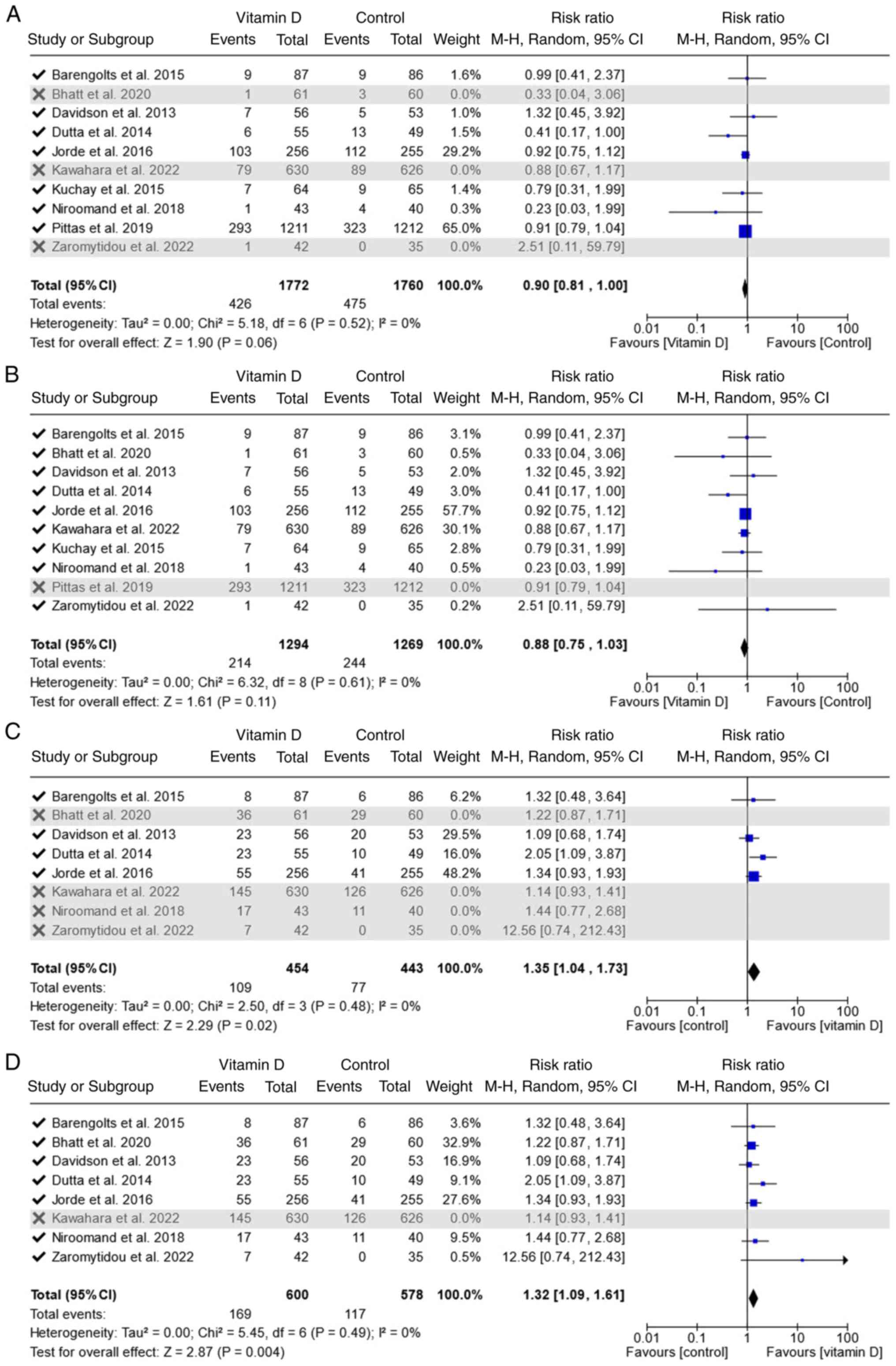
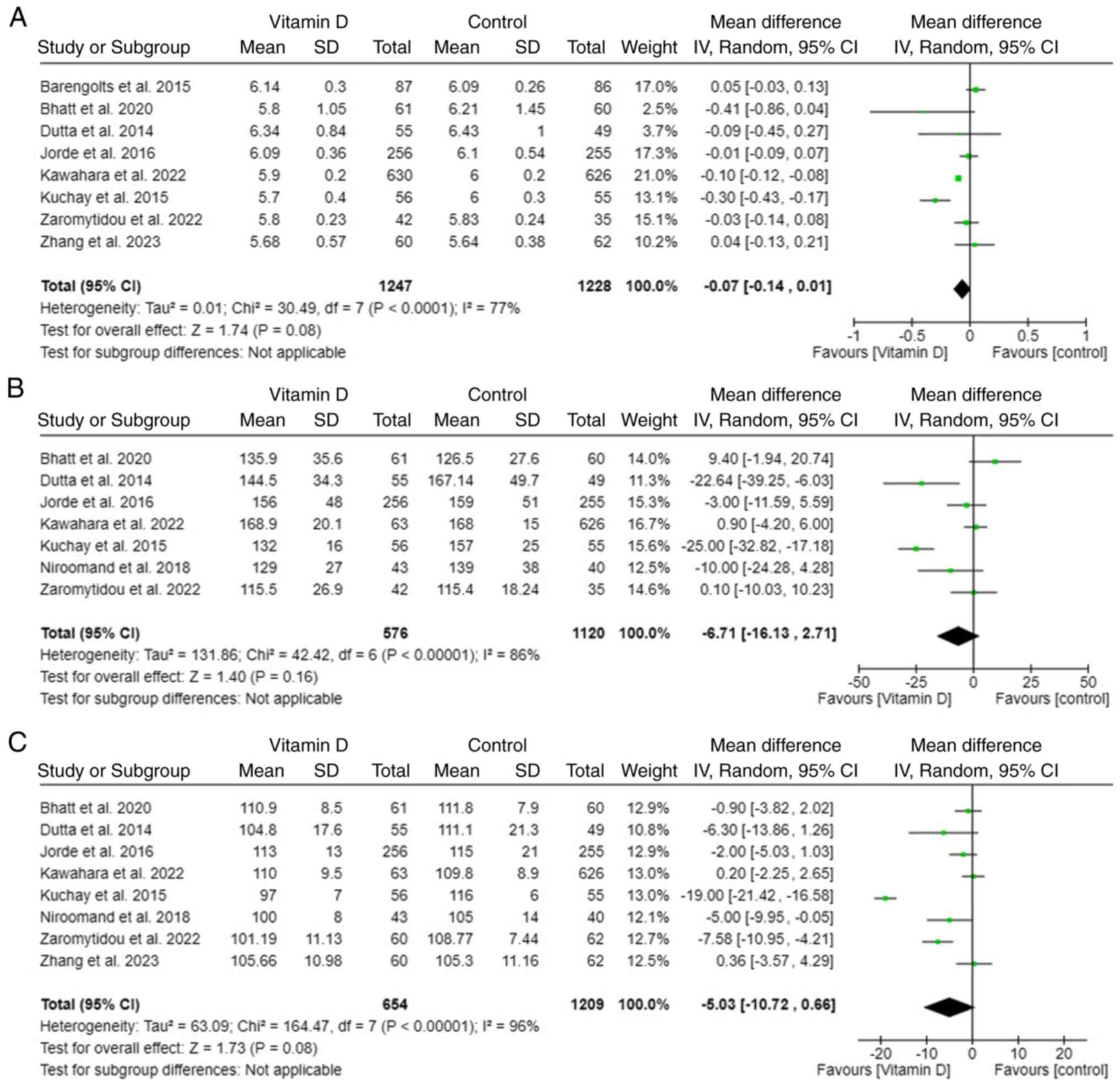
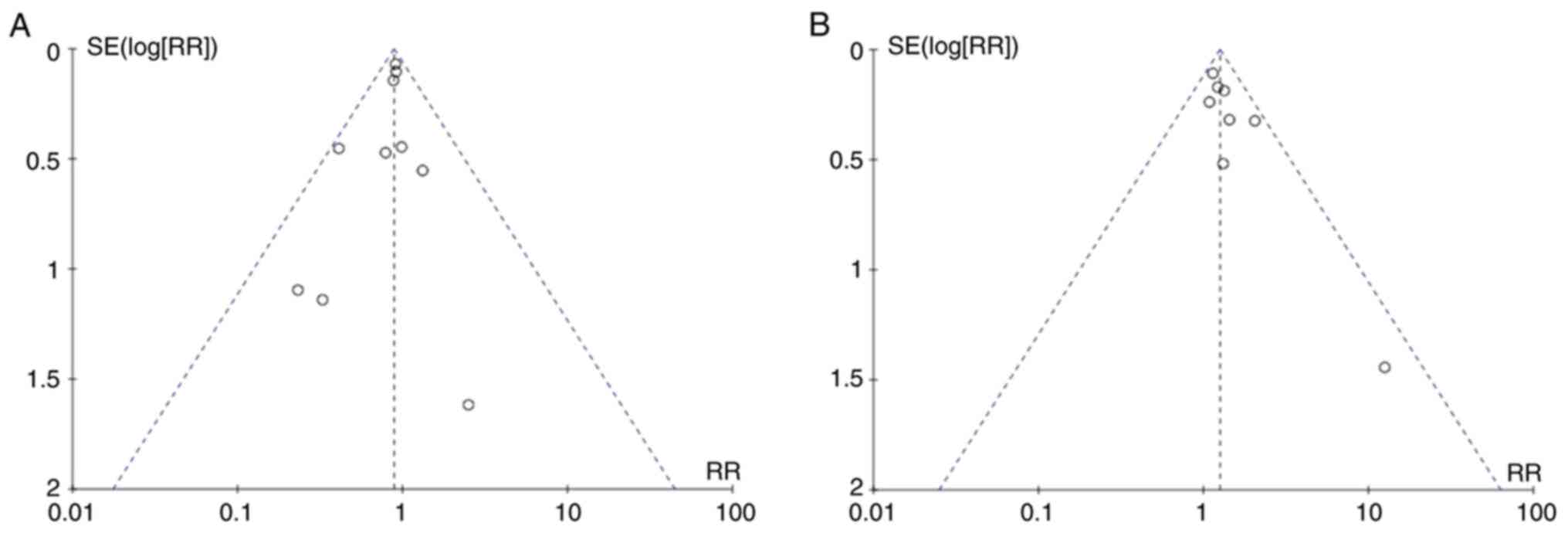
|
1
|
Hu Hanquan A and Teo Li Wen MR: Prevalence
of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus at a tertiary referral centre in Singapore. Proc Singap
Healthc. 30:265–70. 2020.
|
|
2
|
American Diabetes Association. Standards
of medical care in diabetes-2019 abridged for primary care
providers. Clin Diabetes. 37:11–34. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zheng Y, Ley SH and Hu FB: Global
aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:88–98. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kulda V: Vitamin D metabolism. Vnitr Lek.
58:400–404. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Czech).
|
|
5
|
Bouillon R: Optimal vitamin D
supplementation strategies. Endocrine. 56:225–226. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Berridge MJ: Vitamin D: A custodian of
cell signalling stability in health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans.
43:349–358. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Berridge MJ: Vitamin D cell signalling in
health and disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 460:53–71.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Calton EK, Keane KN and Soares MJ: The
potential regulatory role of vitamin D in the bioenergetics of
inflammation. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 18:367–373.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wimalawansa SJ: Vitamin D deficiency is a
surrogate marker for visceral fat content, metabolic syndrome, type
2 diabetes and future metabolic complications. J Diabetes Metab
Disord Control. 3:6–13. 2016.
|
|
10
|
Higgins JPT, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG
and Sterne JAC: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In:
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and
Welch VA (eds). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of
Interventions. 2nd edition. Wiley-Blackwell, pp205-228, 2019.
|
|
11
|
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D,
Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P and Stewart LA: PRISMA-P Group.
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 4(1)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Davidson MB, Duran P, Lee ML and Friedman
TC: High-dose vitamin D supplementation in people with prediabetes
and hypovitaminosis D. Diabetes Care. 36:260–266. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dutta D, Mondal SA, Choudhuri S, Maisnam
I, Hasanoor Reza AH, Bhattacharya B, Chowdhury S and Mukhopadhyay
S: Vitamin-D supplementation in prediabetes reduced progression to
type 2 diabetes and was associated with decreased insulin
resistance and systemic inflammation: an open label randomized
prospective study from Eastern India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
103:e18–23. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gonzalez S, Duran P, Friedman T and
Davidson M (eds): The effect of six months of vitamin D
supplemention in minorities with pre-diabetes and hypovitaminosis
D. Journal of investigative medicine: Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins 530 Walnut St, Philadelphia, PA 19106-3621 USA, 2012.
|
|
15
|
Kawahara T: Eldecalcitol, a vitamin D
analog, for diabetes prevention in impaired glucose tolerance (DPVD
study). Diabetes. 67 (Suppl 1):S120–LB. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Kawahara T, Suzuki G, Inazu T, Mizuno S,
Kasagi F, Okada Y and Tanaka Y: Rationale and design of diabetes
prevention with active vitamin D (DPVD): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMJ Open.
6(e011183)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kawahara T, Suzuki G, Inazu T, Mizuno S,
Kasagi F, Okada Y and Tanaka Y: DPVD clinical study group.
Eldecalcitol, a vitamin D analogue, for diabetes prevention in
impaired glucose tolerance: DPVD study. Diabetologia. 61 (Suppl
1)(S78)2018.
|
|
18
|
Barengolts E, Manickam B, Eisenberg Y,
Akbar A, Kukreja S and Ciubotaru I: Effect of high-dose vitamin D
repletion on glycemic control in African-American males with
prediabetes and hypovitaminosis D. Endocr Pract. 21:604–612.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bhatt SP, Misra A, Pandey RM, Upadhyay AD,
Gulati S and Singh N: Vitamin D supplementation in overweight/obese
Asian Indian women with prediabetes reduces glycemic measures and
truncal subcutaneous fat: A 78 weeks randomized placebo-controlled
trial (PREVENT-WIN trial). Sci Rep. 10(220)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Davidson MB, Duran P, Lee ML and Friedman
TC: High-dose vitamin D supplementation in people with prediabetes
and hypovitaminosis D. Diabetes Care. 36:260–266. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dutta D, Mondal SA, Choudhuri S, Maisnam
I, Reza AHH, Bhattacharya B, Chowdhury S and Mukhopadhyay S:
Vitamin-D supplementation in prediabetes reduced progression to
type 2 diabetes and was associated with decreased insulin
resistance and systemic inflammation: An open label randomized
prospective study from Eastern India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
103:e18–e23. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jorde R, Sollid ST, Svartberg J, Schirmer
H, Joakimsen RM, Njølstad I, Fuskevåg OM, Figenschau Y and
Hutchinson MY: Vitamin D 20,000 IU per week for five years does not
prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 101:1647–1655. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kawahara T, Suzuki G, Mizuno S, Inazu T,
Kasagi F, Kawahara C, Okada Y and Tanaka Y: Effect of active
vitamin D treatment on development of type 2 diabetes: DPVD
randomised controlled trial in Japanese population. BMJ.
377(e066222)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kuchay MS, Laway BA, Bashir MI, Wani AI,
Misgar RA and Shah ZA: Effect of vitamin D supplementation on
glycemic parameters and progression of prediabetes to diabetes: A
1-year, open-label randomized study. Indian J Endocrinol Metab.
19:387–392. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Niroomand M, Fotouhi A, Irannejad N and
Hosseinpanah F: Does high-dose vitamin D supplementation impact
insulin resistance and risk of development of diabetes in patients
with pre-diabetes? A double-blind randomized clinical trial.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 148:1–9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pittas AG, Dawson-Hughes B, Sheehan P,
Ware JH, Knowler WC, Aroda VR, Brodsky I, Ceglia L, Chadha C,
Chatterjee R, et al: Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 381:520–530. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zaromytidou E, Koufakis T, Dimakopoulos G,
Drivakou D, Konstantinidou S, Antonopoulou V, Grammatiki M, Manthou
E, Iakovou I, Gotzamani-Psarrakou A and Kotsa K: The effect of
vitamin D supplementation on glycemic status of elderly people with
prediabetes: A 12-month open-label, randomized-controlled study.
Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 15:89–97. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang D, Zhong X, Cheng C, Su Z, Xue Y,
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Feng M, Xu Z, Zhao T, et al: Effect of vitamin D
and/or calcium supplementation on pancreatic β-cell function in
subjects with prediabetes: A randomized, controlled trial. J Agric
Food Chem. 71:347–357. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Aparna P, Muthathal S, Nongkynrih B and
Gupta SK: Vitamin D deficiency in India. J Family Med Prim Care.
7:324–330. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shrivastava U, Misra A, Mohan V,
Unnikrishnan R and Bachani D: Obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular
diseases in India: Public health challenges. Curr Diabetes Rev.
13:65–80. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu J, Wei X, Tan N, Zhang
J, Zhang J, Wang W and Wang Y: Association of vitamin D or calcium
supplementation with cardiovascular outcomes and mortality: A
meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. J Nutr Health Aging.
25:263–270. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bargagli M, Ferraro PM, Vittori M,
Lombardi G, Gambaro G and Somani B: Calcium and vitamin D
supplementation and their association with kidney stone disease: A
narrative review. Nutrients. 13(4363)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Golzarand M, Hollis BW, Mirmiran P, Wagner
CL and Shab-Bidar S: Vitamin D supplementation and body fat mass: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 72:1345–1357.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Perna S: Is vitamin D supplementation
useful for weight loss programs? A systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicina (Kaunas).
55(368)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Tan H, Tang J, Li J, Chong W, Hai
Y, Feng Y, Lunsford LD, Xu P, Jia D and Fang F: Effects of vitamin
D supplementation on prevention of type 2 diabetes in patients with
prediabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care.
43:1650–1658. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Barbarawi M, Zayed Y, Barbarawi O, Bala A,
Alabdouh A, Gakhal I, Rizk F, Alkasasbeh M, Bachuwa G and Manson
JE: Effect of vitamin D supplementation on the incidence of
diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 105:2857–2868.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|