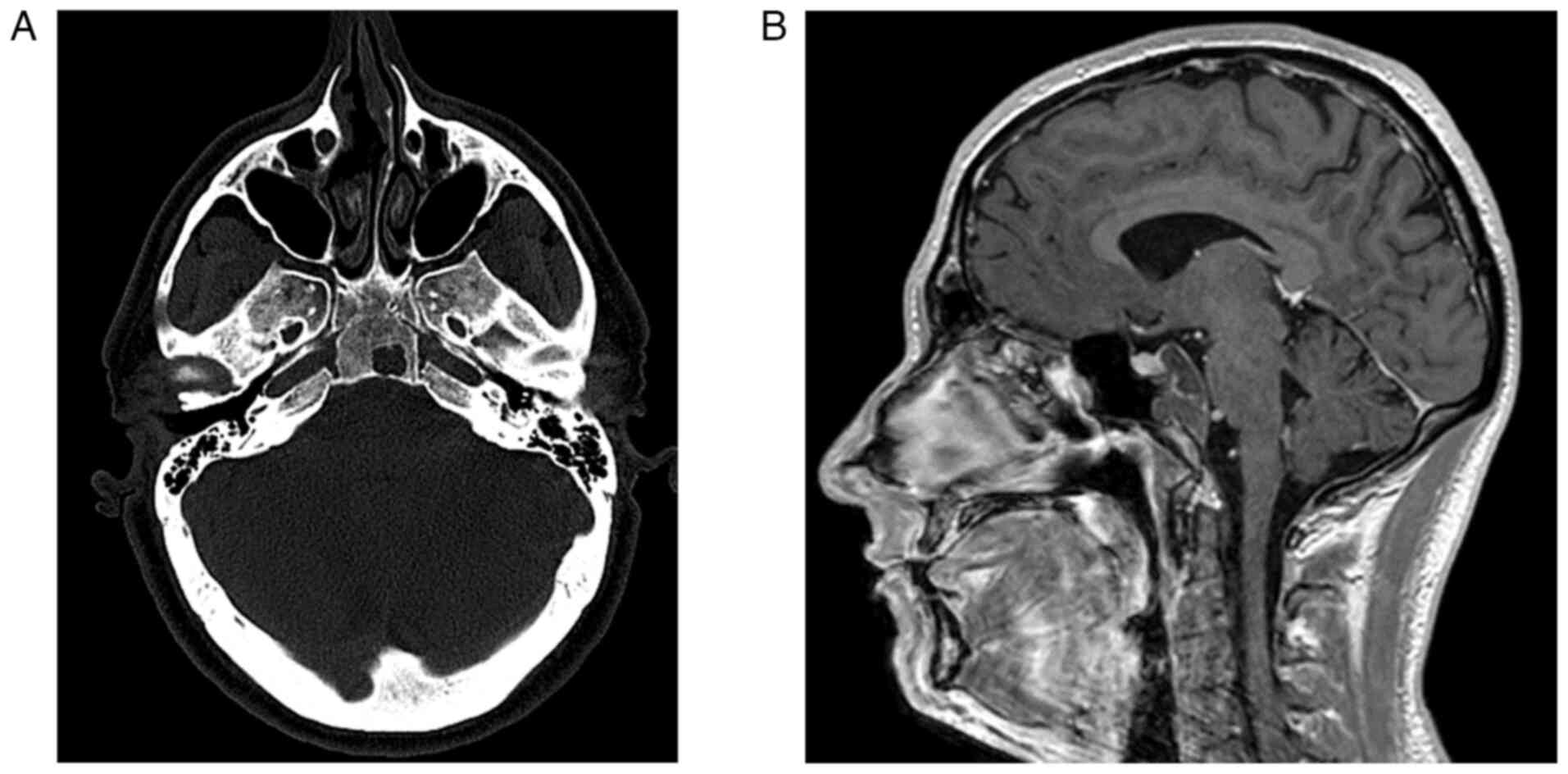
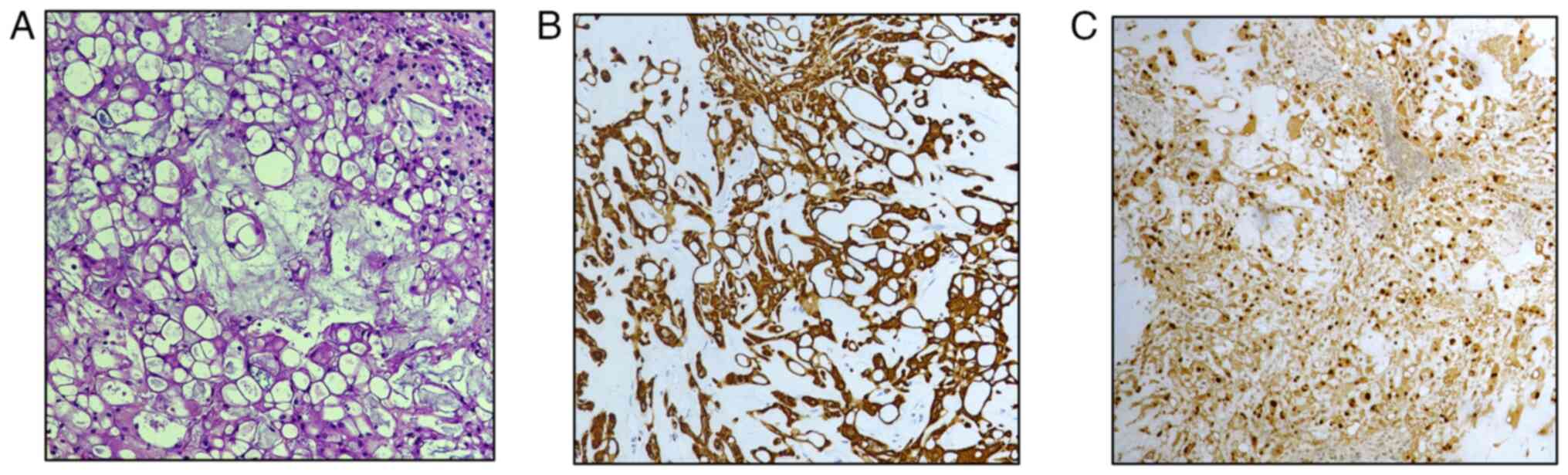
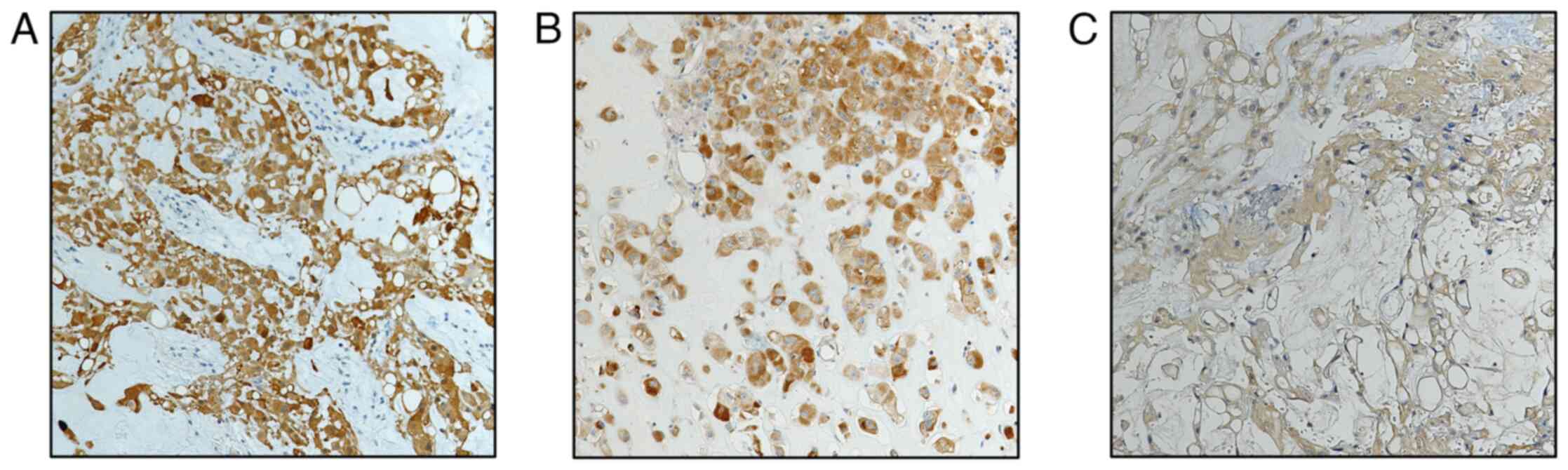
|
1
|
Ieni A, Pizzimenti C, Broggi G, Caltabiano
R, Germanò A, Barbagallo GMV, Vigneri P, Giuffrè G and Tuccari G:
Immunoexpression of p62/SQSTM1/Sequestosome-1 in human primary and
recurrent IDH1/2 wild-type glioblastoma: A pilot study. Oncol Lett.
24:3362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pizzimenti C, Fiorentino V, Franchina M,
Martini M, Giuffrè G, Lentini M, Silvestris N, Di Pietro M, Fadda
G, Tuccari G and Ieni A: Autophagic-related proteins in brain
gliomas: Role, mechanisms, and targeting agents. Cancers (Basel).
15:26222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Broggi G, Ieni A, Russo D, Varricchi S,
Puzzo L, Russo A, Reibaldi M, Longo A, Tuccari G, Staibano S and
Caltabiano R: The macro-autophagy-related protein beclin-1
immunohistochemical expression correlates with tumor cell type and
clinical behavior of uveal melanoma. Front Oncol. 10:5898492020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yun CW and Lee SH: The roles of autophagy
in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:34662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yun CW, Jeon J, Go G, Lee JH and Lee SH:
The dual role of autophagy in cancer development and a therapeutic
strategy for cancer by targeting autophagy. Int J Mol Sci.
22:1792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh SS, Vats S, Chia AYQ, Tan TZ, Deng
S, Ong MS, Arfuso F, Yap CT, Goh BC, Sethi G, et al: Dual role of
autophagy in hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene. 37:1142–1158. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karpathiou G, Dumollard JM, Dridi M, Dal
Col P, Barral FG, Boutonnat J and Peoc'h M: Chordomas: A review
with emphasis on their pathophysiology, pathology, molecular
biology, and genetics. Pathol Res Pract. 216:1530892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fletcher C, Bridge J, Hogendoom P and
Mertens F: Notochordal tumours. WHO Classification of Tumours. Soft
Tissue and Bone Tumors. 5th edition. IARC; Lyon, France: pp.
449–456. 2020
|
|
9
|
George B, Bresson D, Herman P and Froelich
S: Chordomas: A review. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 26:437–452. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Santegoeds RGC, Temel Y,
Beckervordersandforth JC, Van Overbeeke JJ and Hoeberigs CM:
State-of-the-art imaging in human chordoma of the skull base. Curr
Radiol Rep. 6:162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ulici V and Hart J: Chordoma. Arch Pathol
Lab Med. 146:386–395. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schläfli AM, Adams O, Galván JA, Gugger M,
Savic S, Bubendorf L, Schmid RA, Becker KF, Tschan MP, Langer R and
Berezowska S: Prognostic value of the autophagy markers LC3 and
p62/SQSTM1 in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
7:39544–39555. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niu J, Yan T, Guo W, Wang W and Zhao Z:
Insight into the role of autophagy in osteosarcoma and its
therapeutic implication. Front Oncol. 9:12322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barresi V, Ieni A, Branca G and Tuccari G:
Brachyury: A diagnostic marker for the differential diagnosis of
chordoma and hemangioblastoma versus neoplastic histological
mimickers. Dis Markers. 2014:5147532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jovanović L, Nikolić A, Dragičević S,
Jović M and Janković R: Prognostic relevance of autophagy-related
markers p62, LC3, and Beclin1 in ovarian cancer. Croat Med J.
63:453–460. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lazova R, Camp RL, Klump V, Siddiqui SF,
Amaravadi RK and Pawelek JM: Punctate LC3B expression is a common
feature of solid tumors and associated with proliferation,
metastasis, and poor outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 18:370–379. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gillson J, Abd El-Aziz YS, Leck LYW,
Jansson PJ, Pavlakis N, Samra JS, Mittal A and Sahni S: Autophagy:
A key player in pancreatic cancer progression and a potential drug
target. Cancers (Basel). 14:35282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Chen Z, Guo J, Wang L and Liu X:
Ambra1 induces autophagy and desensitizes human prostate cancer
cells to cisplatin. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201707702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yurube T, Hirata H, Ito M, Terashima Y,
Kakiuchi Y, Kuroda R and Kakutani K: Involvement of autophagy in
rat tail static compression-induced intervertebral disc
degeneration and notochordal cell disappearance. Int J Mol Sci.
22:56482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng Y, Shen J, Gao Y, Liao Y, Cote G,
Choy E, Chebib I, Mankin H, Hornicek F and Duan Z: Expression of
programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and prevalence of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in chordoma. Oncotarget.
6:11139–11149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mathios D, Ruzevick J, Jackson CM, Xu H,
Shah SR, Taube JM, Burger PC, McCarthy EF, Quinones-Hinojosa A,
Pardoll DM and Lim M: PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2 expression in the chordoma
microenvironment. J Neurooncol. 121:251–259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou M, Pan Y, Huang W, Zhang TL, Escobar
D, Wang XB, Jiang Y, She XL, Lv GH and Li J: A four-factor immune
risk score signature predicts the clinical outcome of patients with
spinal chordoma. Clin Transl Med. 10:224–237. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu J, Shi Q, Wang B, Ji T, Guo W, Ren T
and Tang X: The role of tumor immune microenvironment in chordoma:
Promising immunotherapy strategies. Front Immunol. 14:12572542023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Y and Zhang H: Immune
microenvironment and immunotherapy for chordoma. Front Oncol.
14:13742492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|