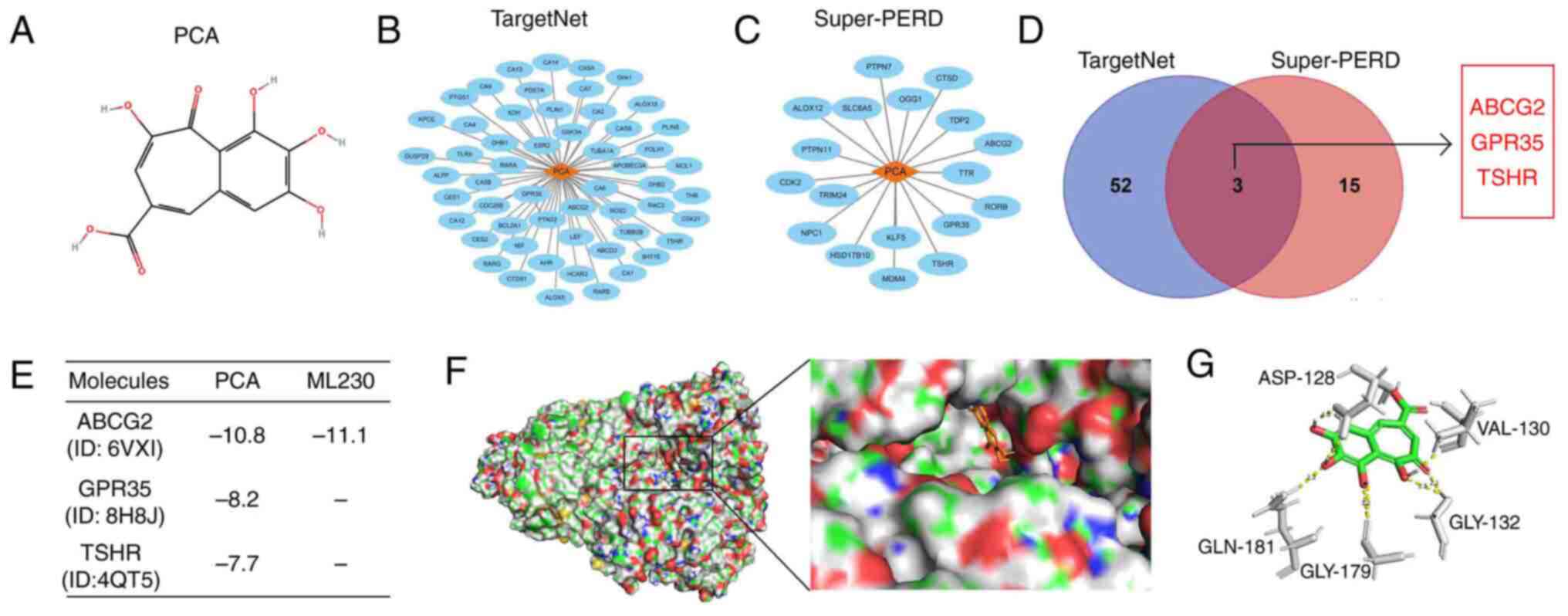
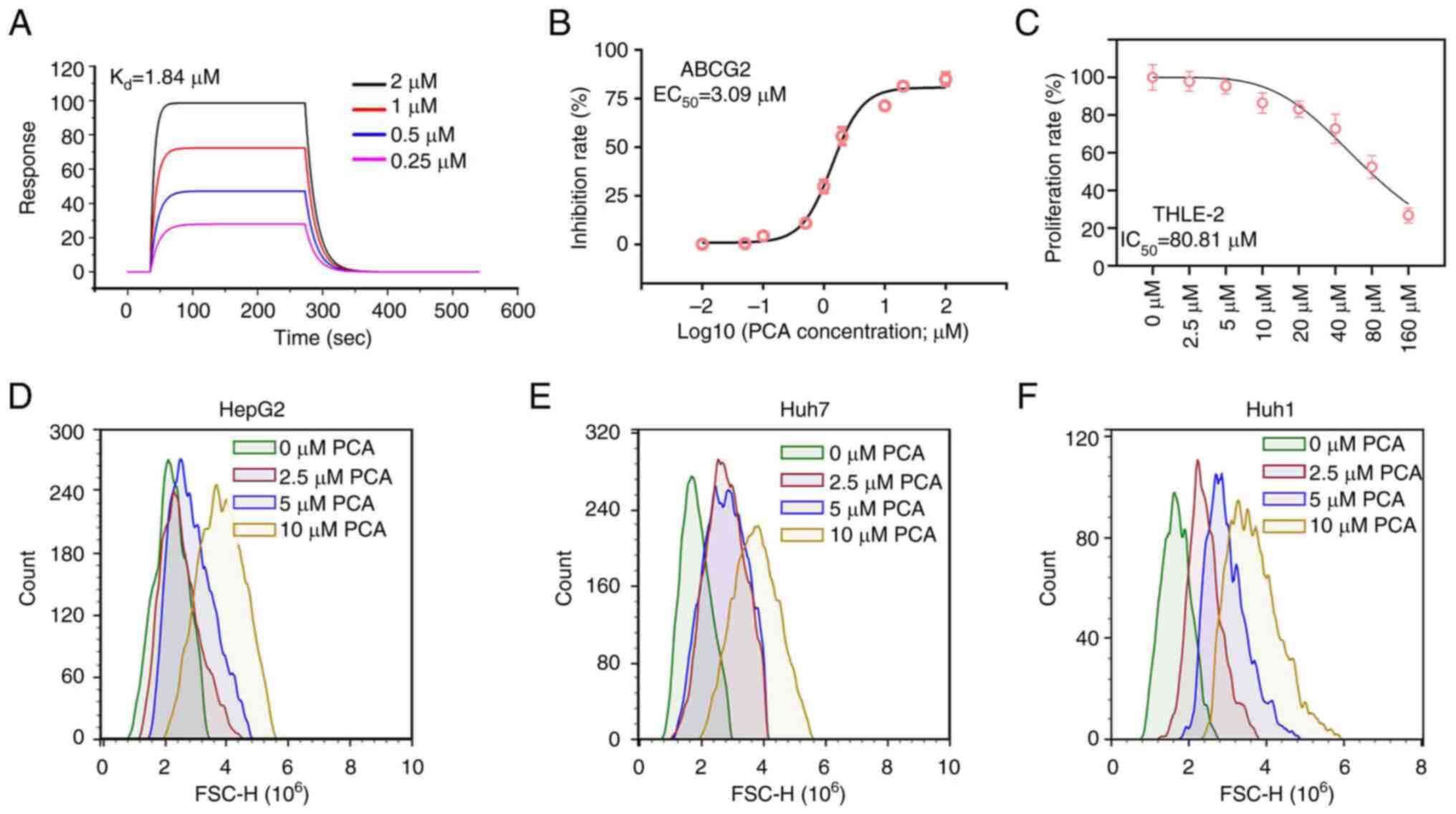
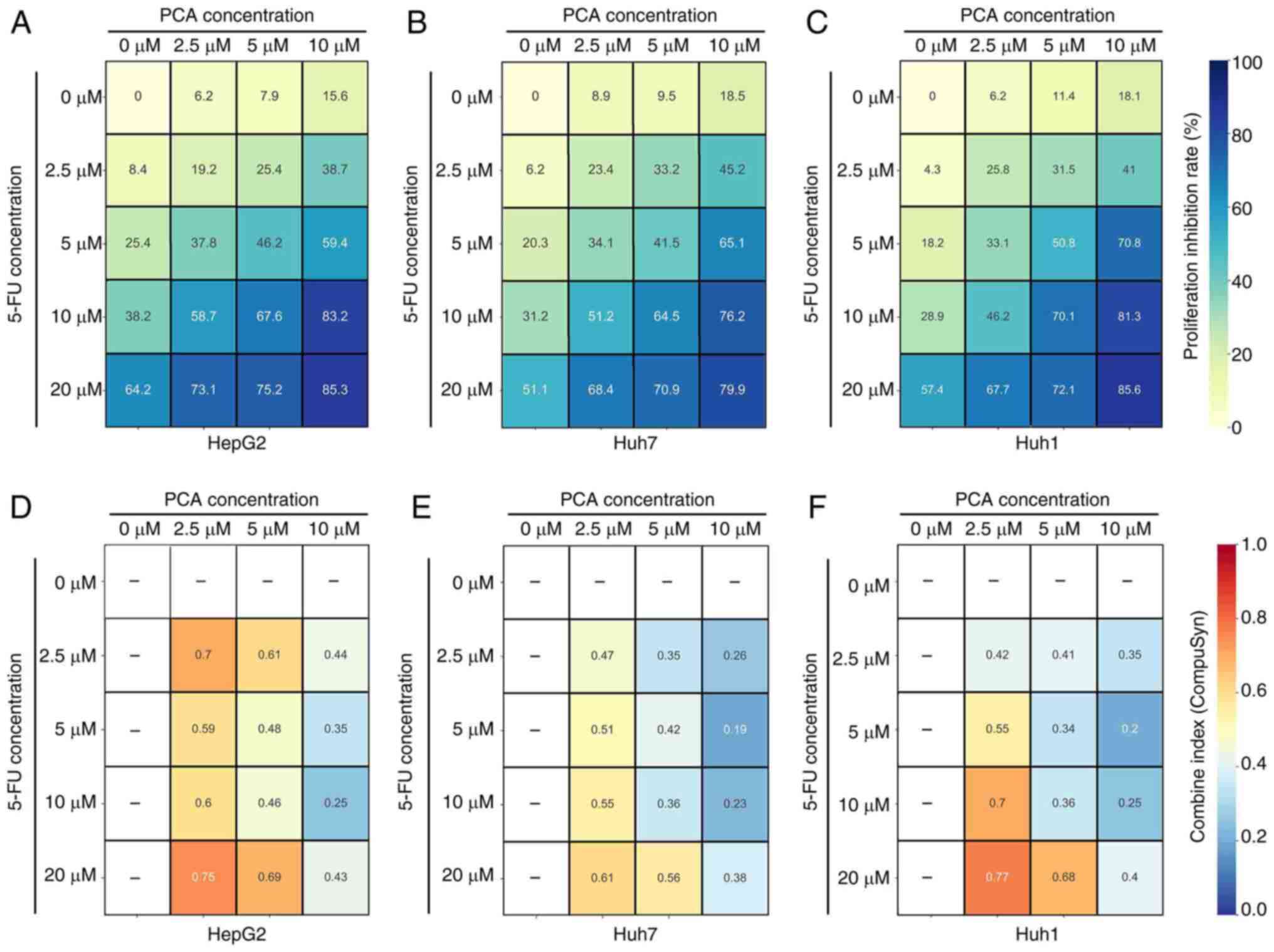
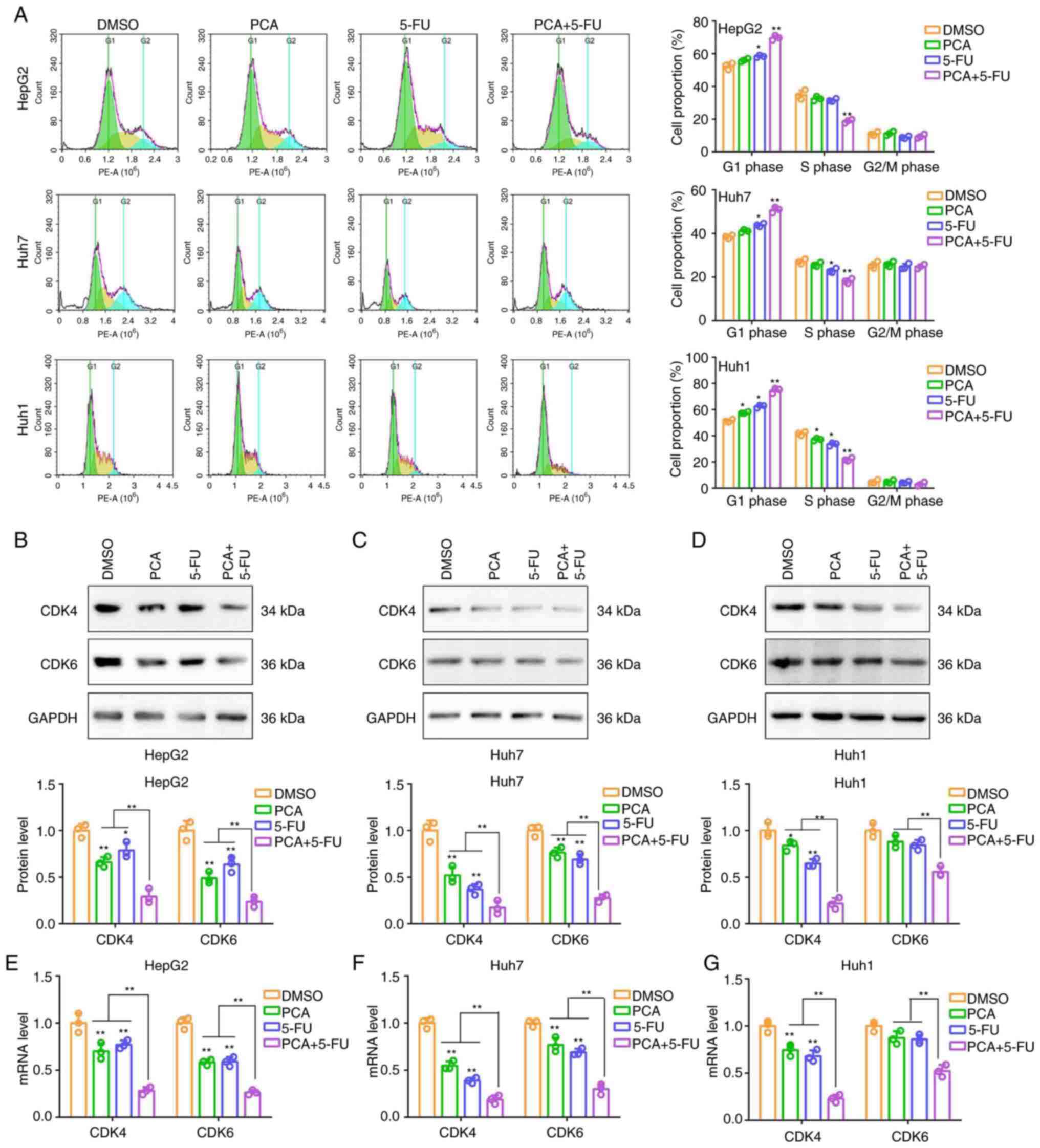
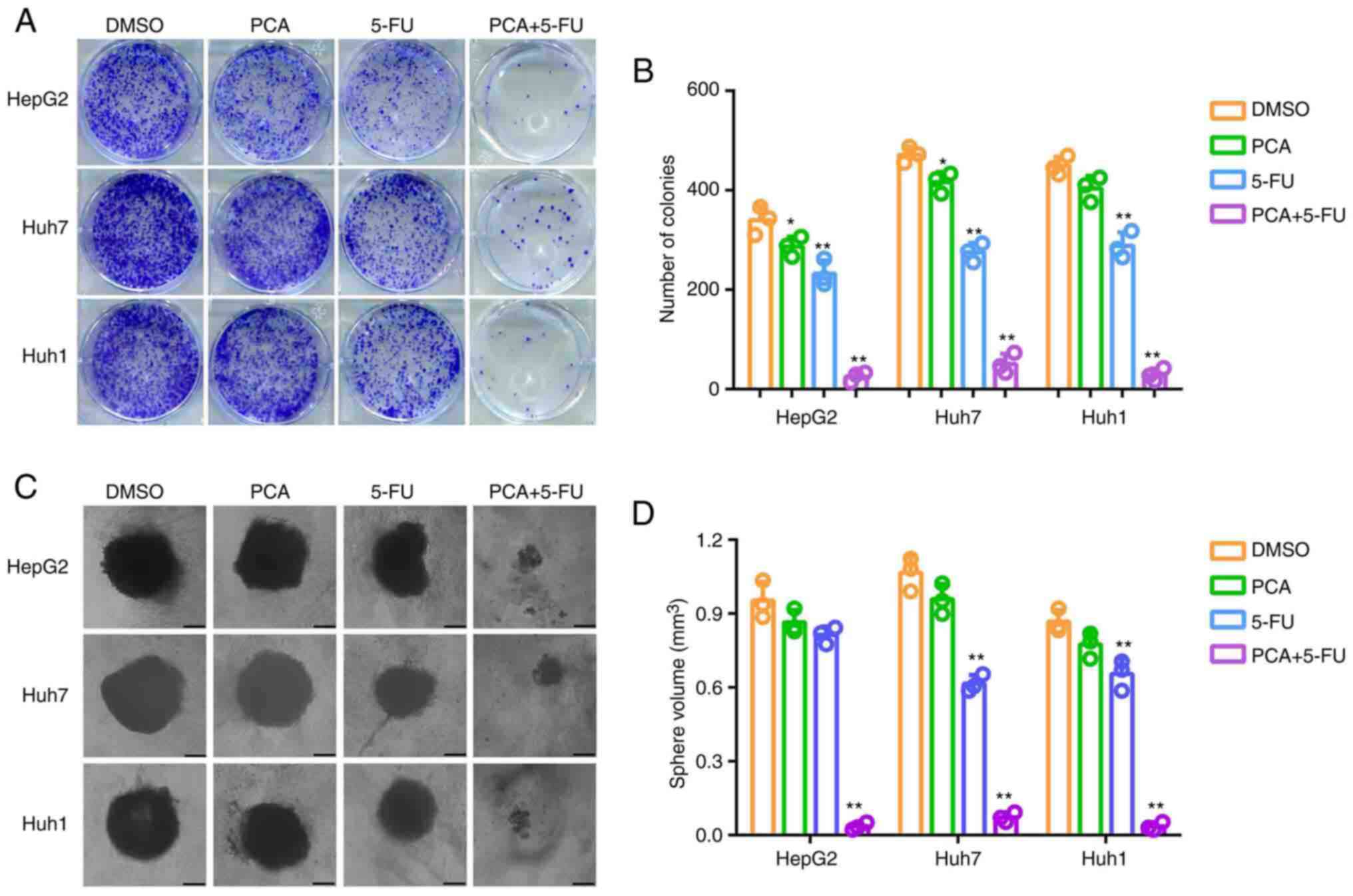
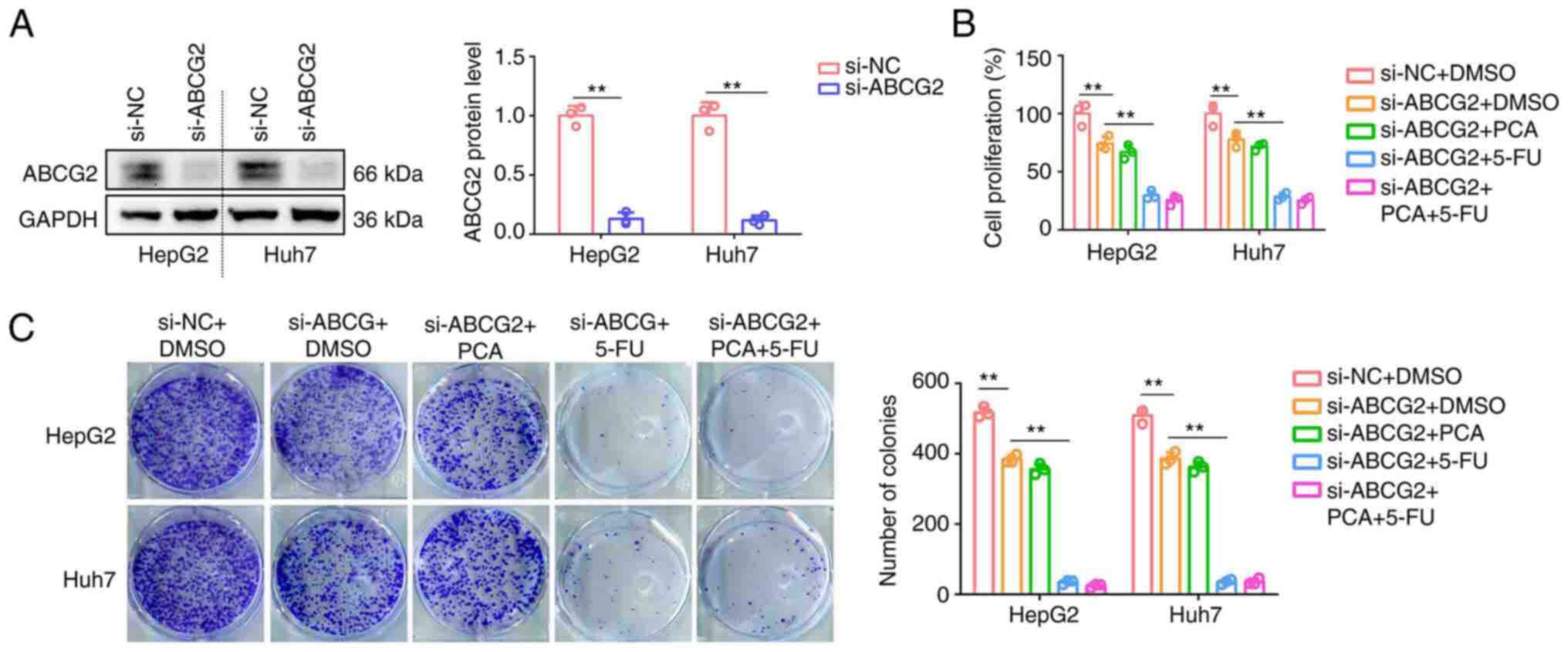
|
1
|
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N and Chen WQ:
Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A
secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J
(Engl). 134:783–791. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chakraborty E and Sarkar D: Emerging
therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancers (Basel).
14(2798)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li QJ, He MK, Chen HW, Fang WQ, Zhou YM,
Xu L, Wei W, Zhang YJ, Guo Y, Guo RP, et al: Hepatic arterial
infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus
transarterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma:
A randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 40:150–160.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ray EM and Sanoff HK: Optimal therapy for
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and resistance or
intolerance to sorafenib: Challenges and solutions. J Hepatocell
Carcinoma. 4:131–138. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu T, Guo P, Pi C, He Y, Yang H, Hou Y,
Feng X, Jiang Q, Wei Y and Zhao L: Synergistic Effects of curcumin
and 5-fluorouracil on the hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo and
vitro through regulating the expression of COX-2 and NF-κB. J
Cancer. 11:3955–3964. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Dai W, Gao Q, Qiu J, Yuan J, Wu G and Shen
G: Quercetin induces apoptosis and enhances 5-FU therapeutic
efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:6307–6313.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zeng LH and Wu TW: Purpurogallin is a more
powerful protector of kidney cells than trolox and allopurinol.
Biochem Cell Biol. 70:684–690. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zeng LH, Rootman DS, Burnstein A, Wu J and
Wu TW: Morin hydrate: A better protector than purpurogallin of
corneal endothelial cell damage induced by xanthine oxidase and
SIN-1. Curr Eye Res. 17:149–152. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rambabu M and Jayanthi S: Virtual
screening of national cancer institute database for claudin-4
inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular
dynamics studies. J Cell Biochem. 120:8588–8600. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mollazadeh S, Sahebkar A, Hadizadeh F,
Behravan J and Arabzadeh S: Structural and functional aspects of
P-glycoprotein and its inhibitors. Life Sci. 214:118–123.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kodan A, Futamata R, Kimura Y, Kioka N,
Nakatsu T, Kato H and Ueda K: ABCB1/MDR1/P-gp employs an
ATP-dependent twist-and-squeeze mechanism to export hydrophobic
drugs. FEBS Lett. 595:707–716. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zattoni IF, Delabio LC, Dutra JP, Kita DH,
Scheiffer G, Hembecker M, Pereira GDS, Moure VR and Valdameri G:
Targeting breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2): Functional
inhibitors and expression modulators. Eur J Med Chem.
237(114346)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen YL, Chen PM, Lin PY, Hsiau YT and Chu
PY: ABCG2 overexpression confers poor outcomes in hepatocellular
carcinoma of elderly patients. Anticancer Res. 36:2983–2988.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobayashi K, Higai K, Mukozu T, Matsui D,
Amanuma M, Yoshimine N, Ogino Y, Matsui T, Wakui N, Shinohara M, et
al: Tivantinib decreases hepatocyte growth factor-induced BCRP
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Biol Pharm
Bull. 43:1421–1425. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hou Z, Liu J, Jin Z, Qiu G, Xie Q, Mi S
and Huang J: Use of chemotherapy to treat hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biosci Trends. 16:31–45. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li S, Gao M, Li Z, Song L, Gao X, Han J,
Wang F, Chen Y, Li W and Yang J: p53 and P-glycoprotein influence
chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Biosci (Elite
Ed). 10:461–468. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu X: ABC family transporters. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1141:13–100. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mao Q and Unadkat JD: Role of the breast
cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in drug transport-an update.
AAPS J. 17:65–82. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han LW, Gao C and Mao Q: An update on
expression and function of P-gp/ABCB1 and BCRP/ABCG2 in the
placenta and fetus. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 14:817–829.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yin W, Xiang D, Wang T, Zhang Y, Pham CV,
Zhou S, Jiang G, Hou Y, Zhu Y, Han Y, et al: The inhibition of
ABCB1/MDR1 or ABCG2/BCRP enables doxorubicin to eliminate liver
cancer stem cells. Sci Rep. 11(10791)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang M, Wang Z, Zhi X, Ding W, Xiong J,
Tao T, Yang Y, Zhang H, Zi X, Zhou W and Huang G: SOX9 enhances
sorafenib resistance through upregulating ABCG2 expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110315)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu P, Sun H, Zhang L, Hou H, Zhang L, Zhao
F, Ge C, Yao M, Wang T and Li J: Isocorydine targets the
drug-resistant cellular side population through PDCD4-related
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med. 18:1136–1146.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wei CT, Chen LC, Hsiang YP, Hung YJ, Chien
PH, Pan HL and Chen YJ: Chrysin-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation
enhances the sensitivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to
sorafenib. Anticancer Res. 39:695–701. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Guo X, To KKW, Chen Z, Wang X, Zhang J,
Luo M, Wang F, Yan S and Fu L: Dacomitinib potentiates the efficacy
of conventional chemotherapeutic agents via inhibiting the drug
efflux function of ABCG2 in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 37(31)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bharathiraja P, Yadav P, Sajid A, Ambudkar
SV and Prasad NR: Natural medicinal compounds target signal
transduction pathways to overcome ABC drug efflux
transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist
Updat. 71(101004)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aung TN, Qu Z, Kortschak RD and Adelson
DL: Understanding the effectiveness of natural compound mixtures in
cancer through their molecular mode of action. Int J Mol Sci.
18(656)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zeng YP, Yang ZR, Guo XF, Jun W and Dong
WG: Synergistic effect of puerarin and 5-fluorouracil on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 8:2436–2442. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li F, Wang J, Wu N, Zhang H, Li Z and Wei
N: H1, a derivative of tetrandrine, enhances the efficacy of 5-FU
in Bel7402/5-FU cells via suppressing STAT3/MCL-1 and inducing
PUMA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 520:93–98. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao J, Huang J, Gui S and Chu X:
Preparation, synergism, and biocompatibility of in situ liquid
crystals loaded with sinomenine and 5-fluorouracil for treatment of
liver cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 16:3725–3739. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|