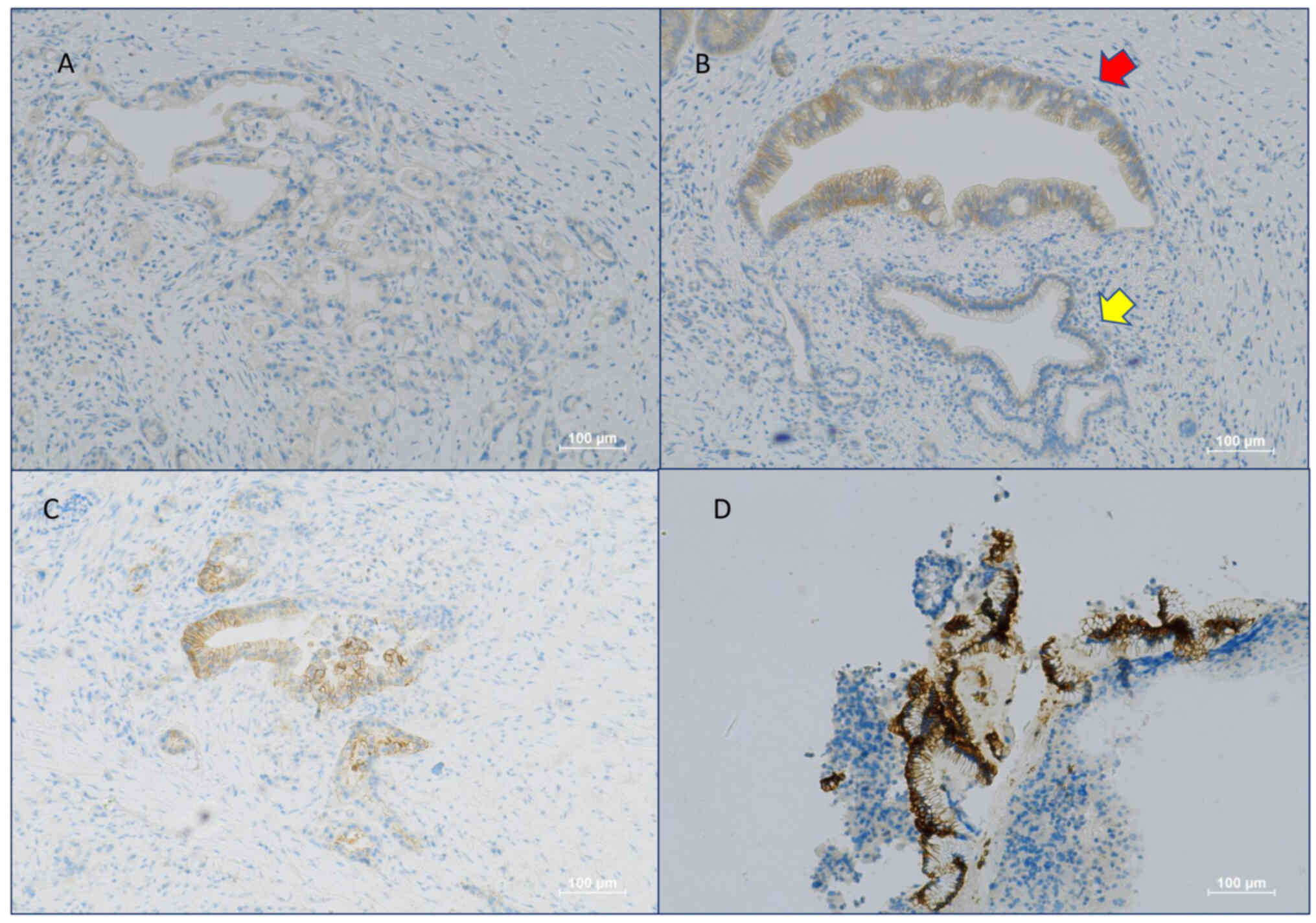
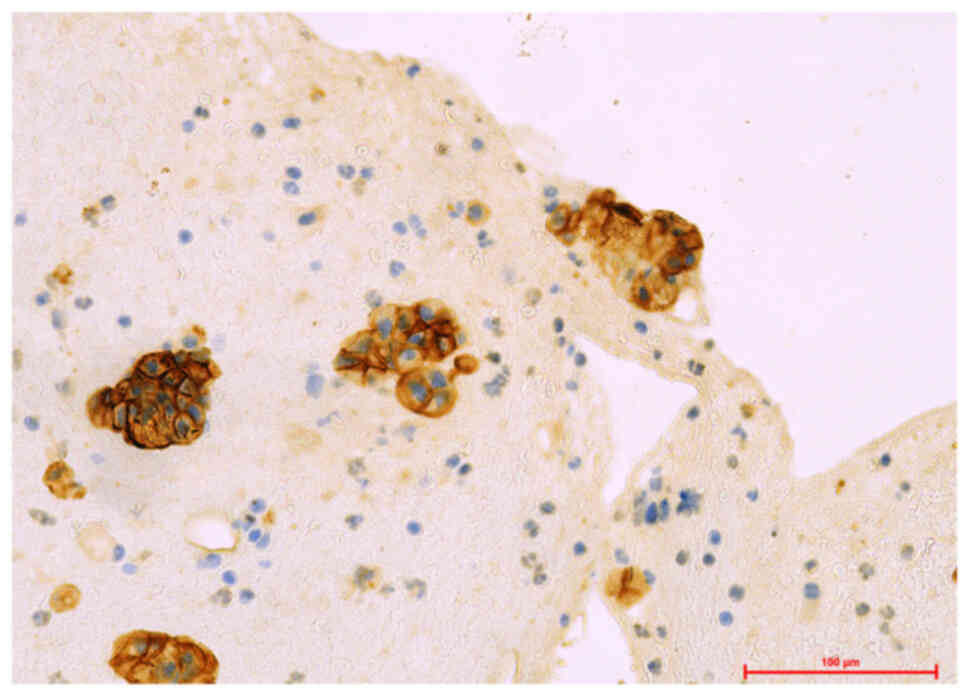
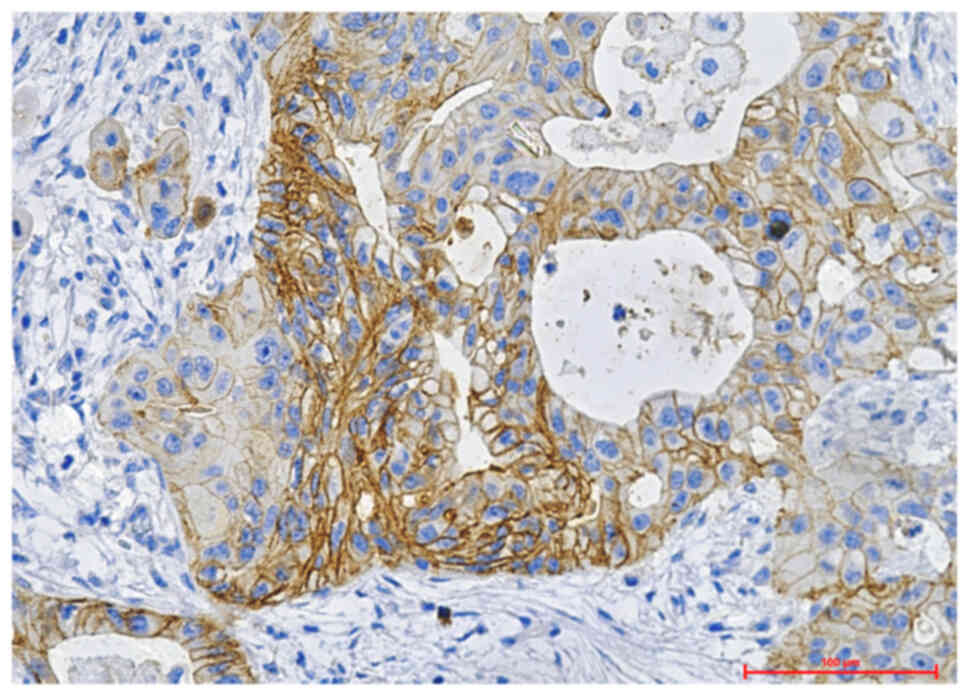
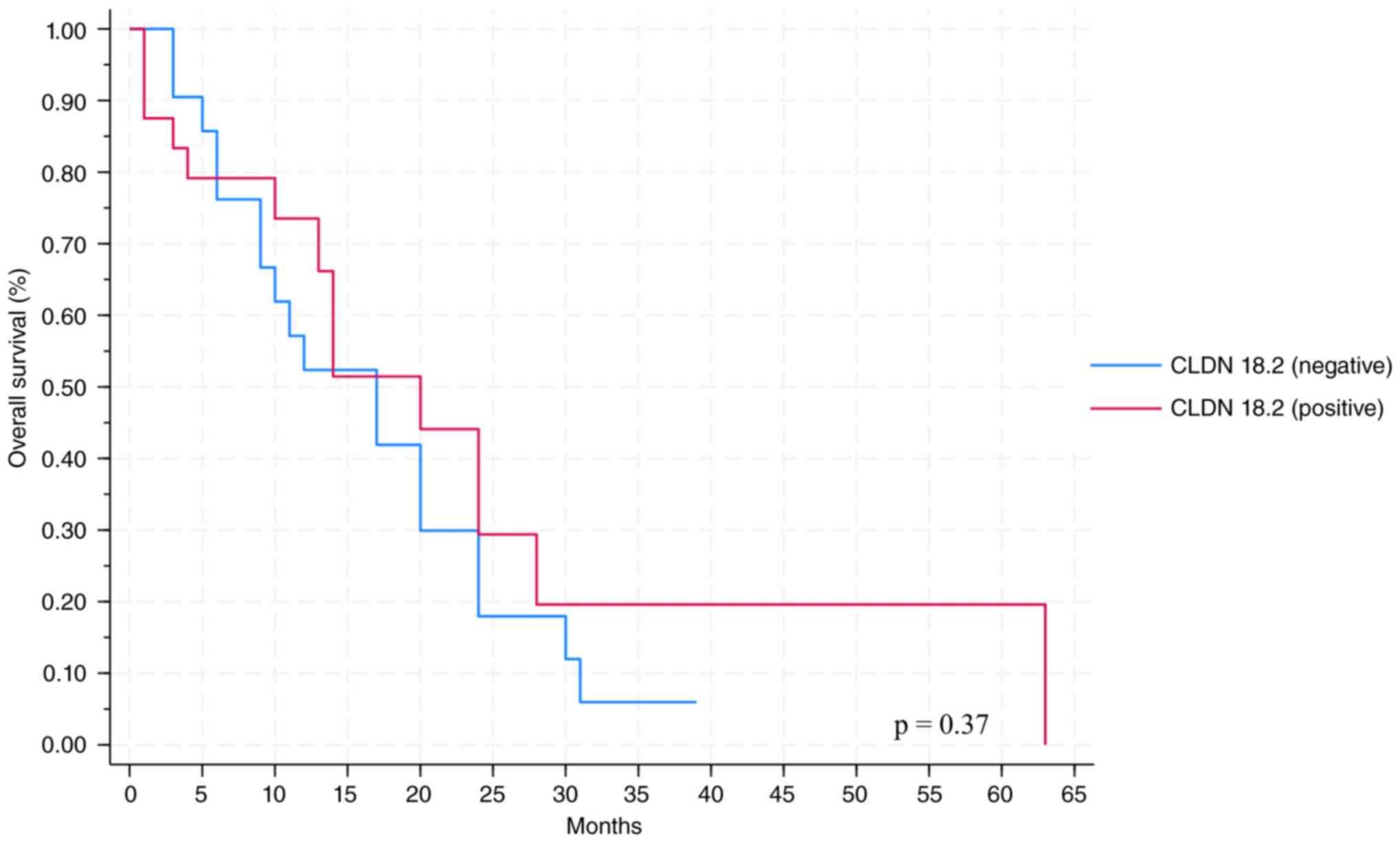
|
1
|
Stoffel EM, Randall E, Brand RE and
Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer: Changing epidemiology and new
approaches to risk assessment, early detection, and prevention.
Gastroenterology. 164:752–765. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Park W, Chawla A and O'Reilly EM:
Pancreatic cancer: A review. JAMA. 326:851–862. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Wu N, Pei B, Ma X and Yang W:
Claudin and pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. 13:11362272023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ren B, Cui M, Yang G, Wang H, Feng M, You
L and Zhao Y: Tumor microenvironment participates in metastasis of
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:1082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sahin U, Koslowski M, Dhaene K, Usener D,
Brandenburg G, Seitz G, Huber C and Türeci O: Claudin-18 splice
variant 2 is a pan-cancer target suitable for therapeutic antibody
development. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7624–7634. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sugimoto M, Takagi T, Suzuki R, Konno N,
Asama H, Sato Y, Irie H, Okubo Y, Nakamura J, Takasumi M, et al:
Drug treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in
patients with pancreatic cancer. Fukushima J Med Sci. 68:1–10.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hosein AN, Dougan SK, Aguirre AJ and
Maitra A: Translational advances in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma therapy. Nat Cancer. 3:272–286. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K
and Tsukita S: Claudin-1 and −2: Novel integral membrane proteins
localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to
occludin. J Cell Biol. 141:1539–1550. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nichols LS, Ashfaq R and Iacobuzio-Donahue
CA: Claudin 4 protein expression in primary and metastatic
pancreatic cancer: Support for use as a therapeutic target. Am J
Clin Pathol. 121:226–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hashimoto I and Oshima T: Claudins and
gastric cancer: An overview. Cancers (Basel). 14:2902022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Krause G, Winkler L, Mueller SL, Haseloff
RF, Piontek J and Blasig IE: Structure and function of claudins.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:631–645. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lal-Nag M and Morin PJ: The claudins.
Genome Biol. 10:2352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hong JY, An JY, Lee J, Park S.H, Park JO,
Park YS, Lim HY, Kim KM, Kang WK and Kim ST: Claudin 18.2
expression in various tumor types and its role as a potential
target in advanced gastric cancer. Transl Cancer Res. 9:3367–3374.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pellino A, Brignola S, Riello E, Niero M,
Murgioni S, Guido M, Nappo F, Businello G, Sbaraglia M, Bergamo F,
et al: Association of CLDN18 protein expression with
clinicopathological features and prognosis in advanced gastric and
gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinomas. J Pers Med. 11:10952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dottermusch M, Krüger S, Behrens H.M,
Halske C and Röcken C: Expression of the potential therapeutic
target claudin-18.2 is frequently decreased in gastric cancer:
Results from a large Caucasian cohort study. Virchows Arch.
475:563–571. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhou L, Zhang M and Liang
Z: Investigation of clinical application of claudin 18 isoform 2 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 302
Chinese patients. Histol Histopathol. 37:1031–1040. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Swisshelm K, Macek R and Kubbies M: Role
of claudins in tumorigenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 57:919–928. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang D, Huang G, Liu J and Wei W:
Claudin18.2-targeted cancer theranostics. Am J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 13:64–69. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kubota Y and Shitara K: Zolbetuximab for
Claudin 18.2-positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer.
Ther Adv Med Oncol. 16:175883592312179672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao W, Xing H, Li Y, Tian W, Song Y, Jiang
Z and Yu J: Claudin18.2 is a novel molecular biomarker for
tumor-targeted immunotherapy. Biomarker Res. 10:382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wöll S, Schilitter AM, Dhaene K, Roller M,
Esposito I, Sahin U and Türeci Ö: Claudin 18.2 is a target for
IMAB362 antibody in pancreatic neoplasms. Int J Cancer.
134:731–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh P, Toom S and Huang Y: Anti-claudin
18.2 antibody as new targeted therapy for advanced gastric cancer.
J Hematol Oncol. 10:1052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Zhang CS, Dong XY, Hu Y, Duan BJ,
Bai J, Wu YY, Fan L, Liao XH, Kang Y, et al: Claudin 18.2 is a
potential therapeutic target for zolbetuximab in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 14:1252–1264. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park S, Shin K, Kim I.H, Hong T, Kim Y,
Suh J and Lee M: Clinicopathological features and prognosis of
resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients with claudin-18
overexpression. J Clin Med. 12:53942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kayikcioglu E and Yüceer RO: The role of
claudin 18.2 and HER-2 in pancreatic cancer outcomes. Medicine
(Baltimore). 102:e328822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lyu SI, Fretter C, Simon AG, Spielmann SM,
Damanakis AI, Zhao Y, Bruns CJ, Schmidt T, Popp FC, Waldschmidt D,
et al: Extent and clinical significance of the therapy-relevant
tight junction protein claudin 18.2 in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma-real-world evidence. Transl Oncol. 47:1020442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shain U, Türeci Ö, Manikhas G, Lordick F,
Rusyn A, Vynnychenko I, Dudon V, Bazin I, Bondarenko I, Melichar B,
et al: FAST: A randomised phase II study of zolbetuximab (IMAB362)
plus EOX versus EOX alone for first-line treatment of advanced
CLDN18.2-positive gastric and gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
Ann Oncol. 32:609–619. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lordick F, Al-Batran SE, Ganguli A,
Morlock R, Sahin U and Türeci Ö: Patient-reported outcomes from the
phase II FAST trial of zolbetuximab plus EOX compared to EOX alone
as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic CLDN18.2+
gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastric Cancer. 24:721–730. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shah MA, Shitara K, Ajani JA, Bang YJ,
Enzinger P, Ilson D, Lordick F, Van Cutsem E, Gallego Plazas J,
Huang J, et al: Zolbetuximab plus CAPOX in CLDN18.2-positive
gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: The
randomized, phase 3 GLOW trial. Nat Med. 29:2133–2141. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shitara K, Lordick F, Bang YJ, Enzinger P,
Ilson D, Shah MA, Van Cutsem E, Xu RH, Aprile G, Xu J, et al:
Zolbetuximab plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with CLDN18.2-positive,
HER2-negative, untreated, locally advanced unresectable or
metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
(SPOTLIGHT): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3
trial. Lancet. 401:1655–1668. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Türeci Ö, Mitnacht-Kraus R, Wöll S, Yamada
T and Sahin U: Characterization of zolbetuximab in pancreatic
cancer models. Oncoimmunology. 8:e15230962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tanaka M, Shibahara J, Fukushima N,
Shinozaki A, Umeda M, Ishikawa S, Kokudo N and Fukayama M:
Claudin-18 is an early-stage marker of pancreatic carcinogenesis. J
Histochem Cytochem. 59:942–952. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|