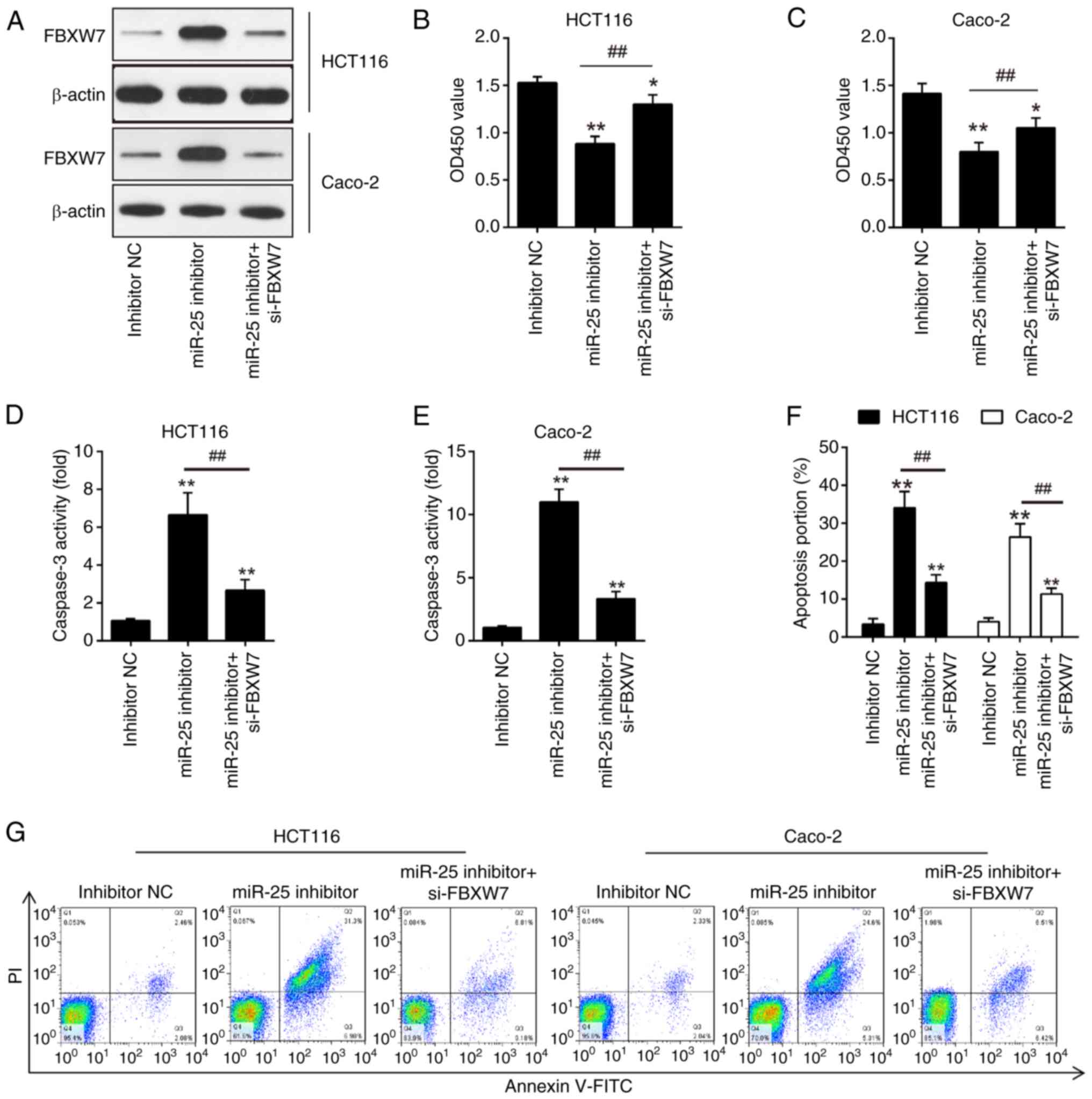
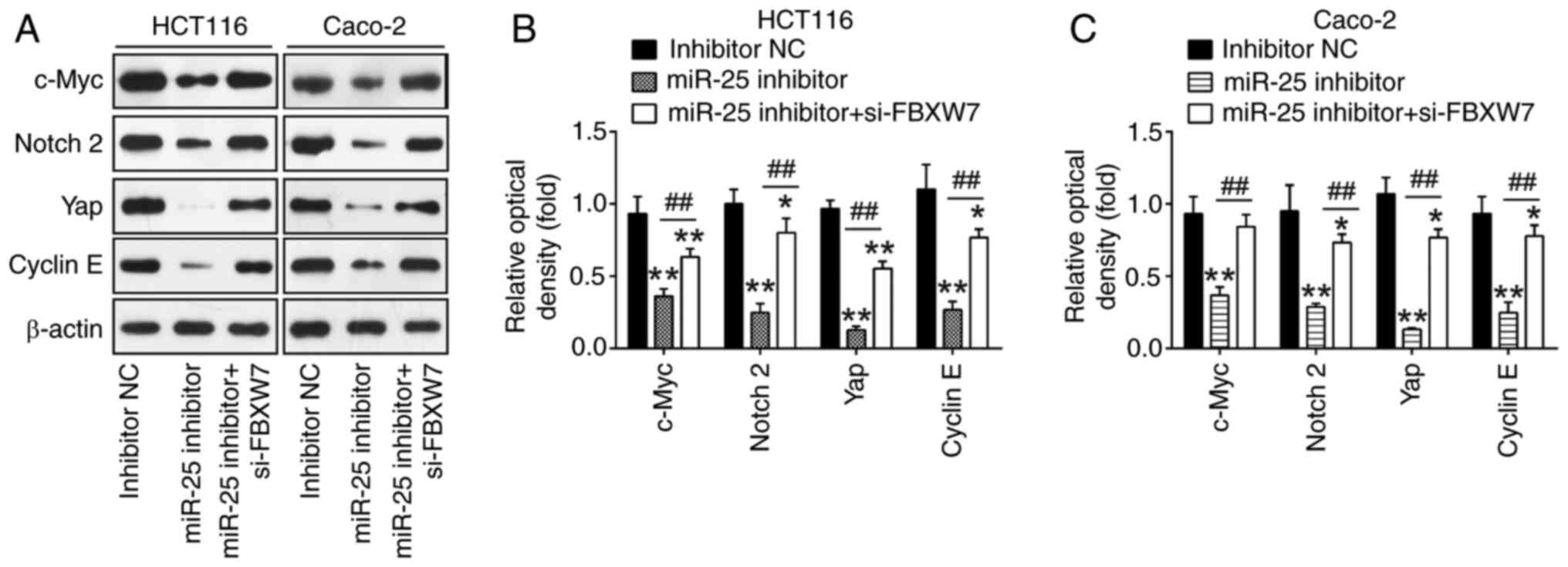
|
1
|
Biller LH and Schrag Dg: Diagnosis and
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA.
325:669–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Liu W, Zhao L, Güngör C, Xu Y, Song
X, Wang D, Zhou Z, Zhou Y, Li C, et al: Nomograms predicting
overall survival and cancer-specific survival for synchronous
colorectal liver-limited metastasis. J Cancer. 11:6213–6225. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Yin W and Chen P: MicroRNA-374a-5p
promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting GRB7.
Panminerva Med. 63:555–557. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu QD, Zhou QQ, Dong L, Huang Z, Wu F and
Deng X: MiR-199a-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting ROCK1. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 17:15330346187755092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang N, Hu X, Du Y and Du J: The role of
miRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and chemoradiotherapy.
Biomed Pharmacother. 134:1110992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Santos DAR, Gaiteiro C, Santos M, Santos
L, Dinis-Ribeiro M and Lima L: MicroRNA biomarkers as promising
tools for early colorectal cancer screening-a comprehensive review.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:110232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou W, Yang W, Duan L, Wang X, Lv P, Hu
Z, Zhao Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y and Hong L: MicroRNA-483 functions as an
oncogene in colorectal cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 51:30–37.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Chen Z, Lin S, Zheng Y, Liu Y, Gao
J and Chen S: MiR-202 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer by targeting UHRF1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 51:598–606. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu T, Chen W, Kong D, Li X, Lu H, Liu S,
Wang J, Du L, Kong Q, Huang X and Lu Z: miR-25 targets the
modulator of apoptosis 1 gene in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis.
36:925–935. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, Xiao B, Zhuang Y,
Mao XH, Wu C, Yang SM, Zeng H, Zou QM and Guo G: MicroRNA-25
promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by
directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor
survival. Oncogene. 34:2556–2565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Geng WM, Wu YG and
Qin CK: Upregulation of microRNA-25 associates with prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 9:472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Zhang Z and Gao Q: Transfer of
microRNA-25 by colorectal cancer cell-derived extracellular
vesicles facilitates colorectal cancer development and metastasis.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:552–564. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mo X, Shen X, Mo X, Yu F, Tan W, Deng Z,
He J, Luo Z, Chen Z and Yang J: CEMIP promotes small cell lung
cancer proliferation by activation of glutamine metabolism via
FBXW7/c-Myc-dependent axis. Biochem Pharmacol. 209:1154462023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Davis RJ, Welcker M and Clurman BE: Tumor
suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: Mechanisms and
opportunities. Cancer Cell. 26:455–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye Z, Zhuo Q, Hu Q, Xu X, Liu M, Zhang Z,
Xu W, Liu W, Fan G, Qin Y, et al: FBW7-NRA41-SCD1 axis
synchronously regulates apoptosis and ferroptosis in pancreatic
cancer cells. Redox Biol. 38:1018072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Ishii H, Yokobori T,
Takatsuno Y, Sato T, Toh H, Onoyama I, Nakayama KI, Baba H and Mori
M: Loss of FBXW7, a cell cycle regulating gene, in colorectal
cancer: Clinical significance. Int J Cancer. 126:1828–1837. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhan P, Wang Y, Zhao S, Liu C, Wang Y, Wen
M, Mao JH, Wei G and Zhang P: FBXW7 negatively regulates ENO1
expression and function in colorectal cancer. Lab Invest.
95:995–1004. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grafals-Ruiz N, Sánchez-Álvarez AO,
Santana-Rivera Y, Lozada-Delgado EL, Rabelo-Fernandez RJ,
Rios-Vicil CI, Valiyeva F and Vivas-Mejia PE: MicroRNA-92b targets
tumor suppressor gene FBXW7 in glioblastoma. Front Oncol.
13:12496492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun XF, Sun JP, Hou HT, Li K, Liu X and Ge
QX: MicroRNA-27b exerts an oncogenic function by targeting Fbxw7 in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:15325–15332. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Mezayen H, Yamamura K, Yusa T, Nakao Y,
Uemura N, Kitamura F, Itoyama R, Yamao T, Higashi T, Hayashi H, et
al: MicroRNA-25 exerts an oncogenic function by regulating the
ubiquitin ligase Fbxw7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
28:7973–7982. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Z, Ma T, Duan J, Liu X and Liu L:
MicroRNA-223-induced inhibition of the FBXW7 gene affects the
proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via the
Notch and Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Med Rep. 23:1542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hozaka Y, Kita Y, Yasudome R, Tanaka T,
Wada M, Idichi T, Tanabe K, Asai S, Moriya S, Toda H, et al:
RNA-sequencing based microRNA expression signature of colorectal
cancer: The impact of oncogenic targets regulated by miR-490-3p.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:98762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang G, Wu X, Li S, Xu X, Zhu H and Chen
X: The long noncoding RNA CASC2 functions as a competing endogenous
RNA by sponging miR-18a in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 6:265242016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamada NO and Senda T: Circulating
microRNA-92a-3p in colorectal cancer: A review. Med Mol Morphol.
54:193–202. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Ide S, Imaoka
H, Boland CR and Goel A: Circulating microRNA-203 predicts
prognosis and metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Gut.
66:654–665. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sahami-Fard MH, Kheirandish S and Sheikhha
MH: Expression levels of miR-143-3p and −424-5p in colorectal
cancer and their clinical significance. Cancer Biomark. 24:291–297.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu X, Chen X, Xu M, Liu X, Pan B, Qin J,
Xu T, Zeng K, Pan Y, He B, et al: miR-375-3p suppresses
tumorigenesis and partially reverses chemoresistance by targeting
YAP1 and SP1 in colorectal cancer cells. Aging (Albany NY).
11:7357–7385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mo WY and Cao SQ: MiR-29a-3p: A potential
biomarker and therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl
Oncol. 25:563–577. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ding X, Zhang J, Feng Z, Tang Q and Zhou
X: MiR-137-3p inhibits colorectal cancer cell migration by
regulating a KDM1A-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Dig
Dis Sci. 66:2272–2282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li D, Zhang T, Lai J, Zhang J, Wang T,
Ling Y, He S and Hu Z: MicroRNA-25/ATXN3 interaction regulates
human colon cancer cell growth and migration. Mol Med Rep.
19:4213–4221. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan Y, Liu J, Gao Y, Guo Y, Wang C, Liang
Z, Wu M, Qian Y, Li Y, Shen J, et al: FBXW7 loss of function
promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via
elevating MAP4 and ERK phosphorylation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li N, Lorenzi F, Kalakouti E, Normatova M,
Babaei-Jadidi R, Tomlinson I and Nateri AS: FBXW7-mutated
colorectal cancer cells exhibit aberrant expression of
phosphorylated-p53 at Serine-15. Oncotarget. 6:9240–9256. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen S, Leng P, Guo J and Zhou H: FBXW7 in
breast cancer: Mechanism of action and therapeutic potential. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 42:2262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li M, Ouyang L, Zheng Z, Xiang D, Ti A, Li
L, Dan Y, Yu C and Li W: E3 ubiquitin ligase FBW7α inhibits
cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation by downregulating c-Myc and
cyclin E. Oncol Rep. 37:1627–1636. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Onoyama I, Nakayama
KI and Shinohara T: Skp1-Cullin-F-box (SCF)-type ubiquitin ligase
FBXW7 negatively regulates spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:8826–8831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tu K, Yang W, Li C, Zheng X, Lu Z, Guo C,
Yao Y and Liu Q: Fbxw7 is an independent prognostic marker and
induces apoptosis and growth arrest by regulating YAP abundance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aydin IT, Melamed RD, Adams SJ,
Castillo-Martin M, Demir A, Bryk D, Brunner G, Cordon-Cardo C,
Osman I, Rabadan R and Celebi JT: FBXW7 mutations in melanoma and a
new therapeutic paradigm. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1072014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu K, Dou R, Yang C, Di Z, Shi D, Zhang
C, Song J, Fang Y, Huang S, Xiang Z, et al: Exosome-transmitted
miR-29a induces colorectal cancer metastasis by destroying the
vascular endothelial barrier. Carcinogenesis. 44:356–367. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang XJ, Zhang D, Yang YT, Li XY, Li HN,
Zhang XP, Long JY, Lu YQ, Liu L, Yang G, et al: Suppression of
microRNA-222-3p ameliorates ulcerative colitis and
colitis-associated colorectal cancer to protect against oxidative
stress via targeting BRG1 to activate Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Front Immunol. 14:10898092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mo JS, Lamichhane S, Yun KJ and Chae SC:
MicroRNA 452 regulates SHC1 expression in human colorectal cancer
and colitis. Genes Genomics. 45:1295–1304. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pan S, Wu W, Ren F, Li L, Li Y, Li W, Wang
A, Liu D and Dong Y: MiR-346-5p promotes colorectal cancer cell
proliferation in vitro and in vivo by targeting FBXL2 and
activating the β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci.
244:1173002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin Y, Chen Z, Lin S, Zheng Y, Liu Y, Gao
J and Chen S: MiR-202 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer by targeting UHRF1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 51:1305–1306. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen B, Xia Z, Deng YN, Yang Y, Zhang P,
Zhu H, Xu N and Liang S: Emerging microRNA biomarkers for
colorectal cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Open Biol. 9:1802122019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zeng Z, Li Y, Pan Y, Lan X, Song F, Sun J,
Zhou K, Liu X, Ren X, Wang F, et al: Cancer-derived exosomal
miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing
vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 9:53952018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang L, Tong Z, Sun Z, Zhu G, Shen E and
Huang Y: MiR-25-3p targets PTEN to regulate the migration,
invasion, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR202019012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang L, Li L, Chang P, Wei M, Chen J, Zhu
C and Jia J: miR-25 regulates gastric cancer cell growth and
apoptosis by targeting EGR2. Front Genet. 12:6901962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rao HC, Wu ZK, Wei SD, Jiang Y, Guo QX,
Wang JW, Chen CX and Yang HY: MiR-25-3p serves as an oncogenic
MicroRNA by downregulating the expression of merlin in
osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag Res. 12:8989–9001. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu JY, Yang LL, Ma C, Huang YL, Zhu GX and
Chen QL: MiR-25-3p attenuates the proliferation of tongue squamous
cell carcinoma cell line Tca8113. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:743–747.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Yang C, Wang X, Zhang J, Zhang R and
Liu R: The expression of miR-25 is increased in colorectal cancer
and is associated with patient prognosis. Med Oncol. 31:7812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yeh CH, Bellon M and Nicot C: FBXW7: A
critical tumor suppressor of human cancers. Mol Cancer. 17:1152018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tan Y, Sangfelt O and Spruck C: The
Fbxw7/hCdc4 tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Lett.
271:1–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N,
Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D,
Marth C, et al: FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human
cancer. Cancer Res. 67:9006–9012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D,
Tseng A, Maser RS, Zhai B, Wan L, Gutierrez A, Lau AW, et al:
SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Romano M, De Francesco F, Pirozzi G,
Gringeri E, Boetto R, Di Domenico M, Zavan B, Ferraro GA and Cillo
U: Expression of cancer stem cell biomarkers as a tool for a
correct therapeutic approach to hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncoscience. 2:443–456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kawashita Y, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Saito Y,
Iwahashi S, Yamada S, Higashijima J, Imura S, Ogawa H, Yagi T and
Shimada M: Loss of Fbxw7 expression is a predictor of recurrence in
colorectal liver metastasis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci.
24:576–583. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chang CC, Lin HH, Lin JK, Lin CC, Lan YT,
Wang HS, Yang SH, Chen WS, Lin TC, Jiang JK and Chang SC: FBXW7
mutation analysis and its correlation with clinicopathological
features and prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Biol
Markers. 30:e88–e95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wei W, Qin B, Wen W, Zhang B, Luo H, Wang
Y, Xu H, Xie X, Liu S, Jiang X, et al: FBXW7β loss-of-function
enhances FASN-mediated lipogenesis and promotes colorectal cancer
growth. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:1872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|