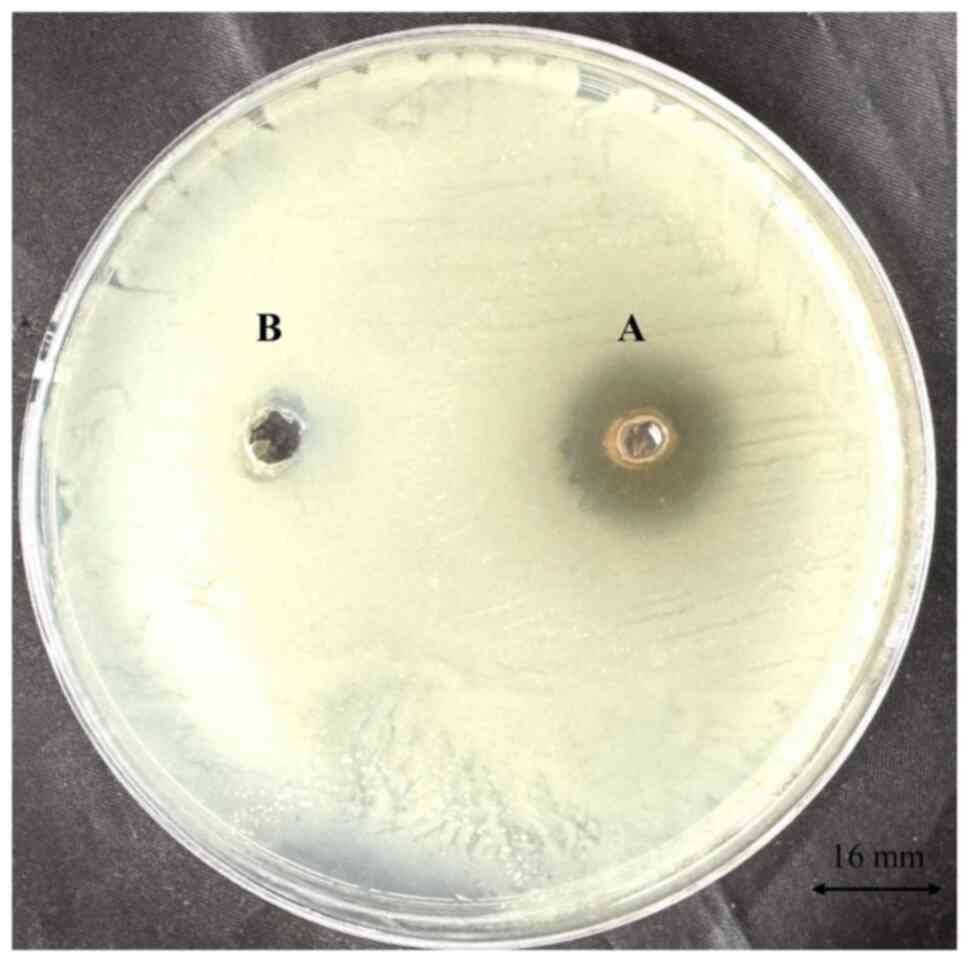
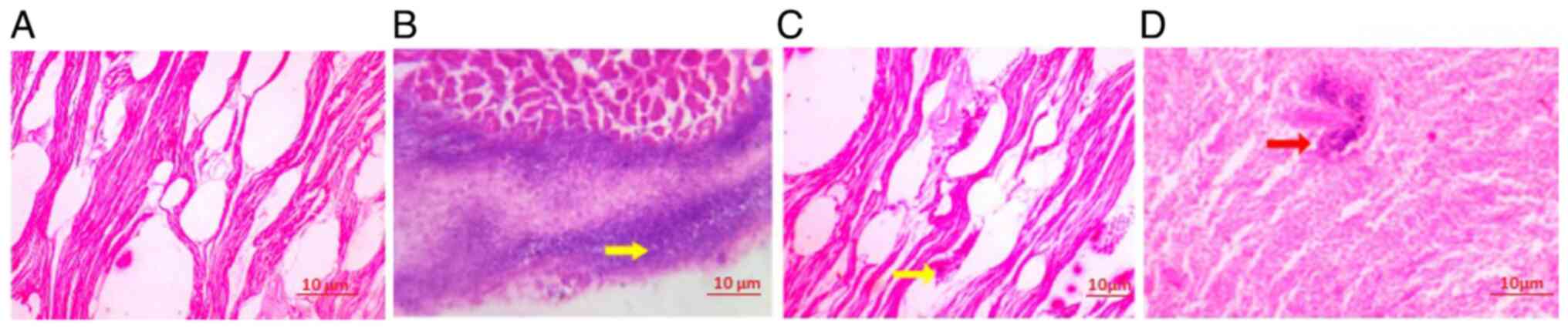
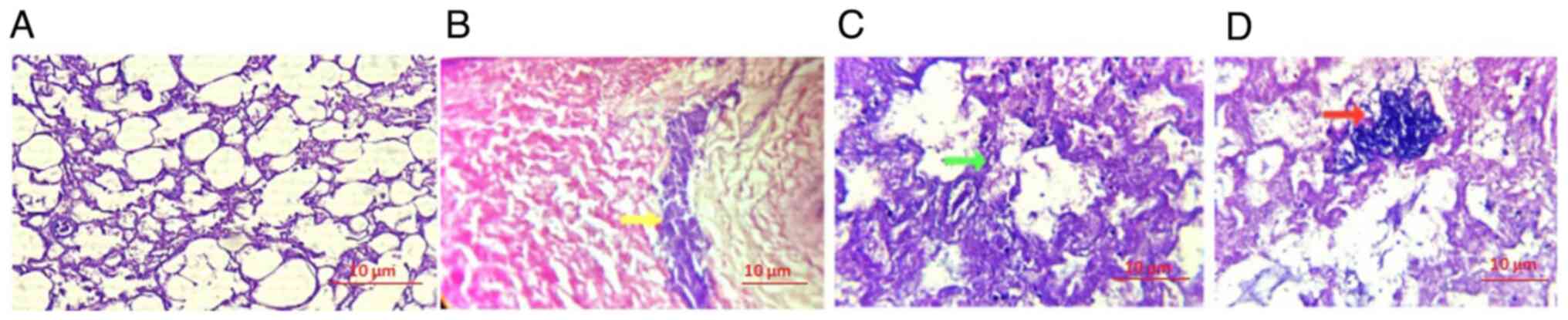
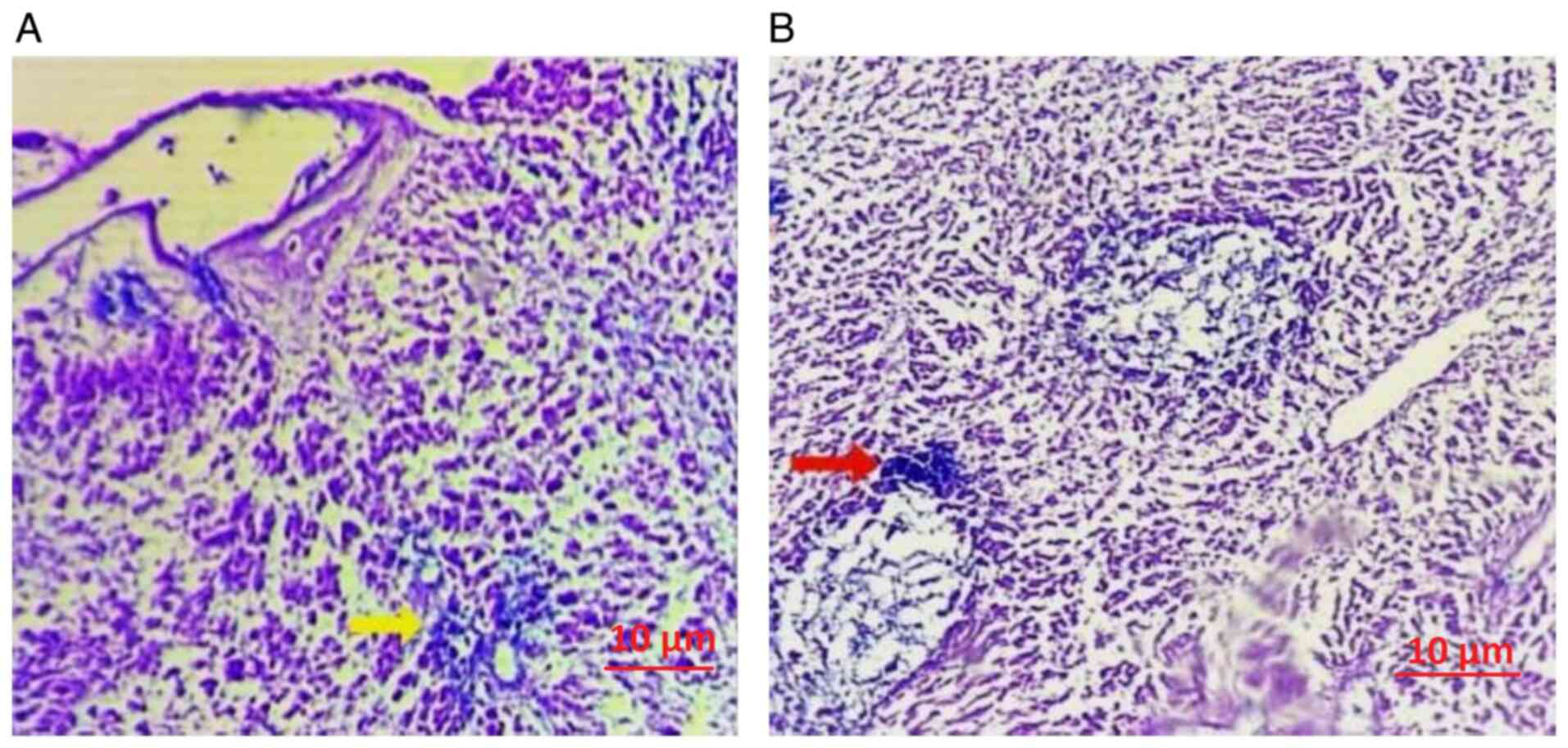
|
1
|
Ibrahim S, Al-Saryi N, Al-Kadmy IMS and
Aziz SN: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii as an emerging
concern in hospitals. Mol Biol Rep. 48:6987–6998. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pathoor NN, Ganesh PS and Gopal RK:
Microbiome interactions: Acinetobacter baumannii biofilms as a
co-factor in oral cancer progression. World J Microbiol Biotechnol.
40(398)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gedefie A, Demsis W, Ashagrie M, Kassa Y,
Tesfaye M, Tilahun M, Bisetegn H and Sahle Z: Biofilm formation and
its role in disease pathogenesis: A review. Infect Drug Resist.
14:3711–3719. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Müller C, Reuter S, Wille J, Xanthopoulou
K, Stefanik D, Grundmann H, Higgins PG and Seifert H: A global view
on carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. mBio.
14(e0226023)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Girija ASS: Acinetobacter baumannii as an
oro-dental pathogen: A red alert!! J Appl Oral Sci.
32(e20230382)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Loehfelm TW, Luke NR and Campagnari AA:
Identification and characterization of an Acinetobacter baumannii
biofilm-associated protein. J Bacteriol. 190:1036–1044.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pai L, Patil S, Liu S and Wen F: A growing
battlefield in the war against biofilm-induced antimicrobial
resistance: Insights from reviews on antibiotic resistance. Front
Cell Infect Microbiol. 13(1327069)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Smiline Girija SA: Hijacking the
epigenetic mechanisms of A. baumannii. Mol Biol Res Commun.
13:51–53. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pathoor NN, Viswanathan A, Wadhwa G and
Ganesh PS: Understanding the biofilm development of Acinetobacter
baumannii and novel strategies to combat infection. APMIS.
132:317–335. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mohajeri P, Farahani A, Feizabadi MM and
Norozi B: Clonal evolution multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter
baumannii by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Indian J Med
Microbiol. 33:87–91. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mohajeri P, Sharbati S, Farahani A and
Rezaei Z: Evaluate the frequency distribution of nonadhesive
virulence factors in carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter
baumannii isolated from clinical samples in Kermanshah. J Nat Sci
Biol Med. 7:58–61. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nasim N, Sandeep IS and Mohanty S:
Plant-derived natural products for drug discovery: Current
approaches and prospects. Nucleus (Calcutta). 65:399–411.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kalinowska M, Gołębiewska E, Świderski G,
Męczyńska-Wielgosz S, Lewandowska H, Pietryczuk A, Cudowski A,
Astel A, Świsłocka R, Samsonowicz M, et al: Plant-derived and
dietary hydroxybenzoic acids-a comprehensive study of structural,
anti-/pro-oxidant, lipophilic, antimicrobial, and cytotoxic
activity in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines. Nutrients.
13(3107)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Greenleaf J, Karimzadeh R and Park YL:
Spatial patterns of Frangula alnus (Rosales: Rhamnaceae):
Implications for invasive plant management. Biology (Basel).
12(1393)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Górniak I, Bartoszewski R and Króliczewski
J: Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant
flavonoids. Phytochem Rev. 18:241–272. 2019.
|
|
16
|
Lahiri D, Nag M, Ray RR and Ghosh S (eds):
Biofilm-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Recovery. CRC
Press, Boca Raton, p391, 2023.
|
|
17
|
Kumar S, Chandra N, Singh L, Hashmi MZ and
Varma A (eds): Biofilms in Human Diseases: Treatment and Control.
Springer Nature, p318, 2019.
|
|
18
|
Labis V, Gaiduk I, Bazikyan E, Khmelenin
D, Zhigalina O, Dyachkova I, Zolotov D, Asadchikov V, Kravtsov I,
Polyakov N, et al: The role of metal nanoparticles in the
pathogenesis of stone formation. Int J Mol Sci.
25(9609)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bobenchik AM, Deak E, Hindler JA, Charlton
CL and Humphries RM: Performance of Vitek 2 for antimicrobial
susceptibility testing of Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with Vitek 2 (2009
FDA) and CLSI M100S 26th edition breakpoints. J Clin Microbiol.
55:450–456. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Soni M, Naseef Pathoor N, Viswanathan A,
Veeraragavan GR and Sankar Ganesh P: Exploring the antimicrobial
and antibiofilm activities of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. against
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. World Acad Sci J. 6(50)2024.
|
|
21
|
Hudzicki J: Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion
Susceptibility Test Protocol. American Society for Microbiology,
Washington, DC, pp55-63, 2009.
|
|
22
|
Howard A, O'Donoghue M, Feeney A and
Sleator RD: Acinetobacter baumannii: An emerging opportunistic
pathogen. Virulence. 3:243–250. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Peer Mohammed S, Pathoor N, Veeraragavan G
and Ganesh P: Unlocking the antibiofilm and anti-virulence
potential of Pithecellobium dulce against Chromobacterium violaceum
CV12472. World Acad Sci J. 7(14)2024.
|
|
24
|
Bancroft JD and Gamble M (eds): Theory and
practice of histological techniques. 6th edition. Elsevier Health
Sciences, p744, 2008.
|
|
25
|
Venkatramanan M, Sankar Ganesh P, Senthil
R, Akshay J, Veera Ravi A, Langeswaran K, Vadivelu J, Nagarajan S,
Rajendran K and Shankar EM: Inhibition of quorum sensing and
biofilm formation in Chromobacterium violaceum by fruit extracts of
Passiflora edulis. ACS Omega. 5:25605–25616. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou JW, Luo HZ, Jiang H, Jian TK, Chen ZQ
and Jia AQ: Hordenine: A novel quorum sensing inhibitor and
antibiofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Agric Food
Chem. 66:1620–1628. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sybiya Vasantha Packiavathy IA,
Agilandeswari P, Musthafa KS, Karutha Pandian S and Veera Ravi A:
Antibiofilm and quorum sensing inhibitory potential of Cuminum
cyminum and its secondary metabolite methyl eugenol against
gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Food Res Int. 45:85–92.
2012.
|
|
28
|
Lawrence R, Tripathi P and Jeyakumar E:
Isolation, purification and evaluation of antibacterial agents from
Aloe vera. Braz J Microbiol. 40:906–915. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Miyasaki Y, Rabenstein JD, Rhea J, Crouch
ML, Mocek UM, Kittell PE, Morgan MA, Nichols WS, Van Benschoten MM,
Hardy WD and Liu GY: Isolation and characterization of
antimicrobial compounds in plant extracts against
multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS One.
8(e61594)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hu J, Shuai W, Sumner JT, Moghadam AA and
Hartmann EM: Clinically relevant pathogens on surfaces display
differences in survival and transcriptomic response in relation to
probiotic and traditional cleaning strategies. NPJ Biofilms
Microbiomes. 8(72)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li XZ, Elkins CA and Zgurskaya HI:
Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: mechanisms,
regulation and clinical implications. Springer, New York, NY, p848,
2016.
|
|
32
|
Grygiel I, Bajrak O, Wójcicki M, Krusiec
K, Jończyk-Matysiak E, Górski A, Majewska J and Letkiewicz S:
Comprehensive approaches to combatting Acinetobacter baumannii
biofilms: From biofilm structure to phage-based therapies.
Antibiotics (Basel). 13(1064)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mendhe S, Badge A, Ugemuge S and Chandi D:
Impact of biofilms on chronic infections and medical challenges.
Cureus. 15(e48204)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kostakioti M, Hadjifrangiskou M and
Hultgren SJ: Bacterial biofilms: Development, dispersal, and
therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 3(a010306)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|