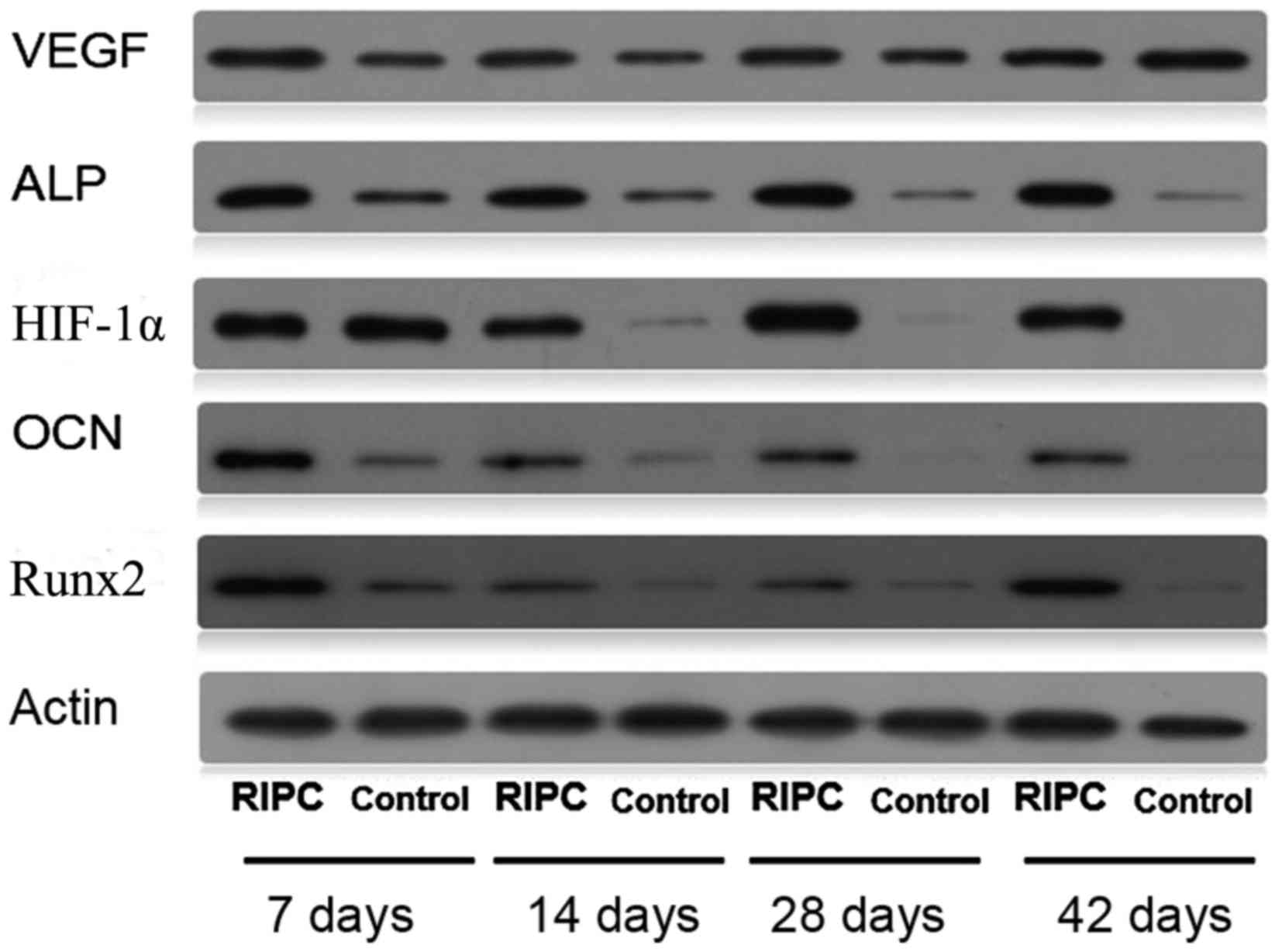
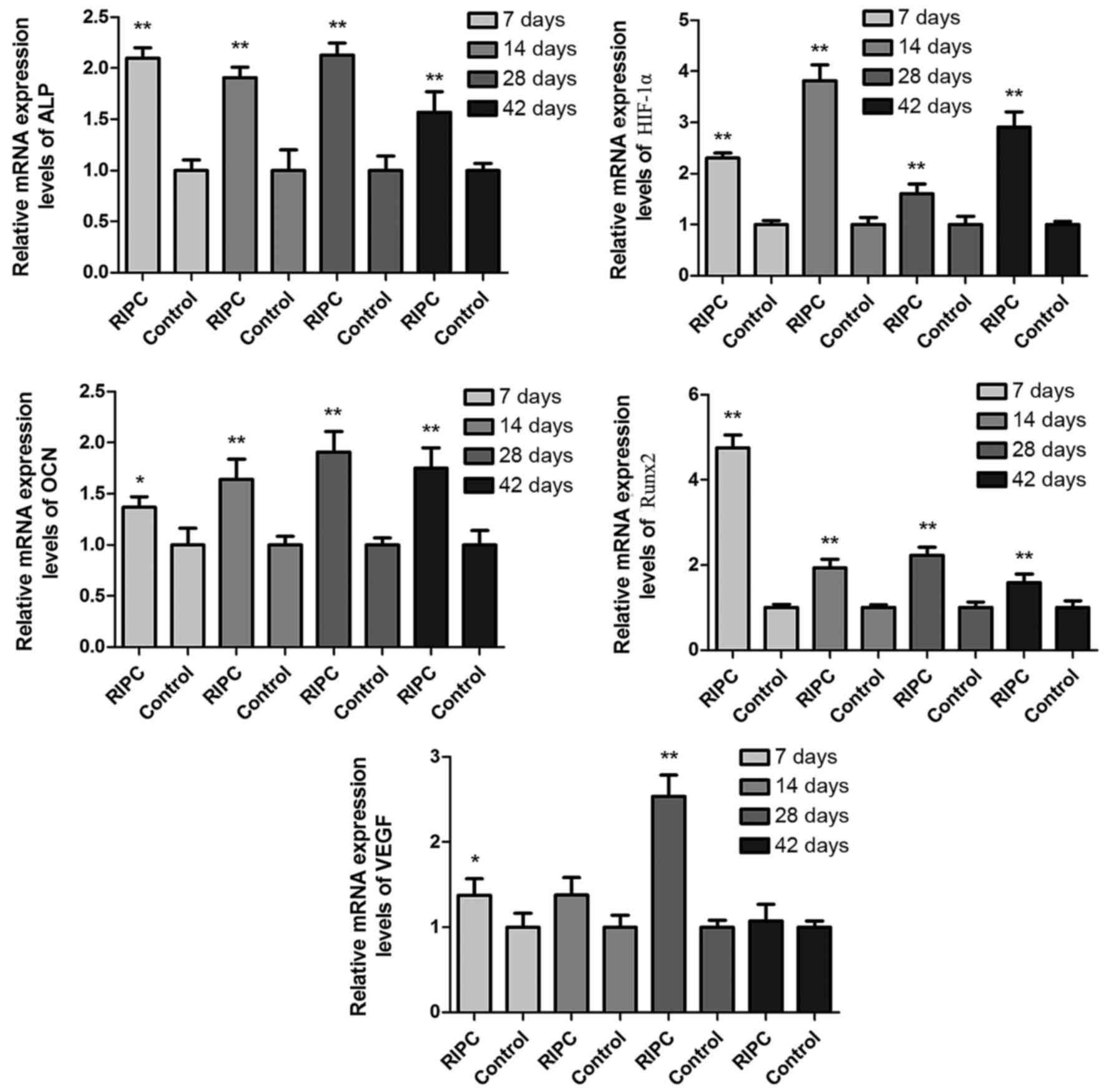
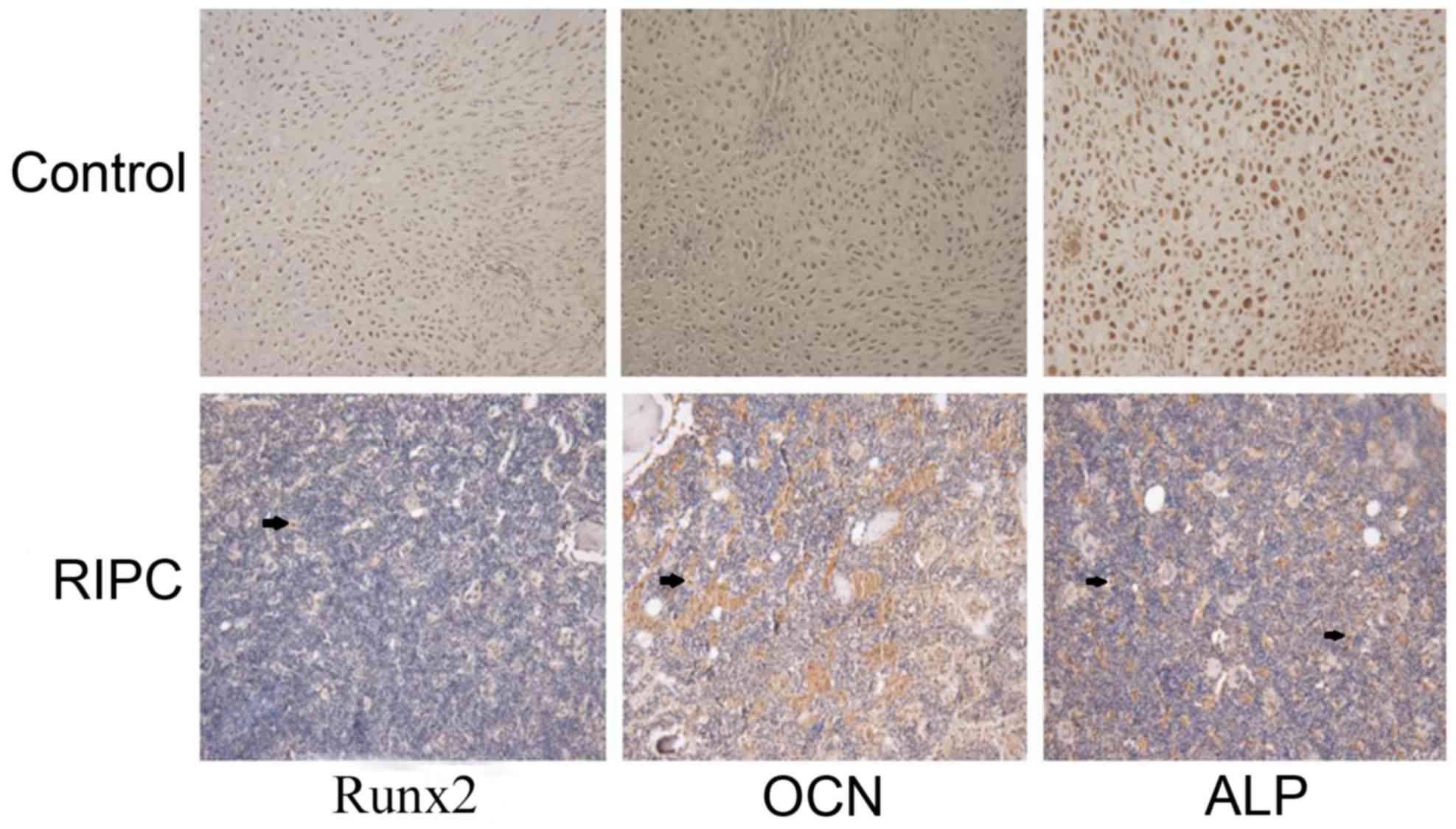
|
1
|
Marsell R and Einhorn TA: The biology of
fracture healing. Injury. 42:551–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giannoudis PV, Jones E and Einhorn TA:
Fracture healing and bone repair. Injury. 42:549–550. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bishop JA, Palanca AA, Bellino MJ and
Lowenberg DW: Assessment of compromised fracture healing. J Am Acad
Orthop Surg. 20:273–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wan C, Gilbert SR, Wang Y, Cao X, Shen X,
Ramaswamy G, Jacobsen KA, Alaql ZS, Eberhardt AW, Gerstenfeld LC,
et al: Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway
accelerates bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:686–691.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raheja LF, Genetos DC and Yellowley CE:
Hypoxic osteocytes recruit human MSCs through an OPN/CD44-mediated
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 366:1061–1066. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Street J, Bao M, deGuzman L, Bunting S,
Peale FV Jr, Ferrara N, Steinmetz H, Hoeffel J, Cleland JL,
Daugherty A, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates
bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:9656–9661. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Loboda A, Jazwa A, Wegiel B, Jozkowicz A
and Dulak J: Heme oxygenase-1-dependent and -independent regulation
of angiogenic genes expression: Effect of cobalt protoporphyrin and
cobalt chloride on VEGF and IL-8 synthesis in human microvascular
endothelial cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 51:347–355.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang J, Liu L, Feng M, An S, Zhou M, Li
Z, Qi J and Shen H: Effect of CoCl2 on fracture repair in a rat
model of bone fracture. Mol Med Rep. 12:5951–5956. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saeedi SS, Karami S, Karami B and
Shokrzadeh M: Toxic effects of cobalt chloride on hematological
factors of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Biol Trace Elem Res.
132:144–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baik SW, Park BS, Kim YH, Kim YD, Kim CH,
Yoon JY and Yoon JU: Effects of remifentanil preconditioning on
osteoblasts under hypoxia-reoxygenation condition. Int J Med Sci.
12:583–589. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalakech H, Tamareille S, Pons S,
Godin-Ribuot D, Carmeliet P, Furber A, Martin V, Berdeaux A, Ghaleh
B and Prunier F: Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1α in remote limb
ischemic preconditioning. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 65:98–104. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stefanini MO, Wu FT, Mac Gabhann F and
Popel AS: A compartment model of VEGF distribution in blood,
healthy and diseased tissues. BMC Syst Biol. 2:772008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szijártó A, Czigány Z, Turóczi Z and
Harsányi L: Remote ischemic perconditioning-a simple, low-risk
method to decrease ischemic reperfusion injury: Models, protocols
and mechanistic background. A review. J Surg Res. 178:797–806.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F,
Wang NP, Guyton RA and Vinten-Johansen J: Inhibition of myocardial
injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: Comparison
with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
285:H579–H588. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Przyklenk K, Bauer B, Ovize M, Kloner RA
and Whittaker P: Regional ischemic ‘preconditioning’ protects
remote virgin myocardium from subsequent sustained coronary
occlusion. Circulation. 87:893–899. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ren C, Yan Z, Wei D, Gao X, Chen X and
Zhao H: Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against
focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1288:88–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiong J, Liao X, Xue FS, Yuan YJ, Wang Q
and Liu JH: Remote ischemia conditioning-an endogenous
cardioprotective strategy from outside the heart. Chin Med J
(Engl). 124:2209–2215. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leosco D, Rengo G, Iaccarino G, Sanzari E,
Golino L, De Lisa G, Zincarelli C, Fortunato F, Ciccarelli M,
Cimini V, et al: Prior exercise improves age-dependent vascular
endothelial growth factor downregulation and angiogenesis responses
to hind-limb ischemia in old rats. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
62:471–480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Petersen W, Wildemann B, Pufe T, Raschke M
and Schmidmaier G: The angiogenic peptide pleiotrophin (PTN/HB-GAM)
is expressed in fracture healing: An immunohistochemical study in
rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 124:603–607. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren C, Wang P, Wang B, Li N, Li W, Zhang
C, Jin K and Ji X: Limb remote ischemic per-conditioning in
combination with post-conditioning reduces brain damage and
promotes neuroglobin expression in the rat brain after ischemic
stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 33:369–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Komrakova M, Weidemann A, Dullin C, Ebert
J, Tezval M, Stuermer KM and Sehmisch S: The impact of strontium
ranelate on metaphyseal bone healing in ovariectomized rats. Calcif
Tissue Int. 97:391–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA,
Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ and Muller R: Guidelines for assessment of
bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J
Bone Miner Res. 25:1468–1486. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou M, Shen D, Head JE, Chew EY,
Chévez-Barrios P, Green WR and Chan CC: Ocular clusterin expression
in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Mol Vis. 13:2129–2136.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gerstenfeld LC, Wronski TJ, Hollinger JO
and Einhorn TA: Application of histomorphometric methods to the
study of bone repair. J Bone Miner Res. 20:1715–1722. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gutierrez GE, Edwards JR, Garrett IR,
Nyman JS, McCluskey B, Rossini G, Flores A, Neidre DB and Mundy GR:
Transdermal lovastatin enhances fracture repair in rats. J Bone
Miner Res. 23:1722–1730. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inada M, Yasui T, Nomura S, Miyake S,
Deguchi K, Himeno M, Sato M, Yamagiwa H, Kimura T, Yasui N, et al:
Maturational disturbance of chondrocytes in Cbfa1-deficient mice.
Dev Dyn. 214:279–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lian JB, Javed A, Zaidi SK, Lengner C,
Montecino M, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL and Stein GS: Regulatory
controls for osteoblast growth and differentiation: Role of
Runx/Cbfa/AML factors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 14:1–41. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mimori K, Komaki M, Iwasaki K and Ishikawa
I: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 is involved in
ascorbic acid-induced osteoblastic differentiation in periodontal
ligament cells. J Periodontol. 78:328–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Komatsu DE and Warden SJ: The control of
fracture healing and its therapeutic targeting: Improving upon
nature. J Cell Biochem. 109:302–311. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lim SY and Hausenloy DJ: Remote ischemic
conditioning: From bench to bedside. Front Physiol. 3:272012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oxman T, Arad M, Klein R, Avazov N and
Rabinowitz B: Limb ischemia preconditions the heart against
reperfusion tachyarrhythmia. Am J Physiol. 273:H1707–H1712.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jeanneteau J, Hibert P, Martinez MC,
Tual-Chalot S, Tamareille S, Furber A, Andriantsitohaina R and
Prunier F: Microparticle release in remote ischemic conditioning
mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 303:H871–H877. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Karakoyun R, Koksoy C, Yilmaz TU, Altun H,
Banli O, Albayrak A, Alper M and Sener Z: The angiogenic effects of
ischemic conditioning in experimental critical limb ischemia. Eur J
Vasc Endovasc Surg. 47:172–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Yan F, Min L, Ji X and Luo
Y: Protective effects of remote ischemic preconditioning in rat
hindlimb on ischemia- reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res.
7:583–587. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tapuria N, Kumar Y, Habib MM, Amara Abu M,
Seifalian AM and Davidson BR: Remote ischemic preconditioning: A
novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury-a review.
J Surg Res. 150:304–330. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi W and Vinten-Johansen J: Endogenous
cardioprotection by ischaemic postconditioning and remote
conditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 94:206–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Formenti F, Constantin-Teodosiu D,
Emmanuel Y, Cheeseman J, Dorrington KL, Edwards LM, Humphreys SM,
Lappin TR, McMullin MF, McNamara CJ, et al: Regulation of human
metabolism by hypoxia-inducible factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:12722–12727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Komori T: Regulation of osteoblast
differentiation by transcription factors. J Cell Biochem.
99:1233–1239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Banerjee C, Javed A, Choi JY, Green J,
Rosen V, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB and Stein GS:
Differential regulation of the two principal Runx2/Cbfa1 n-terminal
isoforms in response to bone morphogenetic protein-2 during
development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrinology.
142:4026–4039. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao J, Fu S, Zeng Z, Li F, Niu Q, Jing D
and Feng X: Cyclic stretch promotes osteogenesis-related gene
expression in osteoblast-like cells through a cofilin-associated
mechanism. Mol Med Rep. 14:218–224. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karsenty G and Wagner EF: Reaching a
genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev
Cell. 2:389–406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Murshed M, Harmey D, Millán JL, McKee MD
and Karsenty G: Unique coexpression in osteoblasts of broadly
expressed genes accounts for the spatial restriction of ECM
mineralization to bone. Genes Dev. 19:1093–1104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Remote
ischaemic preconditioning: Underlying mechanisms and clinical
application. Cardiovasc Res. 79:377–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Selzner N, Boehnert M and Selzner M:
Preconditioning, postconditioning, and remote conditioning in solid
organ transplantation: Basic mechanisms and translational
applications. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 26:115–124. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Grall S, Prunier-Mirebeau D, Tamareille S,
Mateus V, Lamon D, Furber A and Prunier F: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress pathway involvement in local and remote myocardial ischemic
conditioning. Shock. 39:433–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kanoria S, Jalan R, Seifalian AM, Williams
R and Davidson BR: Protocols and mechanisms for remote ischemic
preconditioning: A novel method for reducing ischemia reperfusion
injury. Transplantation. 84:445–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao H: The protective effects of ischemic
postconditioning against stroke: From rapid to delayed and remote
postconditioning. Open Drug Discov J. 5:138–147. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hoda MN, Fagan SC, Khan MB, Vaibhav K,
Chaudhary A, Wang P, Dhandapani KM, Waller JL and Hess DC: A 2×2
factorial design for the combination therapy of minocycline and
remote ischemic perconditioning: Efficacy in a preclinical trial in
murine thromboembolic stroke model. Exp Transl Stroke Med.
6:102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang JY, Shen J, Gao Q, Ye ZG, Yang SY,
Liang HW, Bruce IC, Luo BY and Xia Q: Ischemic postconditioning
protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced
injury in rats. Stroke. 39:983–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xing B, Chen H, Zhang M, Zhao D, Jiang R,
Liu X and Zhang S: Ischemic postconditioning inhibits apoptosis
after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat.
Stroke. 39:2362–2369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|