anti-tumour immunity. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:535–545. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Ji J, Zhang H, Fan Z, Zhang L, Shi
L, Zhou F, Chen WR, Wang H and Wang X: Stimulation of dendritic
cells by DAMPs in ALA-PDT treated SCC tumor cells. Oncotarget.
6:44688–44702. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Li J, Lv T, Tu Q, Huang Z and Wang
X: Therapeutic and immune effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid
photodynamic therapy on UVB-induced squamous cell carcinomas in
hairless mice. Exp Dermatol. 22:362–363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakaseko H, Kobayashi M, Akita Y, Tamada Y
and Matsumoto Y: Histological changes and involvement of apoptosis
after photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis. Br J Dermatol.
148:122–127. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gellén E, Fidrus E, Péter M, Szegedi A,
Emri G and Remenyik É: Immunological effects of photodynamic
therapy in the treatment of actinic keratosis and squamous cell
carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 24:342–348. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Souwer IH, Bor JH, Smits P and
Lagro-Janssen AL: Nifedipine vs placebo for treatment of chronic
chilblains: A randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 14:453–459.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zou F, Lu L, Liu J, Xia B, Zhang W, Hu Q,
Liu W, Zhang Y, Lin Y, Jing S, et al: Engineered triple inhibitory
receptor resistance improves anti-tumor CAR-T cell performance via
CD56. Nat Commun. 10:41092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang X, Qin Y, Sheng X, Xing J and Zhan W:
Characterization of CD3+ T lymphocytes of Japanese flounder
(Paralichthys olivaceus) and its response after immunization with
formalin-inactivated Edwardsiella tarda. Fish Shellfish Immunol.
63:220–227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gleich T, Chiticariu E, Huber M and Hohl
D: Keratoacan-thoma: A distinct entity? Exp Dermatol. 25:85–91.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kwiek B and Schwartz RA: Keratoacanthoma
(KA): An update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 74:1220–1233. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Selmer J, Skov T, Spelman L and Weedon D:
Squamous cell carcinoma and keratoacanthomas are biologically
distinct and can be diagnosed by light microscopy: A review.
Histopathology. 69:535–541. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP and Barr RJ:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A comprehensive
clinicopathologic classification-part two. J Cutan Pathol.
33:261–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao Y, Gu Z, Yu Z, Schomann T, Sayedipour
S, Aguilar JC, Ten Dijke P and Cruz LJ: Photodynamic therapy in
combination with the hepatitis B core virus-like particles (HBc
VLPs) to prime anticancer immunity for colorectal cancer treatment.
Cancers (Basel). 14:27242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mossakowska BJ, Shahmoradi Ghahe S,
Cysewski D, Fabisiewicz A, Tudek B and Siedlecki JA: Mechanisms of
resistance to photodynamic therapy (PDT) in vulvar cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:41172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Z, Hu X, Zhou L, He Y, Zhang X, Yang
J, Ju Z, Liou YC, Shen HM, Luo G, et al: Photodynamic therapy
accelerates skin wound healing through promoting
re-epithelialization. Burns Trauma. 9:tkab0082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Y, Wang C, Zhuge Y, Zhang J, Xu K,
Zhang Q, Zhang H, Chen H, Chu M and Jia C: Photodynamic antifungal
activity of hypocrellin a against candida albicans. Front
Microbiol. 10:18102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Zhao T, Han F, Hu Y and Li Y:
Photothermal and gene therapy combined with immunotherapy to
gastric cancer by the gold nanoshell-based system. J
Nanobiotechnology. 17:802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Q, Wu B, Weng Q, Hu F, Lin Y, Xia C,
Peng H, Wang Y, Liu X, Liu L, et al: Regeneration of
immunocompetent B lymphopoiesis from pluripotent stem cells guided
by transcription factors. Cell Mol Immunol. 19:492–503. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Algarin YA, Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Ruiz E
and Patel VA: Advances in topical treatments of cutaneous
malignancies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 24:69–80. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao H, Sun J and Yang Y: Research
progress of photodynamic therapy in wound healing: A literature
review. J Burn Care Res. 44:1327–1333. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao Z, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Zhao Y, Sun X, Hu C,
Wang X and Zhang G: ALA-PDT successfully treated multiple cSCC in
situ and AK in a patient with Epidermodysplasia verruciformis.
Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 35:1023952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aggarwal I, Puyana C, Chandan N, Jetter N
and Tsoukas M: Field cancerization therapies for the management of
actinic keratosis: An updated review. Am J Clin Dermatol.
25:391–405. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Heipertz EL, Zynda ER, Stav-Noraas TE,
Hungler AD, Boucher SE, Kaur N and Vemuri MC: Current perspectives
on ‘Off-The-Shelf’ allogeneic NK and CAR-NK cell therapies. Front
Immunol. 12:7321352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morvan MG and Lanier LL: NK cells and
cancer: You can teach innate cells new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:7–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bryceson YT, March ME, Barber DF,
Ljunggren HG and Long EO: Cytolytic granule polarization and
degranulation controlled by different receptors in resting NK
cells. J Exp Med. 202:1001–1012. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gonçalves-Maia M, Gache Y, Basante M,
Cosson E, Salavagione E, Muller M, Bernerd F, Avril MF, Schaub S,
Sarasin A, et al: NK cell and Fibroblast-Mediated regulation of
skin squamous cell carcinoma invasion by CLEC2A is compromised in
Xeroderma pigmentosum. J Invest Dermatol. 140:1723–1732. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ortner D, Tripp CH, Komenda K, Dubrac S,
Zelger B, Hermann M, Doppler W, Tymoszuk PZ, Boon L, Clausen BE and
Stoitzner P: Langerhans cells and NK cells cooperate in the
inhibition of chemical skin carcinogenesis. Oncoimmunology.
6:e12602152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen X, Chen X, Gao J, Yang H, Duan Y,
Feng Y, He X, Gong X, Wang H, Wu X and Chang J: Astragaloside III
enhances anti-tumor response of NK cells by elevating NKG2D and
IFN-γ. Front Pharmacol. 10:8982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shi J, Wu P, Sheng L, Sun W and Zhang H:
Ferroptosis-related gene signature predicts the prognosis of
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 21:6692021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gill S, Vasey AE, De Souza A, Baker J,
Smith AT, Kohrt HE, Florek M, Gibbs KD Jr, Tate K, Ritchie DS and
Negrin RS: Rapid development of exhaustion and down-regulation of
eomesodermin limit the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred
murine natural killer cells. Blood. 119:5758–5768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oyer JL, Gitto SB, Altomare DA and Copik
AJ: PD-L1 blockade enhances anti-tumor efficacy of NK cells.
Oncoimmunology. 7:e15098192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luci C, Bihl F, Bourdely P, Khou S, Popa
A, Meghraoui-Kheddar A, Vermeulen O, Elaldi R, Poissonnet G, Sudaka
A, et al: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma development is
associated with a temporal infiltration of ILC1 and NK cells with
immune dysfunctions. J Invest Dermatol. 141:2369–2379. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fu XQ, Liu B, Wang YP, Li JK, Zhu PL, Li
T, Tse KW, Chou JY, Yin CL, Bai JXL, et al: Activation of STAT3 is
a key event in TLR4 signaling-mediated melanoma progression. Cell
Death Dis. 11:2462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vuong NL, Cheung KW, Periaswamy B, Vi TT,
Duyen HTL, Leong YS, Binte Hamis ZN, Gregorova M, Ooi EE, Sessions
O, et al: Hyperinflammatory syndrome, natural killer cell function,
and genetic polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of severe dengue. J
Infect Dis. 226:1338–1347. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|