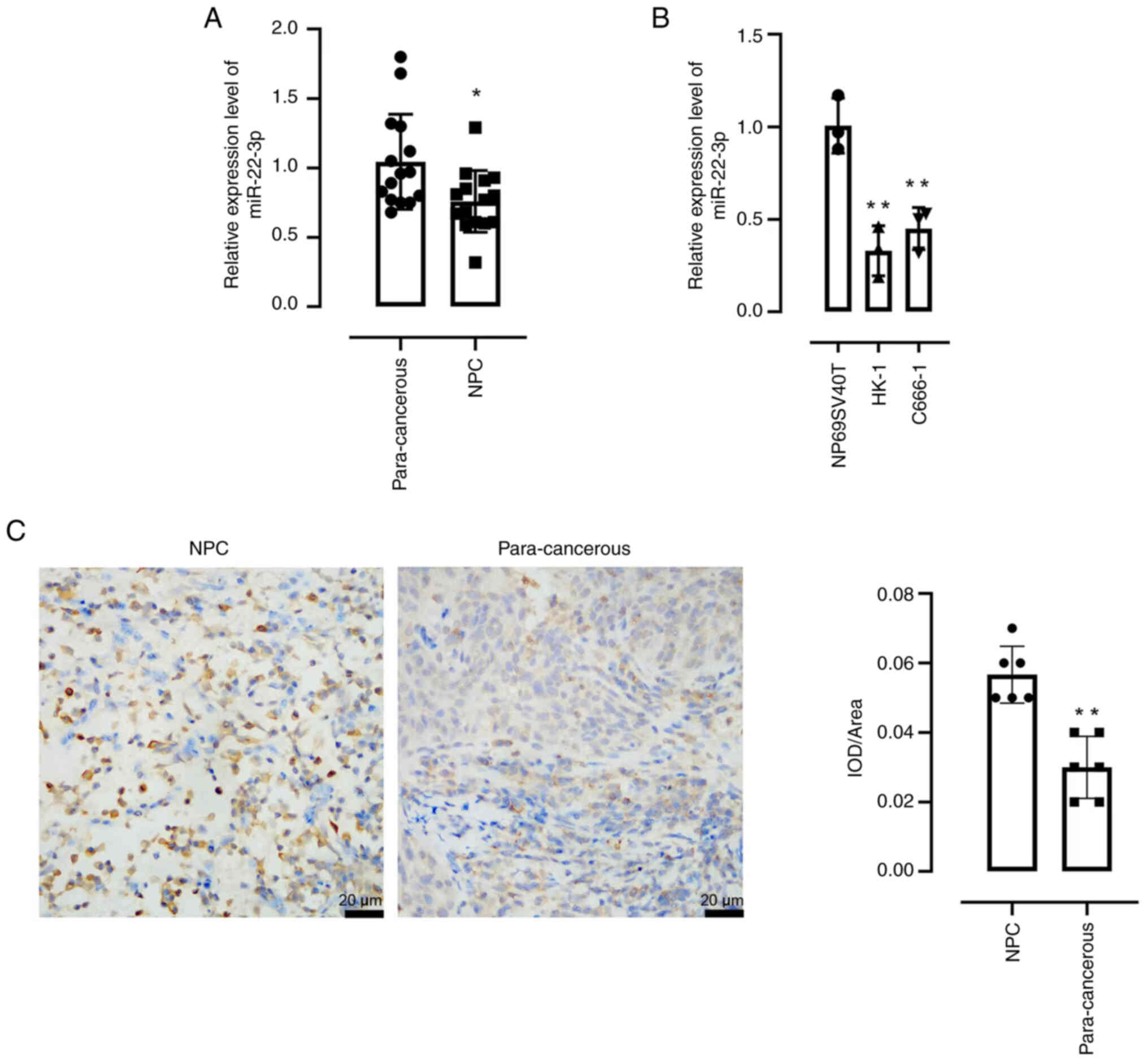
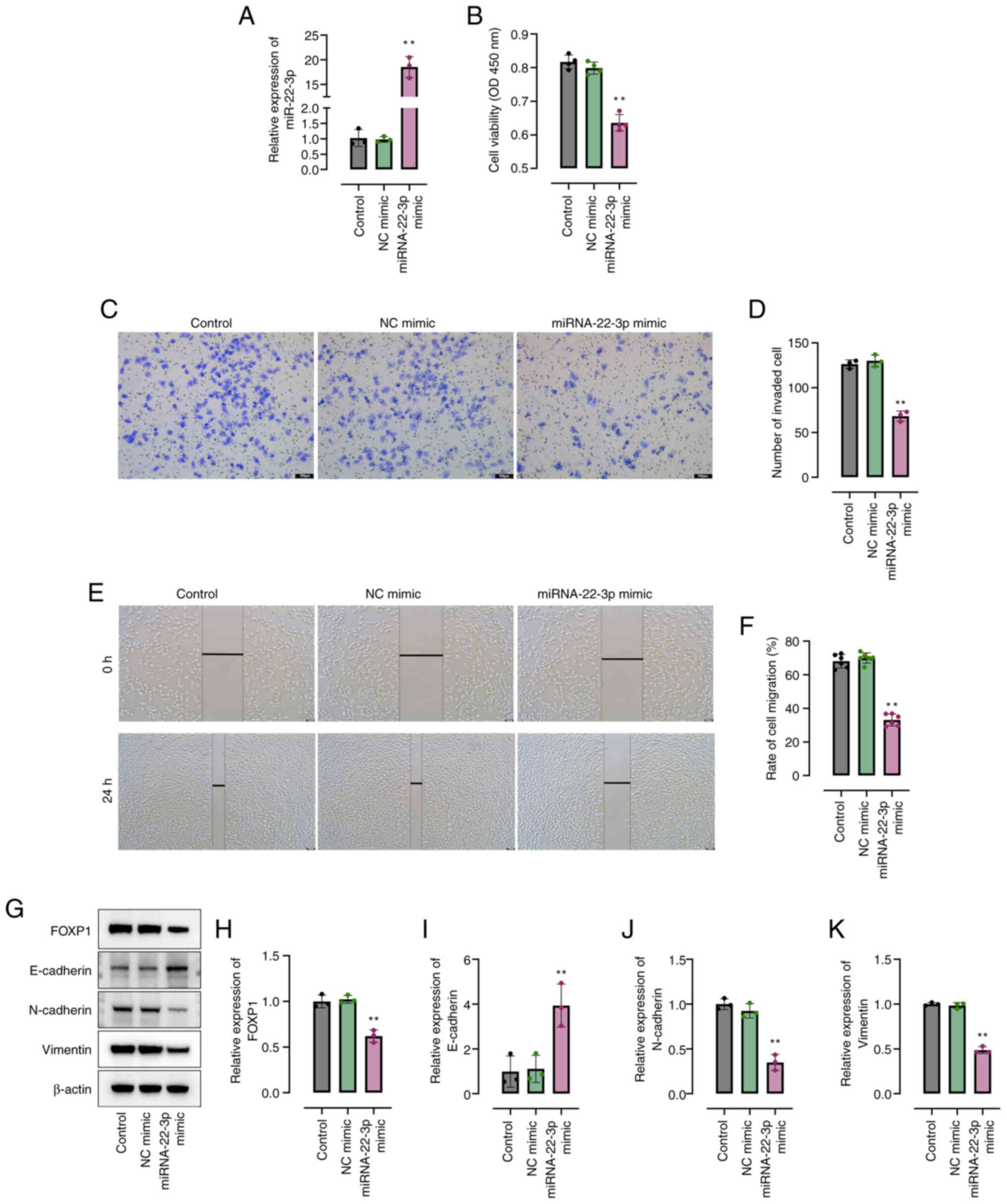
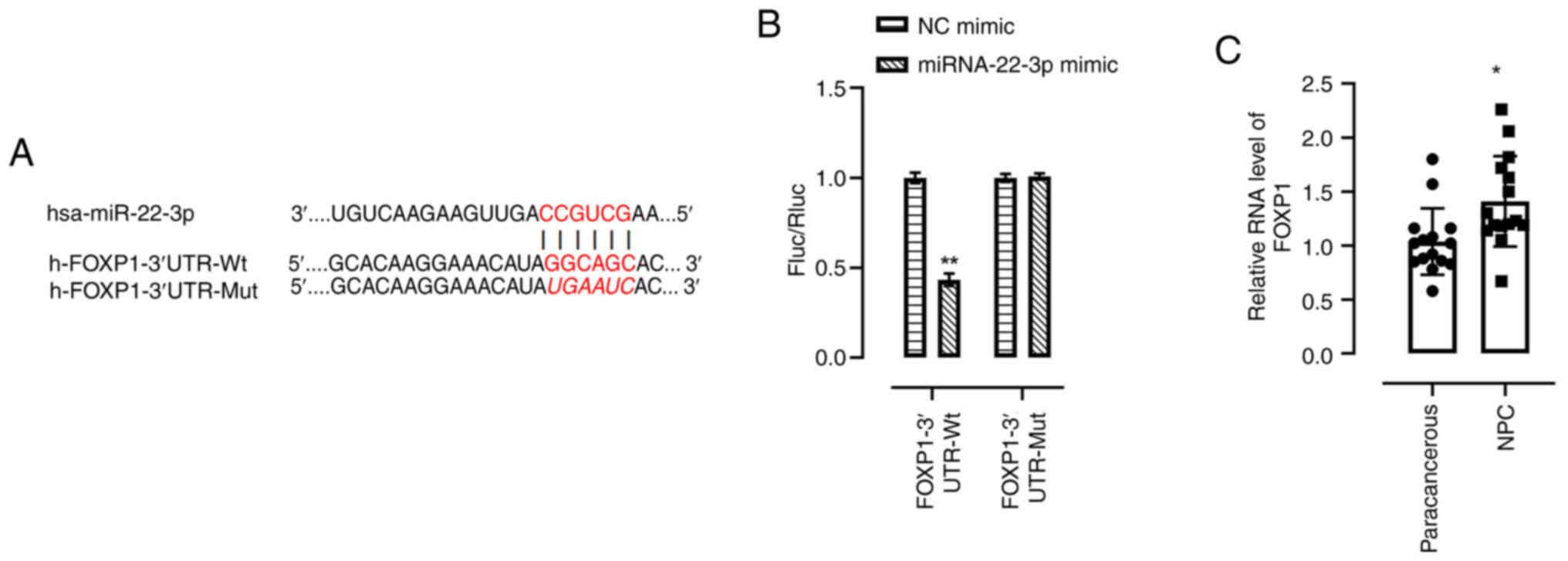
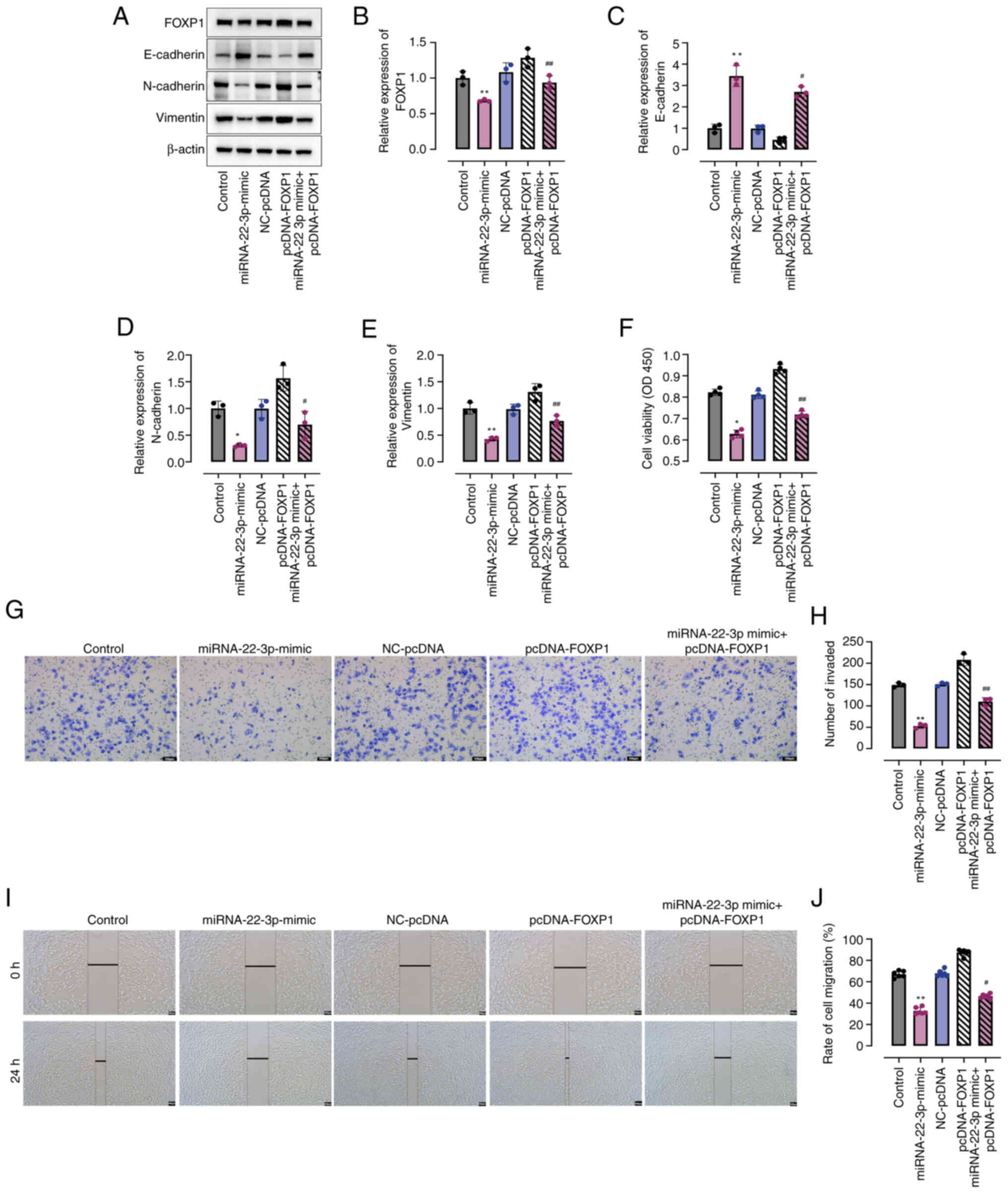
|
1
|
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun
Y and Ma J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 394:64–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chang ET, Ye W, Zeng YX and Adami HO: The
evolving epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 30:1035–1047. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chua MLK, Lee VHF and Lee AWM:
Hyperfractionation for reirradiation of recurrent nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 401:878–879. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guan S, Wei J, Huang L and Wu L:
Chemotherapy and chemo-resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur
J Med Chem. 207:1127582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chekulaeva M: First demonstration of
miRNA-dependent mRNA decay. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:1642023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pozniak T, Shcharbin D and Bryszewska M:
Circulating microRNAs in medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 23:39962022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ruggieri F, Jonas K, Ferracin M, Dengler
M, Jӓger V and Pichler M: MicroRNAs as regulators of tumor
metabolism. Endocr Relat Cancer. 30:e2202672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Q, Zhang Q, Gu M, Zhang K, Xia T,
Zhang S, Chen W, Yin H, Yao H, Fan Y, et al: MIR106A-5p
upregulation suppresses autophagy and accelerates malignant
phenotype in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Autophagy. 17:1667–1683.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin W, Shi L and Mao Y: MiR-194 regulates
nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by modulating MAP3K3
expression. FEBS Open Bio. 9:43–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kong D, Wang X, Wang X, Wang Z and Wang F:
Downregulated miRNA-22-3p promotes the progression and leads to
poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting
CDKN2C. J BUON. 26:409–417. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barut Z and Akdeniz FT: Evaluation of the
relationship between miRNA-22-3p and Gal-9 levels in glioblastoma.
In Vivo. 37:2577–2584. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li C, Li X, Wang H, Guo X, Xue J, Wang X
and Ni J: MicroRNA-22-3p and MicroRNA-149-5p inhibit human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis properties by
regulating methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Curr Issues Mol
Biol. 44:952–962. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koon HB, Ippolito GC, Banham AH and Tucker
PW: FOXP1: A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 11:955–965. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ijichi N, Ikeda K, Horie-Inoue K and Inoue
S: FOXP1 and estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Vitam Horm.
93:203–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen L, Heikkinen L, Wang C, Yang Y, Sun H
and Wong G: Trends in the development of miRNA bioinformatics
tools. Brief Bioinform. 20:1836–1852. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hill M and Tran N: miRNA interplay:
Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0476622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He B, Zhao Z, Cai Q, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Shi
S, Xie H, Peng X, Yin W, Tao Y and Wang X: miRNA-based biomarkers,
therapies, and resistance in cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 16:2628–2647.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y, Chen X, Jing M, Du H and Zeng Y:
Expression of miRNA-146a in nasopharyngeal carcinoma is upregulated
by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. Oncol Rep.
28:1237–1242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan DC, Zhao YR, Qi H, Hou JX and Zhang
TH: MiRNA-506 presents multiple tumor suppressor activities by
targeting EZH2 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx.
47:632–642. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia X, Yang M, Hu W and Cai S:
Overexpression of miRNA-22-3p attenuates osteoporosis by targeting
MAPK14. Exp Ther Med. 22:6922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang SC, Wang M, Wu WB, Wang R, Cui J, Li
W, Li ZL, Li W and Wang SM: Mir-22-3p inhibits arterial smooth
muscle cell proliferation and migration and neointimal hyperplasia
by targeting HMGB1 in arteriosclerosis obliterans. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:2492–2506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang Y, Jin X, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Shen CX,
Zhang YC and Li YG: The lncRNA MALAT1 protects the endothelium
against ox-LDL-induced dysfunction via upregulating the expression
of the miR-22-3p target genes CXCR2 and AKT. FEBS Lett.
589:3189–3196. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gorur A, Bayraktar R, Ivan C, Mokhlis HA,
Bayraktar E, Kahraman N, Karakas D, Karamil S, Kabil NN,
Kanlikilicer P, et al: ncRNA therapy with miRNA-22-3p suppresses
the growth of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 23:930–943. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Human FOX gene family
(Review). Int J Oncol. 25:1495–1500. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Golson ML and Kaestner KH: Fox
transcription factors: From development to disease. Development.
143:4558–4570. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patzelt T, Keppler SJ, Gorka O, Thoene S,
Wartewig T, Reth M, Förster I, Lang R, Buchner M and Ruland J:
Foxp1 controls mature B cell survival and the development of
follicular and B-1 B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:3120–3125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi C, Sakuma M, Mooroka T, Liscoe A, Gao
H, Croce KJ, Sharma A, Kaplan D, Greaves DR, Wang Y and Simon DI:
Down-regulation of the forkhead transcription factor Foxp1 is
required for monocyte differentiation and macrophage function.
Blood. 112:4699–4711. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fox SB, Brown P, Han C, Ashe S, Leek RD,
Harris AL and Banham AH: Expression of the forkhead transcription
factor FOXP1 is associated with estrogen receptor alpha and
improved survival in primary human breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:3521–3527. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng J, Zhang X, Zhu H, Wang X, Ni S and
Huang J: High expression of FoxP1 is associated with improved
survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin
Pathol. 138:230–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Liu J, Yang L,
He S, Chen L and Huang J: Prognostic significance of FOXP1 as an
oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 65:528–533.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han SL, Wu XL, Wan L, Zeng QQ, Li JL and
Liu Z: FOXP1 expression predicts polymorphic histology and poor
prognosis in gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas.
Dig Surg. 26:156–162. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barrans SL, Fenton JAL, Banham A, Owen RG
and Jack AS: Strong expression of FOXP1 identifies a distinct
subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients with poor
outcome. Blood. 104:2933–2935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van Keimpema M, Grüneberg LJ, Mokry M, van
Boxtel R, Koster J, Coffer PJ, Pals ST and Spaargaren M: FOXP1
directly represses transcription of proapoptotic genes and
cooperates with NF-κB to promote survival of human B cells. Blood.
124:3431–3440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gascoyne DM and Banham AH: The
significance of FOXP1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 58:1037–1051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Walker MP, Stopford CM, Cederlund M, Fang
F, Jahn C, Rabinowitz AD, Goldfarb D, Graham DM, Yan F, Deal AM, et
al: FOXP1 potentiates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diffuse large B
cell lymphoma. Sci Signal. 8:ra122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|