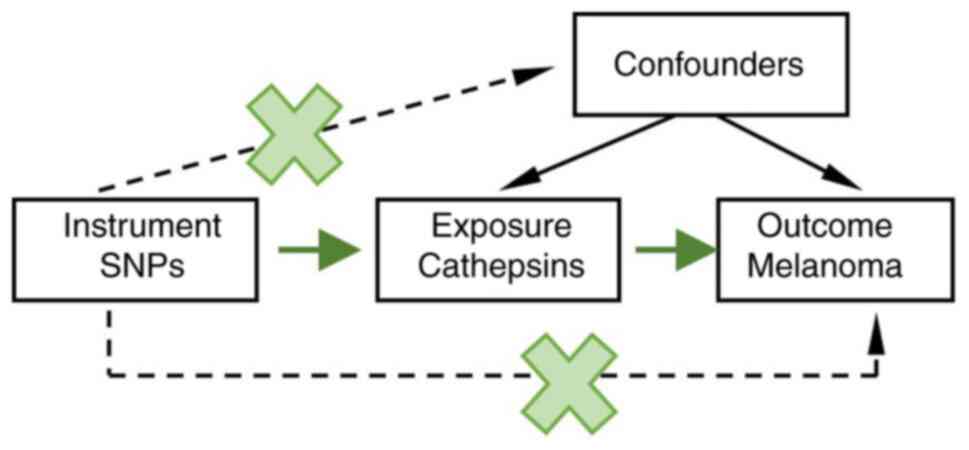
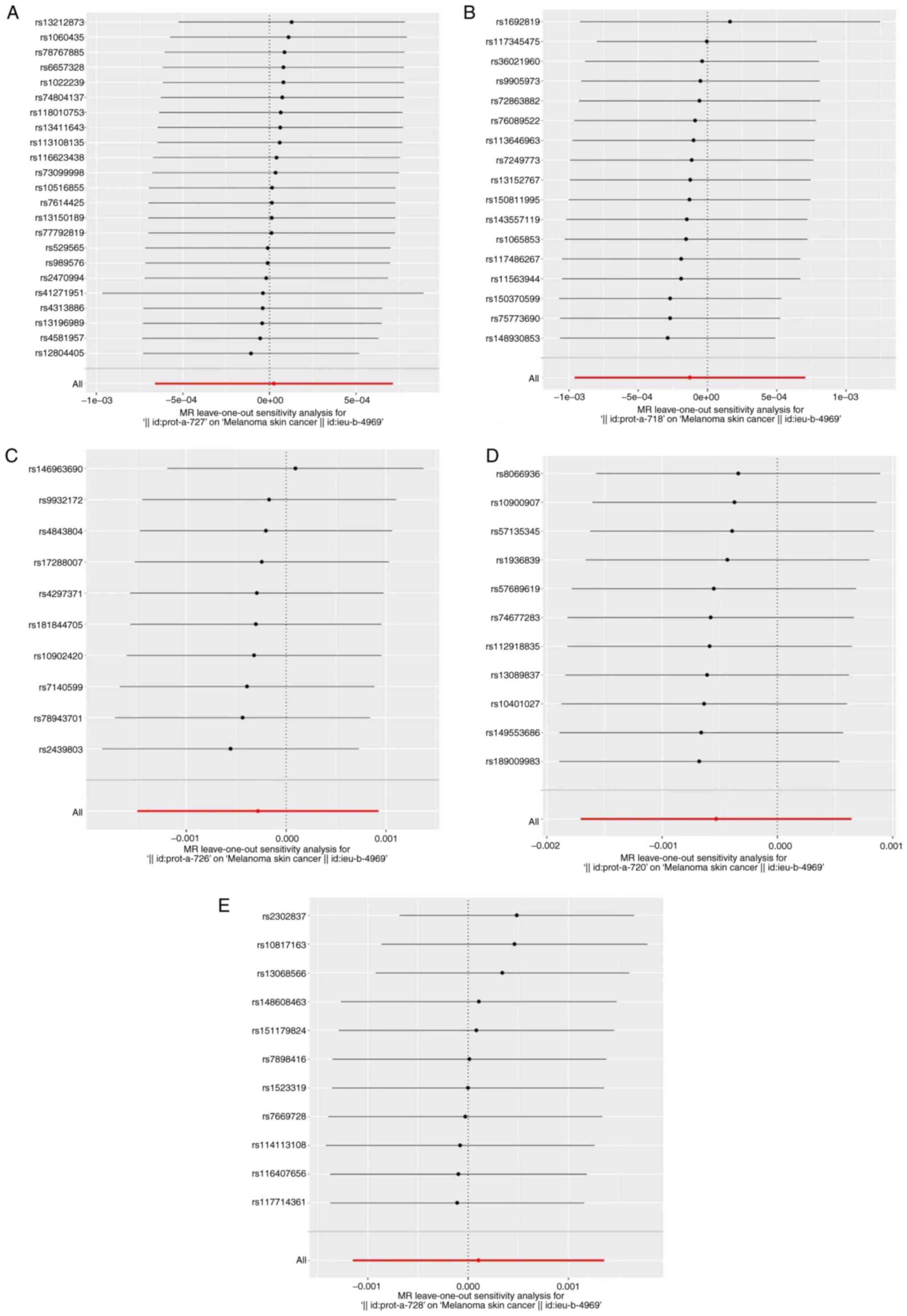
|
1
|
Hasan N, Nadaf A, Imran M, Jiba U, Sheikh
A, Almalki WH, Almujri SS, Mohammed YH, Kesharwani P and Ahmad FJ:
Skin cancer: Understanding the journey of transformation from
conventional to advanced treatment approaches. Mol Cancer.
22(168)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Carr S, Smith C and Wernberg J:
Epidemiology and risk factors of melanoma. Surg Clin North Am.
100:1–12. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Welch HG, Mazer BL and Adamson AS: The
rapid rise in cutaneous melanoma diagnoses. N Engl J Med.
384:72–79. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Whiteman DC, Green AC and Olsen CM: The
growing burden of invasive melanoma: Projections of incidence rates
and numbers of new cases in six susceptible populations through
2031. J Invest Dermatol. 136:1161–1171. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yuan J, Li X and Yu S: Global, Regional,
and National incidence trend analysis of malignant skin melanoma
between 1990 and. 2019, and projections until 2034. Cancer Control.
31(10732748241227340)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Oya K, Nakamura Y, Shen LT, Ishizuki S,
Matsusaka S and Fujisawa Y: Soluble PD-L1 predicts tumor response
and immune-related adverse events in patients with advanced
melanoma treated with anti-PD-1 antibodies. J Dermatol. 51:807–815.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Olson OC and Joyce JA: Cysteine cathepsin
proteases: Regulators of cancer progression and therapeutic
response. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:712–729. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Palermo C and Joyce JA: Cysteine cathepsin
proteases as pharmacological targets in cancer. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 29:22–28. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sudhan DR and Siemann DW: Cathepsin L
targeting in cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 155:105–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mohamed MM and Sloane BF: Cysteine
cathepsins: Multifunctional enzymes in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:764–775. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tripathi R and Plattner R: EnABLing
cathepsin-driven melanoma metastasis. Molr Cell Oncol.
5(e1458016)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tripathi R, Fiore LS, Richards DL, Yang Y,
Liu J, Wang C and Plattner R: Abl and Arg mediate cysteine
cathepsin secretion to facilitate melanoma invasion and metastasis.
Sci Signal. 11(eaao0422)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saenger Y, Magidson J, Liaw B, de Moll E,
Harcharik S, Fu Y, Wassmann K, Fisher D, Kirkwood J, Oh WK and
Friedlander P: Blood mRNA expression profiling predicts survival in
patients treated with tremelimumab. Clin Cancer Res. 20:3310–3318.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kos J, Stabuc B, Schweiger A, Krasovec M,
Cimerman N, Kopitar-Jerala N and Vrhovec I: Cathepsins B, H, and L
and their inhibitors stefin A and cystatin C in sera of melanoma
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 3:1815–1822. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo W, Zhao L, Huang W, Chen J, Zhong T,
Yan S, Hu W, Zeng F, Peng C and Yan H: Sodium-glucose cotransporter
2 inhibitors, inflammation, and heart failure: A two-sample
Mendelian randomization study. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
23(118)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bowden J, Davey Smith G and Burgess S:
Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation
and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol.
44:512–525. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang C, Long C, Zhang Q, He D, Bi H and
Liu X: Mendelian randomization study of the relationship between
serum matrix metalloproteinases and the occurrence of sepsis. Int
Care Res. 3:215–220. 2023.
|
|
18
|
Sun BB, Maranville JC, Peters JE, Stacey
D, Staley JR, Blackshaw J, Burgess S, Jiang T, Paige E, Surendran
P, et al: Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature.
558:73–79. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Swetter SM, Thompson JA, Albertini MR,
Barker CA, Baumgartner J, Boland G, Chmielowski B, DiMaio D, Durham
A, Fields RC, et al: NCCN Guidelines® Insights:
Melanoma: Cutaneous, Version 2.2021. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
19:364–376. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lou J, Cui S, Li J, Jin G, Fan Y and Huang
N: Causal relationship between the gut microbiome and basal cell
carcinoma, melanoma skin cancer, ease of skin tanning: Evidence
from three two-sample mendelian randomisation studies. Front
Immunol. 15(1279680)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chan II, Kwok MK and Schooling CM: The
total and direct effects of systolic and diastolic blood pressure
on cardiovascular disease and longevity using Mendelian
randomisation. Sci Rep. 11(21799)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Agarwal I, Fuller ZL, Myers SR and
Przeworski M: Relating pathogenic loss-of-function mutations in
humans to their evolutionary fitness costs. Elife.
12(e83172)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Burgess S and Thompson SG: Avoiding bias
from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J
Epidemiol. 40:755–764. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao G, Lu Z, Liao Y, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Kang
Z, Feng X, Sun J and Yue W: Association of intestinal
anti-inflammatory drug target genes with psychiatric Disorders: A
Mendelian randomization study. J Adv Res: S2090-S1232, 2024 doi:
10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.002 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Matarrese P, Ascione B, Ciarlo L, Vona R,
Leonetti C, Scarsella M, Mileo AM, Catricalà C, Paggi MG and
Malorni W: Cathepsin B inhibition interferes with metastatic
potential of human melanoma: An in vitro and in vivo study. Mol
Cancer. 9(207)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mijanović O, Branković A, Panin AN,
Savchuk S, Timashev P, Ulasov I and Lesniak MS: Cathepsin B: A
sellsword of cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 449:207–214.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yadati T, Houben T, Bitorina A and
Shiri-Sverdlov R: The ins and outs of cathepsins: Physiological
function and role in disease management. Cells.
9(1679)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fröhlich E, Mack AF, Garbe C and Klessen
C: Distribution and colocalization of markers for proliferation,
invasion, motility and neoangiogenesis in benign melanocytic naevi
and malignant melanomas. Br J Dermatol. 153:1159–1165.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Frade R, Rodrigues-Lima F, Huang S, Xie K,
Guillaume N and Bar-Eli M: Procathepsin-L, a proteinase that
cleaves human C3 (the third component of complement), confers high
tumorigenic and metastatic properties to human melanoma cells.
Cancer Res. 58:2733–2736. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yuan L, Sheng L, He W, Zou C, Hu B, Liu J,
Ge W, Liu Y, Wang J and Ma E: Discovery of novel cathepsin
inhibitors with potent anti-metastatic effects in breast cancer
cells. Bioorg Chem. 81:672–680. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gormley JA, Hegarty SM, O'Grady A,
Stevenson MR, Burden RE, Barrett HL, Scott CJ, Johnston JA, Wilson
RH, Kay EW, et al: The role of Cathepsin S as a marker of prognosis
and predictor of chemotherapy benefit in adjuvant CRC: A pilot
study. Br J Cancer. 105:1487–1494. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Lim SK, Choong LY, Lee H, Chen Y,
Chong PK, Ashktorab H, Wang TT, Salto-Tellez M, Yeoh KG and Lim YP:
Cathepsin S mediates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via
a putative network of metastasis-associated proteins. J Proteome
Res. 9:4767–4778. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gautam J, Bae YK and Kim JA: Up-regulation
of cathepsin S expression by HSP90 and 5-HT7 receptor-dependent
serotonin signaling correlates with triple negativity of human
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 161:29–40. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Small DM, Burden RE, Jaworski J, Hegarty
SM, Spence S, Burrows JF, McFarlane C, Kissenpfennig A, McCarthy
HO, Johnston JA, et al: Cathepsin S from both tumor and
tumor-associated cells promote cancer growth and
neovascularization. Int J Cancer. 133:2102–2112. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Arnlöv J: Cathepsin S as a biomarker:
Where are we now and what are the future challenges? Biomark Med.
6:9–11. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wilkinson RDA, Burden RE, McDowell SH,
McArt DG, McQuaid S, Bingham V, Williams R, Cox ÓT, O'Connor R,
McCabe N, et al: A novel role for cathepsin S as a potential
biomarker in triple negative breast cancer. J Oncol.
2019(3980273)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sangster AB, Chang-McDonald B, Patel J,
Bockett N, Paterson E, Davis PF and Tan ST: Expression of
cathepsins B and D by cancer stem cells in head and neck metastatic
malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 31:426–438. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kawakubo T, Okamoto K, Iwata J, Shin M,
Okamoto Y, Yasukochi A, Nakayama KI, Kadowaki T, Tsukuba T and
Yamamoto K: Cathepsin E prevents tumor growth and metastasis by
catalyzing the proteolytic release of soluble TRAIL from tumor cell
surface. Cancer Res. 67:10869–10878. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Smith-Byrne K, Hedman Å, Dimitriou M,
Desai T, Sokolov AV, Schioth HB, Koprulu M, Pietzner M, Langenberg
C, Atkins J, et al: Identifying therapeutic targets for cancer
among 2074 circulating proteins and risk of nine cancers. Nat
Commun. 15(3621)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Versluis JM, Blankenstein SA, Dimitriadis
P, Wilmott JS, Elens R, Blokx WAM, van Houdt W, Menzies AM, Schrage
YM, Wouters MWJM, et al: Interferon-gamma signature as prognostic
and predictive marker in macroscopic stage III melanoma. J
Immunother Cancer. 12(e008125)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Feng F, Wang T, Qin J, Yin X, Meng
G, Yan C, Xing Z, Duan J, Liu C and Liu J: Laparoscopic
pancreaticoduodenectomy for metastatic pancreatic melanoma: A case
report. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e12940)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Quintanilla-Dieck MJ, Codriansky K, Keady
M, Bhawan J and Rünger TM: Cathepsin K in melanoma invasion. J
Invest Dermatol. 128:2281–2288. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|