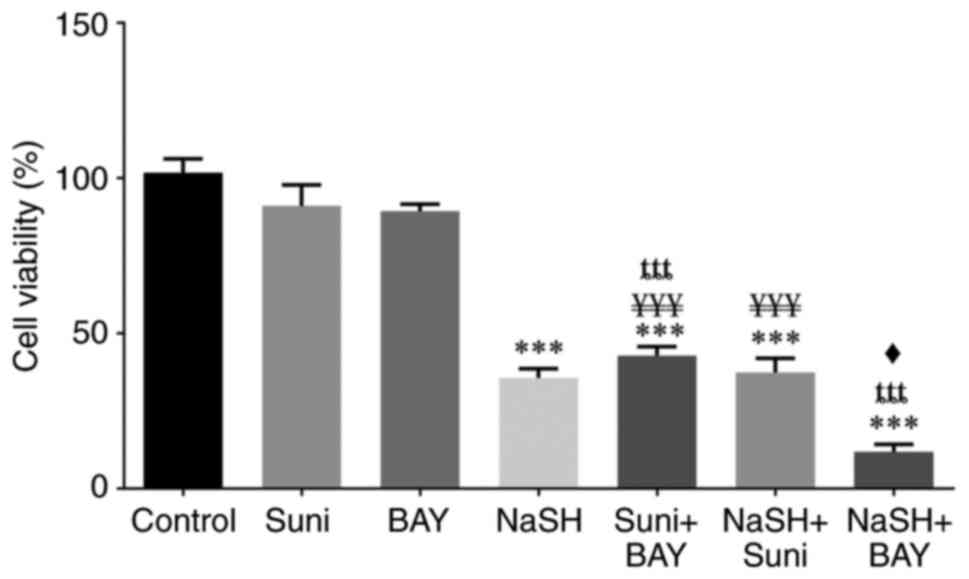
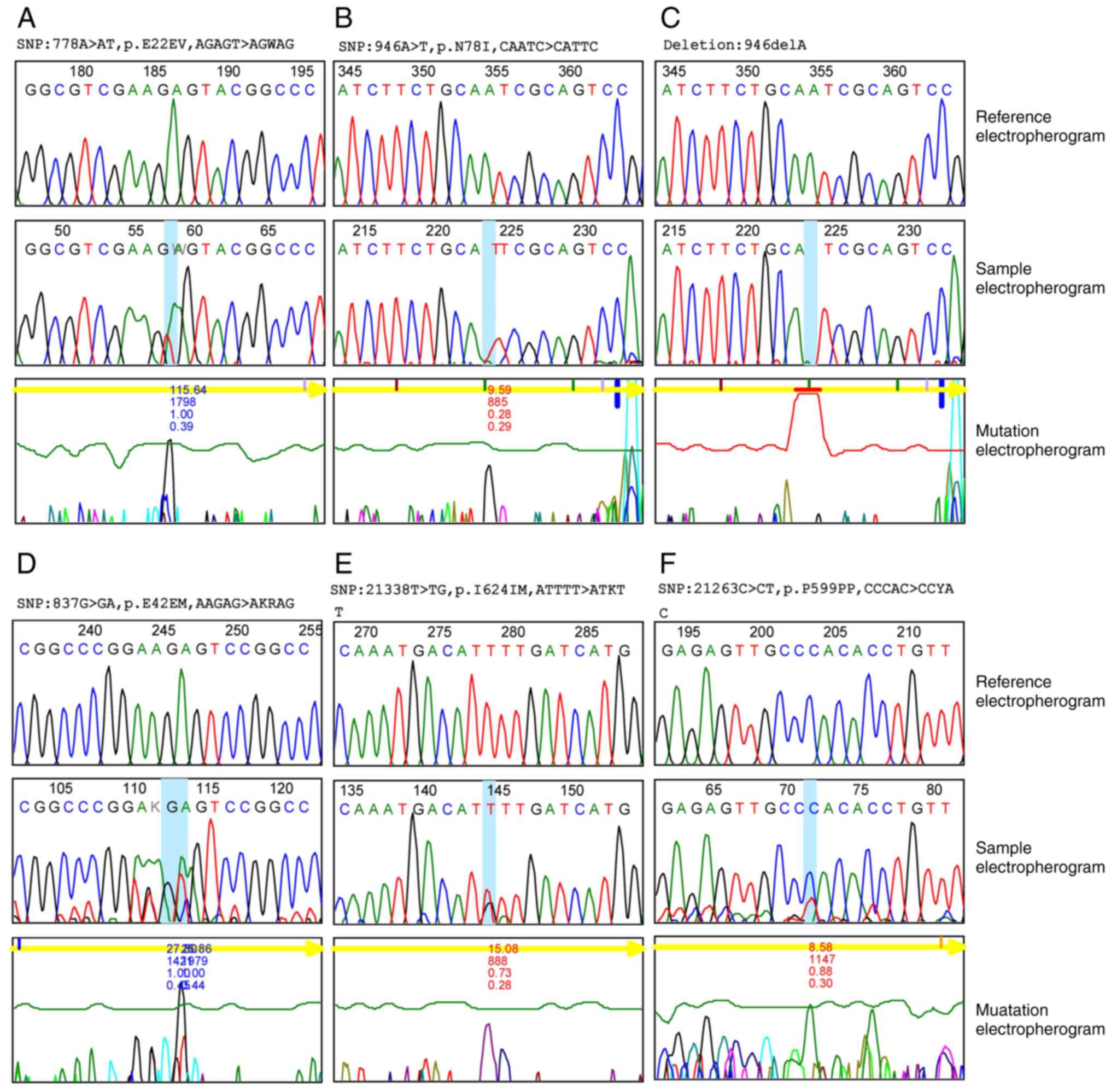
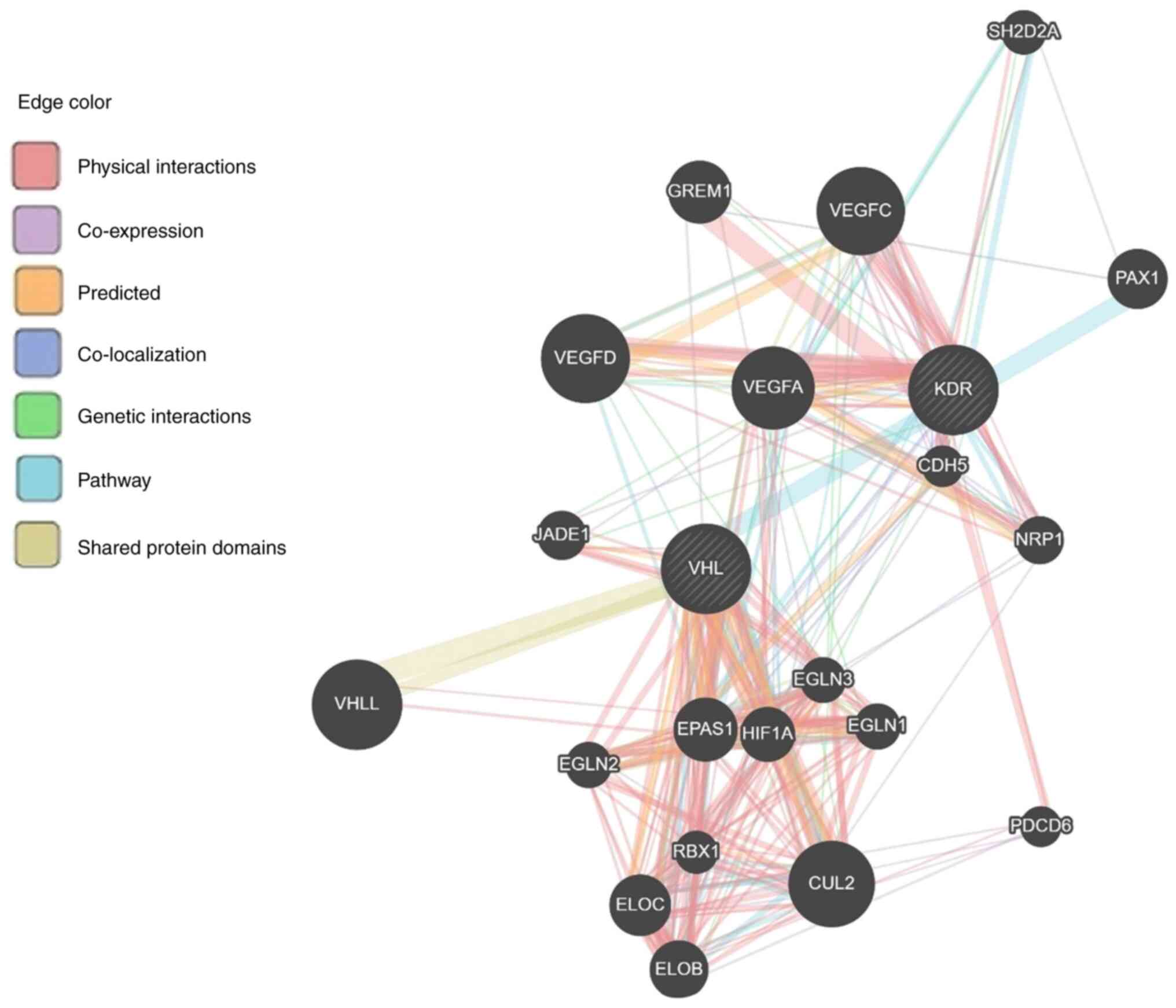
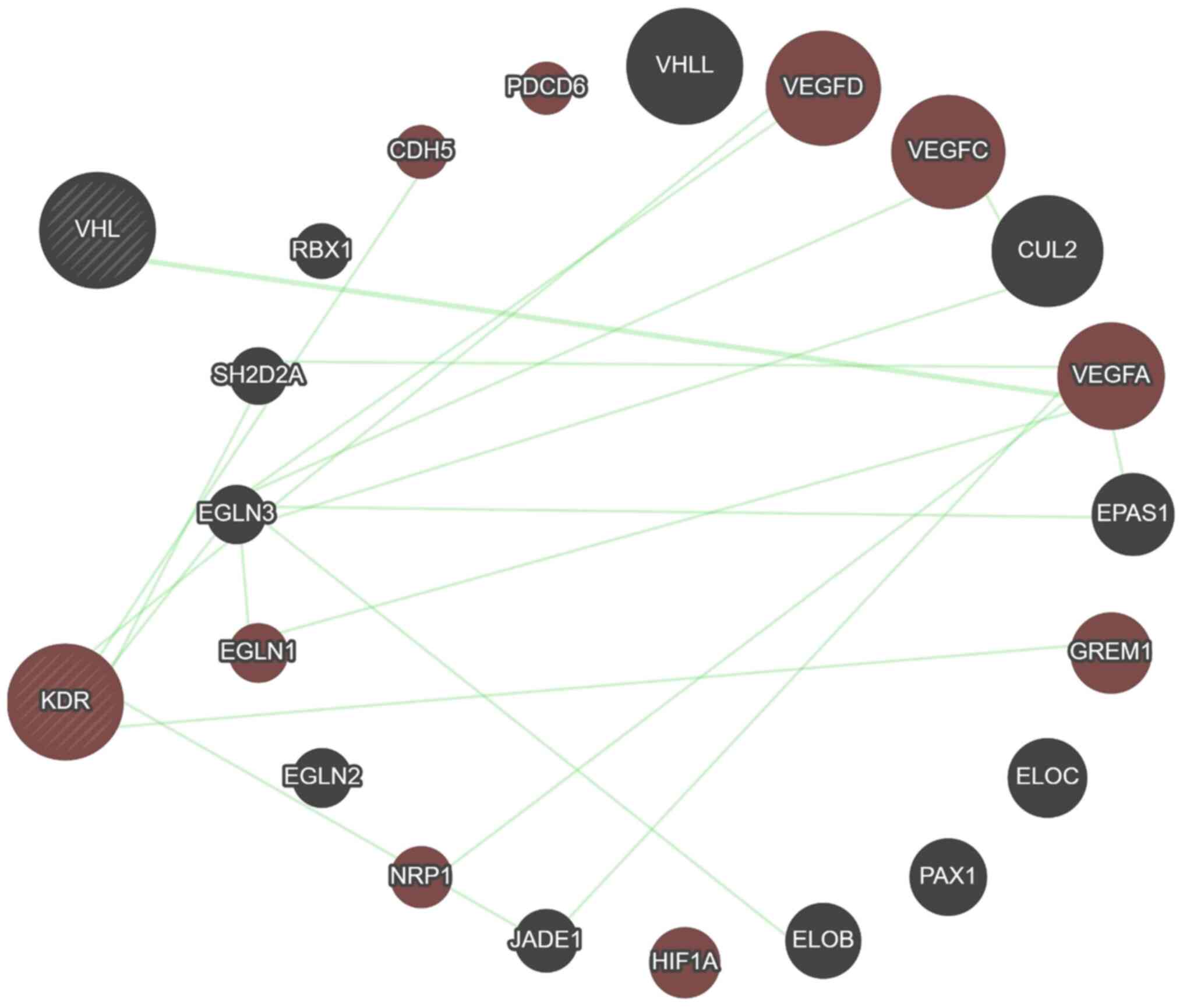
|
1
|
Bahadoram S, Davoodi M, Hassanzadeh S,
Bahadoram M, Barahman M and Mafakher L: Renal cell carcinoma: An
overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G Ital
Nefrol. 39:32–47. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Monjaras-Avila CU, Lorenzo-Leal AC,
Luque-Badillo AC, D'Costa N, Chavez-Muñoz C and Bach H: The tumor
immune microenvironment in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 24(7946)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kase AM, George DJ and Ramalingam S: Clear
cell renal cell carcinoma: From biology to treatment. Cancers
(Basel). 15(665)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Padala SA and Barsouk A, Thandra KC,
Saginala K, Mohammed A, Vakiti A, Rawla P and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. World J Oncol. 11:79–87.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jonasch E, Walker CL and Rathmell WK:
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma ontogeny and mechanisms of
lethality. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:245–261. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nickerson ML, Jaeger E, Shi Y, Durocher
JA, Mahurkar S, Zaridze D, Matveev V, Janout V, Kollarova H, Bencko
V, et al: Improved identification of von Hippel-Lindau gene
alterations in clear cell renal tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4726–4734. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dizman N, Philip EJ and Pal SK: Genomic
profiling in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:435–451.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Williamson SR: Clear cell papillary renal
cell carcinoma: An update after 15 years. Pathology. 53:109–119.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sharma R, Kadife E, Myers M, Kannourakis
G, Prithviraj P and Ahmed N: Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI
and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40(186)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton
C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J and Ficarra V: Renal
cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3(17009)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Makino T, Kadomoto S, Izumi K and Mizokami
A: Epidemiology and prevention of renal cell carcinoma. Cancers
(Basel). 14(4059)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Choi WSW, Boland J and Lin J:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α as a novel target in renal cell
carcinoma. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 8:1–7. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jin J, Xie Y, Zhang JS, Wang JQ, Dai SJ,
He WF, Li SY, Ashby CR Jr, Chen ZS and He Q: Sunitinib resistance
in renal cell carcinoma: From molecular mechanisms to predictive
biomarkers. Drug Resist Updat. 67(100929)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rini BI, Tamaskar I, Shaheen P, Salas R,
Garcia J, Wood L, Reddy S, Dreicer R and Bukowski RM:
Hypothyroidism in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:81–83.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma Y, Wang W, Idowu MO, Oh U, Wang XY,
Temkin SM and Fang X: Ovarian cancer relies on glucose transporter
1 to fuel glycolysis and growth: Anti-tumor activity of BAY-876.
Cancers (Basel). 11(33)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mantle D and Yang G: Hydrogen sulfide and
metal interaction: The pathophysiological implications. Mol Cell
Biochem. 477:2235–2248. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zaorska E, Tomasova L, Koszelewski D,
Ostaszewski R and Ufnal M: hydrogen sulfide in pharmacotherapy,
beyond the hydrogen sulfide-donors. Biomolecules.
10(323)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Khattak S, Rauf MA, Khan NH, Zhang QQ,
Chen HJ, Muhammad P, Ansari MA, Alomary MN, Jahangir M, Zhang CY,
et al: Hydrogen sulfide biology and its role in cancer. Molecules.
27(3389)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cao X, Ding L, Xie ZZ, Yang Y, Whiteman M,
Moore PK and Bian JS: A review of hydrogen sulfide synthesis,
metabolism, and measurement: Is modulation of hydrogen sulfide a
novel therapeutic for cancer? Antioxid Redox Signal. 31:1–38.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Powell CR, Dillon KM and Matson JB: A
review of hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) donors: Chemistry and potential
therapeutic applications. Biochem Pharmacol. 149:110–123.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen G, Zhang Y and Wu X: 786-0 renal
cancer cell line-derived exosomes promote 786-0 cell migration and
invasion in vitro. Oncol Lett. 7:1576–1580. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gu L, Sang Y, Nan X, Zheng Y, Liu F, Meng
L, Sang M and Shan B: circCYP24A1 facilitates esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma progression through binding PKM2 to regulate
NF-κB-induced CCL5 secretion. Mol Cancer. 21(217)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Warren AY and Harrison D: WHO/ISUP
classification, grading and pathological staging of renal cell
carcinoma: Standards and controversies. World J Urol. 36:1913–1926.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Elkassem AA, Allen BC, Sharbidre KG,
Rais-Bahrami S and Smith AD: Update on the role of imaging in
clinical staging and restaging of renal cell carcinoma based on the
AJCC 8th edition, from the AJR special series on cancer staging.
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 217:541–555. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Delahunt B, Eble JN, Samaratunga H,
Thunders M, Yaxley JW and Egevad L: Staging of renal cell
carcinoma: Current progress and potential advances. Pathology.
53:120–128. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Abid MN, Qadir FA and Salihi A:
Association between the serum concentrations and mutational status
of IL-8, IL-27 and VEGF and the expression levels of the hERG
potassium channel gene in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol
Lett. 22(665)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Alves MR, Carneiro FC, Lavorato-Rocha AM,
da Costa WH, da Cunha IW, de Cássio Zequi S, Guimaraes GC, Soares
FA, Carraro DM and Rocha RM: Mutational status of VHL gene and its
clinical importance in renal clear cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch.
465:321–330. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Housein Z, Kareem TS and Salihi A: In
vitro anticancer activity of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide
alongside nickel nanoparticle and novel mutations in their genes in
CRC patients. Sci Rep. 11(2536)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gudmundsson S, Singer-Berk M, Watts NA,
Phu W, Goodrich JK and Solomonson M: Genome Aggregation Database
Consortium. Rehm HL, MacArthur DG and O'Donnell-Luria A: Variant
interpretation using population databases: Lessons from gnomAD. Hum
Mutat. 43:1012–1030. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sondka Z, Bamford S, Cole CG, Ward SA,
Dunham I and Forbes SA: The COSMIC cancer gene census: Describing
genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer.
18:696–705. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Franz M, Rodriguez H, Lopes C, Zuberi K,
Montojo J, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46:W60–W64. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sato H, Siddig S, Uzu M, Suzuki S, Nomura
Y, Kashiba T, Gushimiyagi K, Sekine Y, Uehara T, Arano Y, et al:
Elacridar enhances the cytotoxic effects of sunitinib and prevents
multidrug resistance in renal carcinoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
746:258–266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Amaro F, Pisoeiro C, Valente MJ, Bastos
ML, de Pinho PG, Carvalho M and Pinto J: Sunitinib versus pazopanib
dilemma in renal cell carcinoma: New Insights into the in vitro
metabolic impact, efficacy, and safety. Int J Mol Sci.
23(9898)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Singer K, Kastenberger M, Gottfried E,
Hammerschmied CG, Büttner M, Aigner M, Seliger B, Walter B,
Schlösser H, Hartmann A, et al: Warburg phenotype in renal cell
carcinoma: high expression of glucose-transporter 1 (GLUT-1)
correlates with low CD8(+) T-cell infiltration in the tumor. Int J
Cancer. 128:2085–2095. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Abdolahi M, Alam M, Ghaffarpasand A, Nouri
F, Badkoobeh A, Golkar M, Abassi K and Torbati P: Assessment of the
expression of GLUT1 in renal cell carcinoma and its various
subtypes. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 10:2581–2585. 2022.
|
|
38
|
Wang X, He H, Rui W, Zhang N, Zhu Y and
Xie X: TRIM38 triggers the uniquitination and degradation of
glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) to restrict tumor progression in
bladder cancer. J Transl Med. 19(508)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kollmannsberger C, Soulieres D, Wong R,
Scalera A, Gaspo R and Bjarnason G: Sunitinib therapy for
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: recommendations for management of
side effects. Can Urol Assoc J. 1:S41–S54. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sonke E, Verrydt M, Postenka CO, Pardhan
S, Willie CJ, Mazzola CR, Hammers MD, Pluth MD, Lobb I, Power N, et
al: Inhibition of endogenous hydrogen sulfide production in
clear-cell renal cell carcinoma cell lines and xenografts restricts
their growth, survival and angiogenic potential. Nitric Oxide.
49:26–39. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shackelford RE, Abdulsattar J, Wei EX,
Cotelingam J, Coppola D and Herrera GA: Increased nicotinamide
phosphoribosyltransferase and cystathionine-β-synthase in renal
oncocytomas, renal urothelial carcinoma, and renal clear cell
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 37:3423–3427. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Breza J Jr, Soltysova A, Hudecova S,
Penesova A, Szadvari I, Babula P, Chovancova B, Lencesova L, Pos O,
Breza J, et al: Endogenous H(2)S producing enzymes are involved in
apoptosis induction in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
18(591)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dong Q, Yang B, Han JG, Zhang MM, Liu W,
Zhang X, Yu HL, Liu ZG, Zhang SH, Li T, et al: A novel hydrogen
sulfide-releasing donor, HA-ADT, suppresses the growth of human
breast cancer cells through inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 455:60–72.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sekar H, Krishnamoorthy S, Kumaresan N,
Chandrasekaran D, Ramaswamy P, Sundaram S and Raj N:
Clinicopathological comparison of VHL expression as a prognostic
tumor marker in renal cell carcinoma: A single center experience.
Niger J Clin Pract. 24:614–620. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Audenet F, Yates DR, Cancel-Tassin G,
Cussenot O and Rouprêt M: Genetic pathways involved in
carcinogenesis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Genomics towards
personalized medicine. BJU Int. 109:1864–1870. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW,
Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER and
Ratcliffe PJ: The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets
hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature.
399:271–275. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kondo K, Yao M, Yoshida M, Kishida T,
Shuin T, Miura T, Moriyama M, Kobayashi K, Sakai N, Kaneko S, et
al: Comprehensive mutational analysis of the VHL gene in sporadic
renal cell carcinoma: Relationship to clinicopathological
parameters. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 34:58–68. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lin PH, Huang CY, Yu KJ, Kan HC, Liu CY,
Chuang CK, Lu YC, Chang YH, Shao IH and Pang ST: Genomic
characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma using targeted
gene sequencing. Oncol Lett. 21(169)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shah AA, Kamal MA and Akhtar S: Tumor
angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, pathways and current
biological therapeutic interventions. Curr Drug Metab. 22:50–59.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhu X, Wang Y, Xue W, Wang R, Wang L, Zhu
ML and Zheng L: The VEGFR-2 protein and the VEGFR-2 rs1870377
A>T genetic polymorphism are prognostic factors for gastric
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 20:497–504. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|