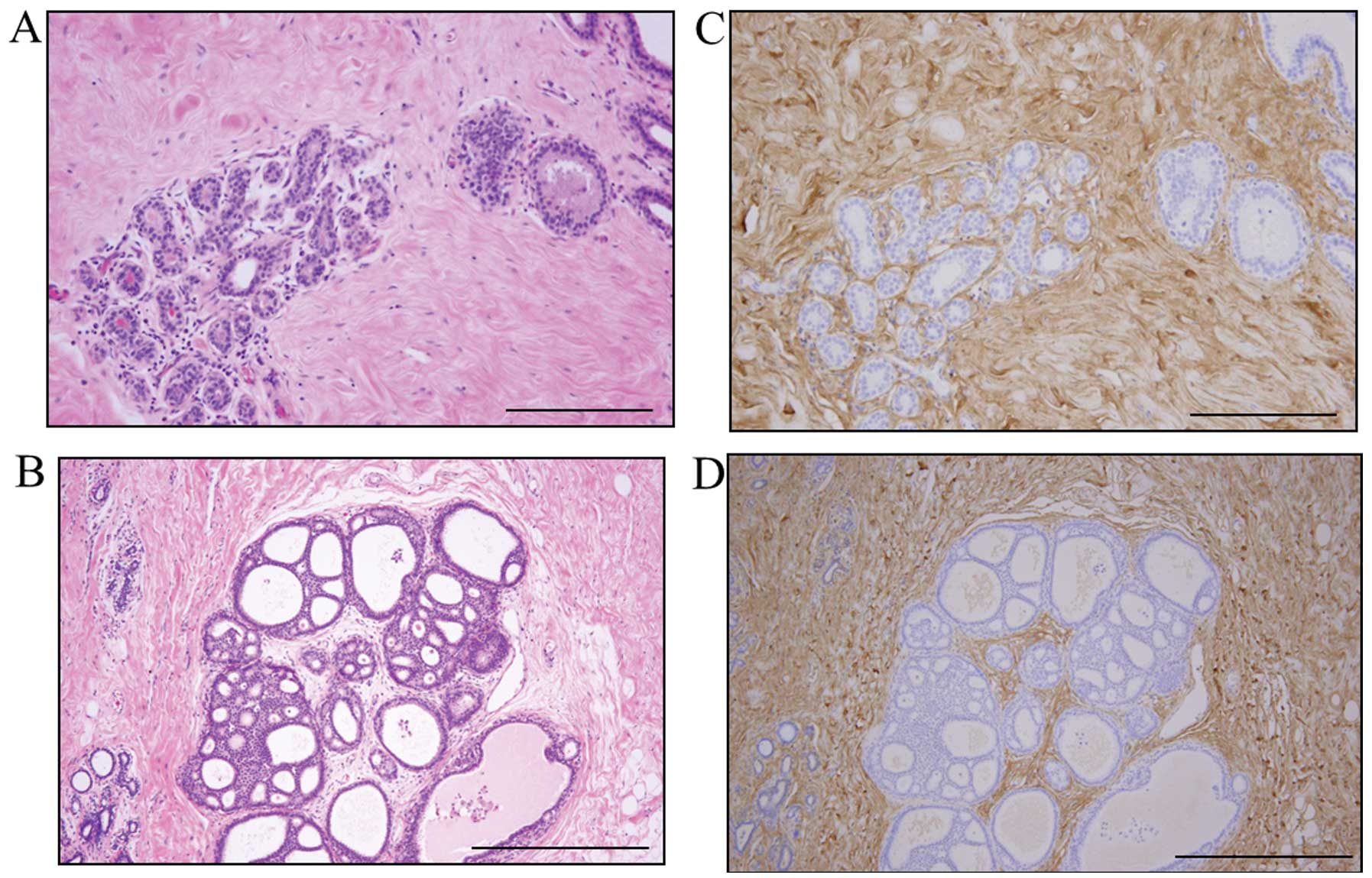
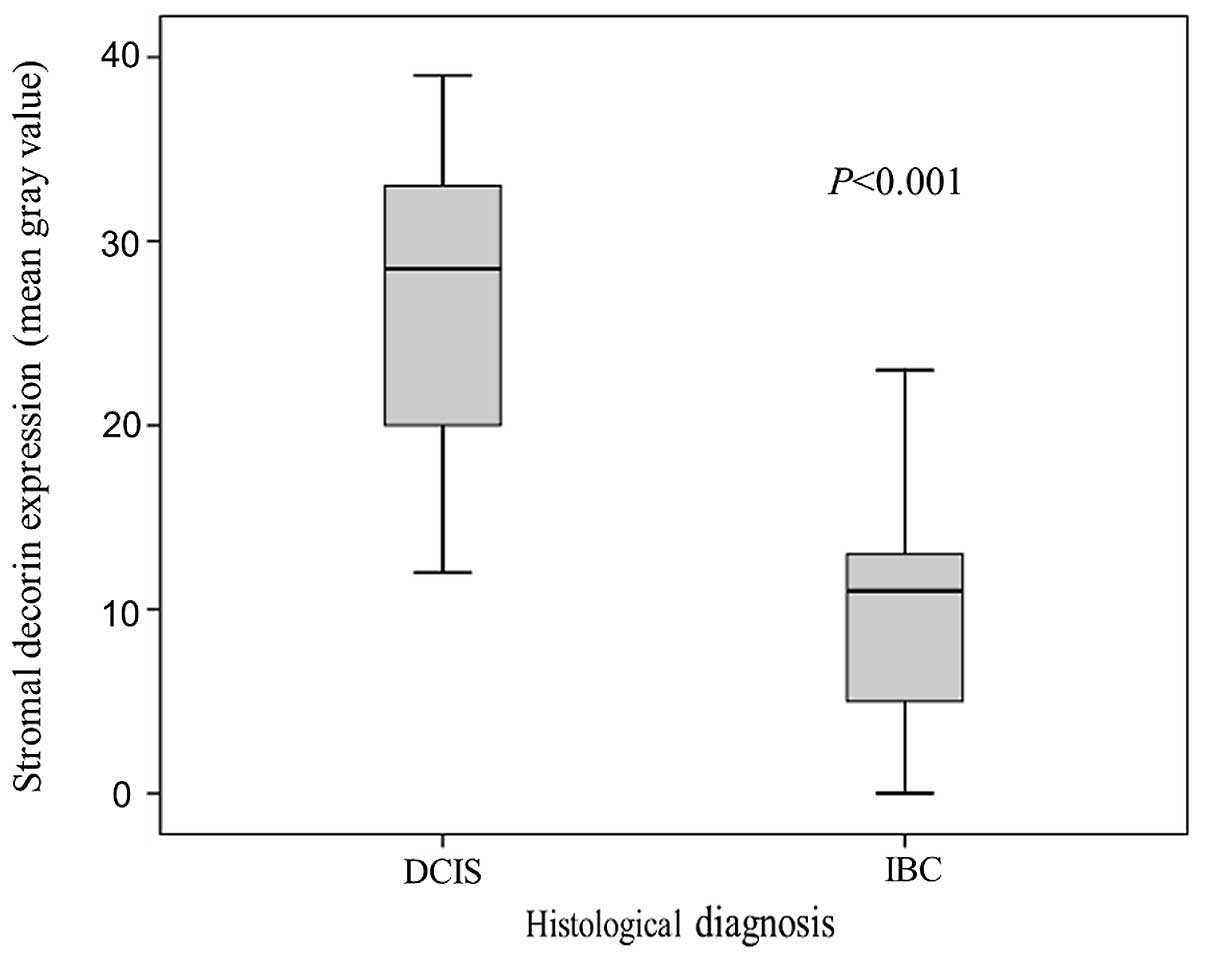
|
1
|
Kim SH, Turnbull J and Guimond S:
Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation
of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J Endocrinol.
209:139–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldoni S and Iozzo R: Tumor
microenvironment: Modulation by decorin and related molecules
harboring leucine-rich tandem motifs. Int J Cancer. 123:2473–2479.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iozzo R: Matrix proteoglycans: from
molecular design to cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem.
67:609–652. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reed CC and Iozzo RV: The role of decorin
in collagen fibrillogenesis and skin homeostasis. Glycoconj J.
19:249–255. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamaguchi Y, Mann D and Ruoslahti E:
Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta by the
proteoglycan decorin. Nature. 346:281–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Araki K, Wakabayashi H, Shintani K, et al:
Decorin suppresses bone metastasis in a breast cancer cell line.
Oncology. 77:92–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldoni S, Seidler D, Heath J, et al: An
antimetastatic role for decorin in breast cancer. Am J Pathol.
173:844–855. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burstein HJ, Polyak K, Wong JS, Lester SC
and Kaelin CM: Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. N Engl J
Med. 350:1430–1441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors. 6th edition. John Wiley &
Sons; New York: 2002
|
|
10
|
Augoff K, Grabowski K, Rabczynski J,
Kolondra A, Tabola R and Sikorski A: Expression of decorin in
esophageal cancer in relation to the expression of three isoforms
of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1, -beta2, and -beta3)
and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Invest. 27:443–452.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Augoff K, Rabczynski J, Tabola R, Czapla
L, Ratajczak K and Grabowski K: Immunohistochemical study of
decorin expression in polyps and carcinomas of the colon. Med Sci
Monit. 14:CR530–CR535. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferdous Z, Wei V, Iozzo R, Höök M and
Grande-Allen K: Decorin-transforming growth factor-interaction
regulates matrix organization and mechanical characteristics of
three-dimensional collagen matrices. J Biol Chem. 282:35887–35898.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ständer M, Naumann U, Dumitrescu L, et al:
Decorin gene transfer-mediated suppression of TGF-beta synthesis
abrogates experimental malignant glioma growth in vivo. Gene Ther.
5:1187–1194. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reiss M and Barcellos-Hoff MH:
Transforming growth factor-beta in breast cancer: a working
hypothesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 45:81–95. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akhurst RJ and Balmain A: Genetic events
and the role of TGF beta in epithelial tumour progression. J
Pathol. 187:82–90. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iozzo R, Moscatello D, McQuillan D and
Eichstetter I: Decorin is a biological ligand for the epidermal
growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 274:4489–4492. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Csordás G, Santra M, Reed C, et al:
Sustained down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
by decorin. A mechanism for controlling tumor growth in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 275:32879–32887. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Polette M, Gilbert N, Stas I, et al:
Gelatinase A expression and localization in human breast cancers.
An in situ hybridization study and immunohistochemical detection
using confocal microscopy. Virchows Arch. 424:641–645. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Imai K, Hiramatsu A, Fukushima D,
Pierschbacher M and Okada Y: Degradation of decorin by matrix
metalloproteinases: identification of the cleavage sites, kinetic
analyses and transforming growth factor-beta1 release. Biochem J.
322:809–814. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iwata H, Kobayashi S, Iwase H, Masaoka A,
Fujimoto N and Okada Y: Production of matrix metalloproteinases and
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas.
Jpn J Cancer Res. 87:602–611. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jones JL, Glynn P and Walker RA:
Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, their inhibitors, and the activator
MT1-MMP in primary breast carcinomas. J Pathol. 189:161–168. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garbett EA, Reed MW, Stephenson TJ and
Brown NJ: Proteolysis in human breast cancer. Mol Pathol.
53:99–106. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jiang WG, Davies G, Martin TA, et al:
Targeting matrilysin and its impact on tumor growth in vivo: the
potential implications in breast cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6012–6019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Quante M, Tu SP, Tomita H, et al: Bone
marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem
cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 19:257–272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsumine A, Shintani K, Kusuzaki K, et
al: Expression of decorin, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan, as a
prognostic factor in soft tissue tumors. J Surg Oncol. 96:411–418.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Troup S, Njue C, Kliewer E, et al: Reduced
expression of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans, lumican, and
decorin is associated with poor outcome in node-negative invasive
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:207–214. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|