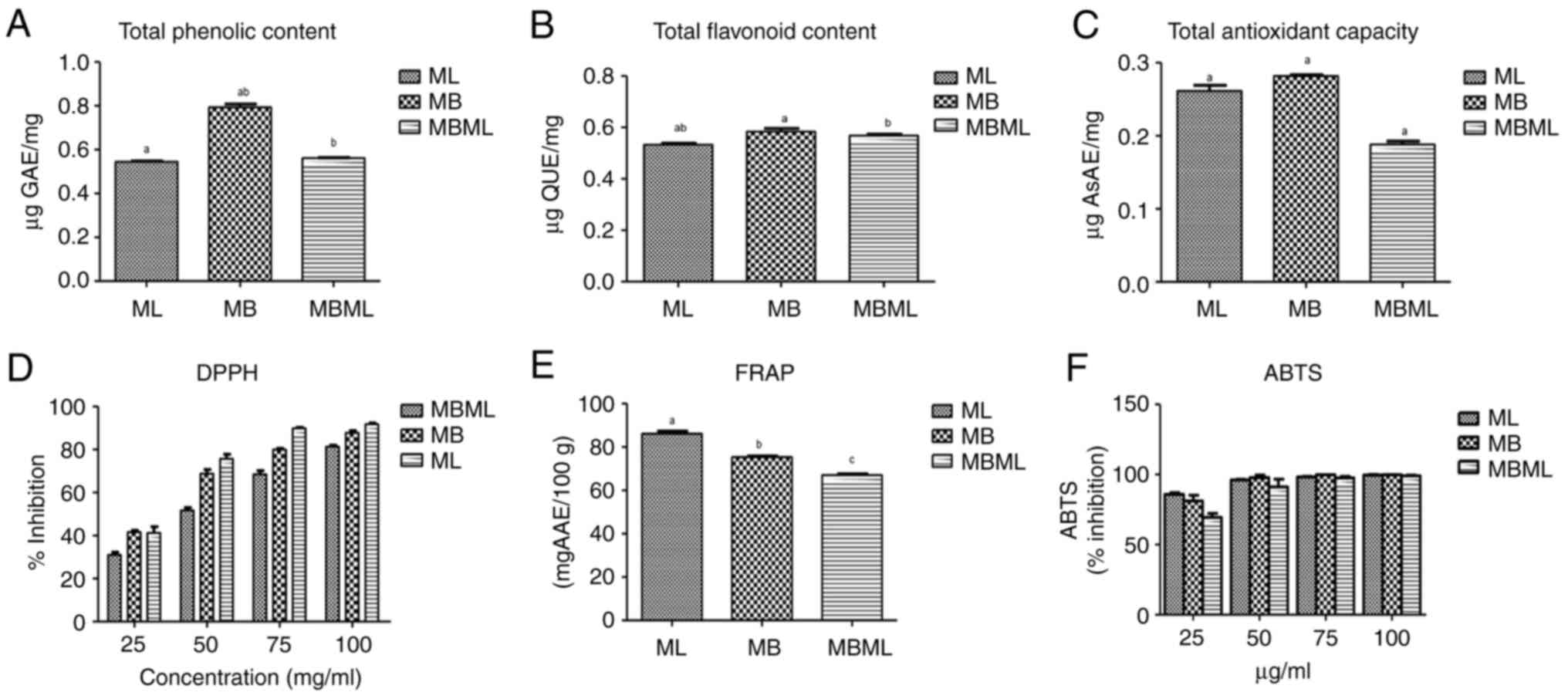
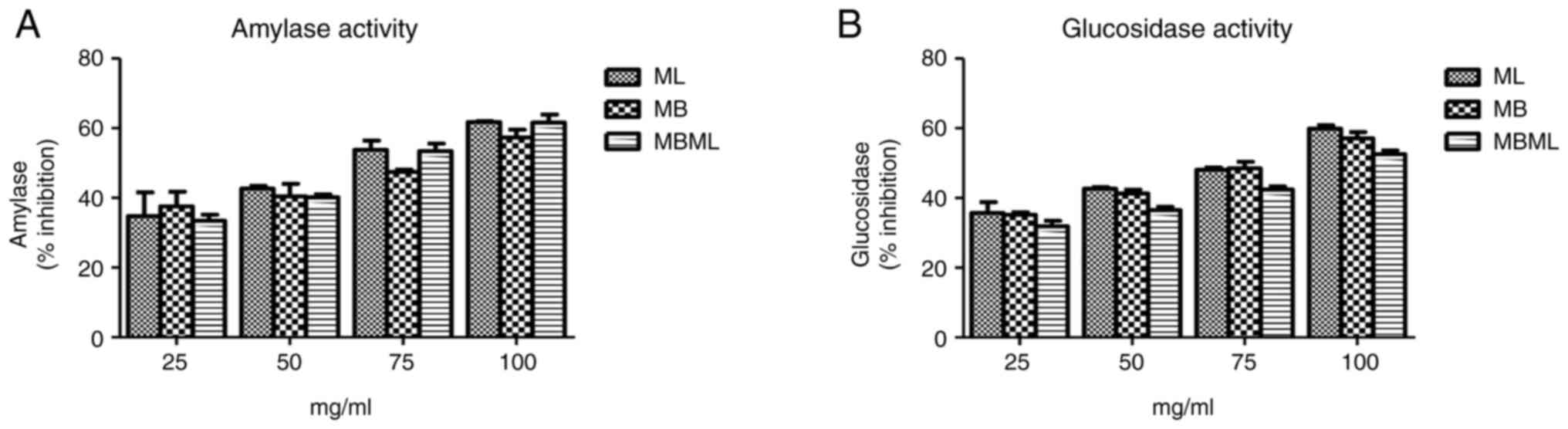
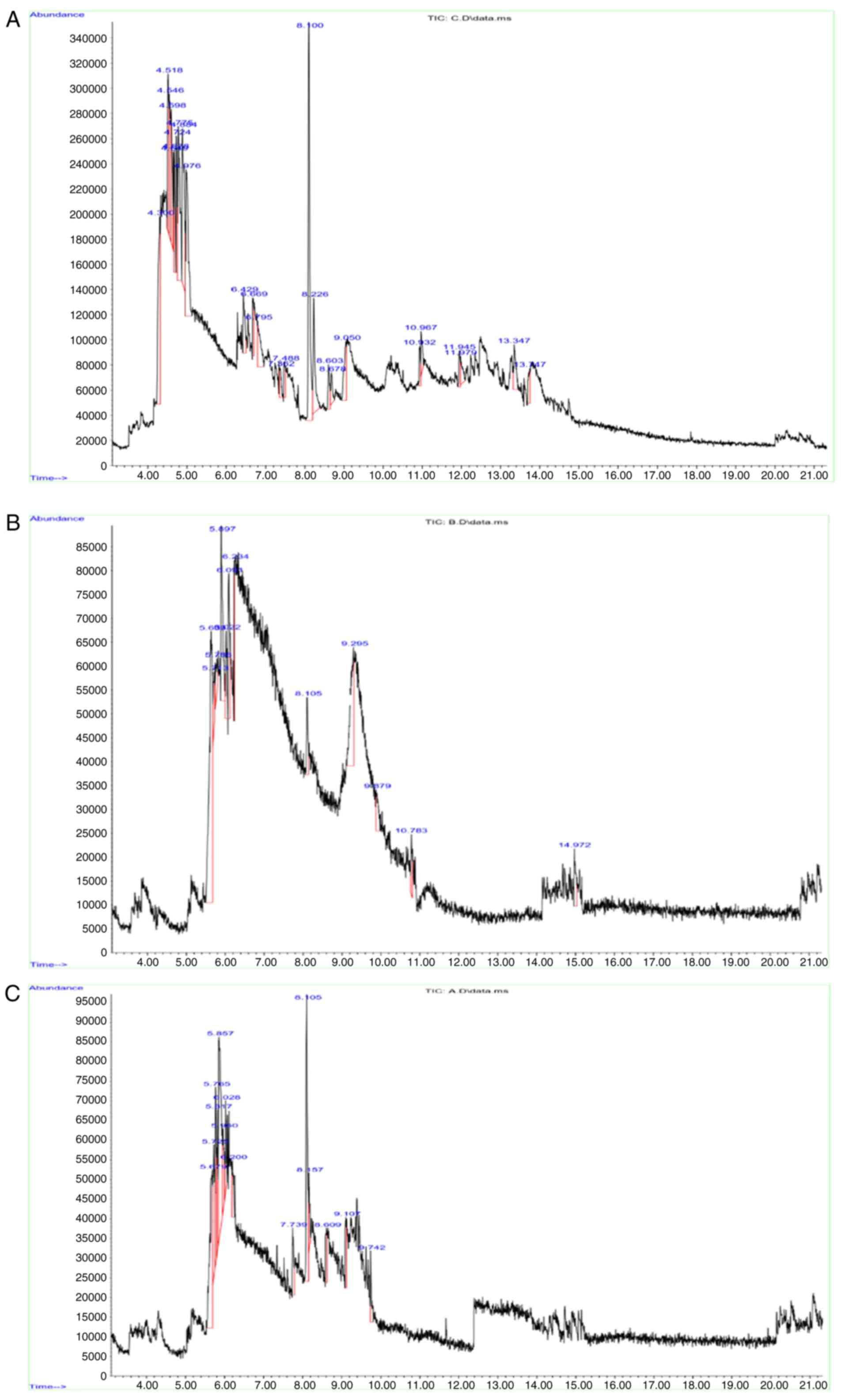
|
1
|
Yaribeygi H, Farrokhi FR, Rezaee R and
Sahebkar A: Oxidative stress induces renal failure: A review of
possible molecular pathways. J Cell Biochem. 119:2990–2998.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu Z, Ren Z, Zhang J, Chuang CC,
Kandaswamy E, Zhou T and Zuo L: Role of ROS and nutritional
antioxidants in human diseases. Front Physiol.
9(477)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jha JC, Banal C, Chow BS, Cooper ME and
Jandeleit-Dahm K: Diabetes and kidney disease: Role of oxidative
stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 25:657–684. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mayer-Davis EJ, Lawrence JM, Dabelea D,
Divers J, Isom S, Dolan L, Imperatore G, Linder B, Marcovina S,
Pettitt DJ, et al: Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
among youths, 2002-2012. N Engl J Med. 376:1419–1429.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yaribeygi H, Butler AE, Barreto GE and
Sahebkar A: Antioxidative potential of antidiabetic agents: A
possible protective mechanism against vascular complications in
diabetic patients. J Cell Physiol. 234:2436–2446. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Batool N, Ilyas N, Shabir S, Saeed M and
Mazhar R: Mini-review-A mini-review of therapeutic potential of
Mangifera indica L. Pak J Pharm Sci. 31:1441–1448.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kulkarni VM and Rathod VK: Exploring the
potential of Mangifera indica leaves extract versus
mangiferin for therapeutic application. Agric Nat Resour.
52:155–161. 2018.
|
|
8
|
Ruiz-Montañez G, Ragazzo-Sánchez JA,
Calderón-Santoyo M, Velázquez-de la Cruz G, de León JA and
Navarro-Ocaña A: Evaluation of extraction methods for preparative
scale obtention of mangiferin and lupeol from mango peels
(Mangifera indica L.). Food Chem. 159:267–272.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mirza B, Croley CR, Ahmad M, Pumarol J,
Das N, Sethi G and Bishayee A: Mango (Mangifera indica L.):
A magnificent plant with cancer preventive and anticancer
therapeutic potential. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 61:2125–2151.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nair SS, Kavrekar V and Mishra A: In vitro
studies on alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory
activities of selected plant extracts. Eur J Exp Biol. 3:128–132.
2013.
|
|
11
|
Kumar Y, Kumar V and Sangeeta :
Comparative antioxidant capacity of plant leaves and herbs with
their antioxidative potential in meat system under accelerated
oxidation conditions. J Food Meas Charact. 14:3250–3262. 2020.
|
|
12
|
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH and Samarakoon
SR: A review on ethnopharmacological applications, pharmacological
activities, and bioactive compounds of Mangifera indica
(Mango). Evid Based Complement Altern Med.
2017(6949835)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Scartezzini P and Speroni E: Review on
some plants of Indian traditional medicine with antioxidant
activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 71:23–43. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Martínez G, Delgado R, Pérez G, Garrido G,
Núñez Sellés AJ and León OS: Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant
activity of Mangifera indica L. extract (Vimang). Phytother
Res. 14:424–427. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Martínez Sánchez G, Candelario-Jalil E,
Giuliani A, León OS, Sam S, Delgado R and Núñez Sellés AJ:
‘Mangifera indica L. extract (QF808) reduces
ischaemia-induced neuronal loss and oxidative damage in the gerbil
brain’. Free Radic Res. 35:465–473. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rymbai H, Srivastav M, Sharma RR, Patel CR
and Singh AK: Bio-active compounds in mango (Mangifera
indica L.) and their roles in human health and plant defence-a
review. J Hortic Sci Biotech. 88:369–379. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Karigidi ME, Olotu O, Adegoke AM, Olugbami
JO and Odunola OA: Cymbopogon citratus extracts inhibit
inflammation and oxidative damage in mice colon by downregulating
IL-6, HSP 70 and upregulating APC protein. Arch Basic Appl Med.
12:68–75. 2024.
|
|
18
|
Kim KH, Tsao R, Yang R and Cui SW:
Phenolic acid profiles and antioxidant activities of wheat bran
extracts and the effect of hydrolysis conditions. Food Chem.
95:466–473. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Zhisten J, Mengcheng T and Jianming W: The
determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their
scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 64:555–559.
1999.
|
|
20
|
Talukdar D: Arsenic-induced oxidative
stress in the common bean legume, Phaseolus vulgaris L. seedlings
and its amelioration by exogenous nitric oxide. Physiol Mol Biol
Plants. 19:69–79. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Prieto P, Pineda M and Aguilar M:
Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the
formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: Specific application to
the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem. 269:337–341.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gyamfi M, Yonamine M and Aniya Y:
Free-radical scavenging action of medicinal herbs from Ghana:
Thonningia sanguinea on experimentally-induced liver injuries. Gen
Pharmacol. 32:661–667. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Benzie IF and Strain JJ: The ferric
reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of ‘antioxidant
power’: The FRAP assay. Anal Biochem. 239:70–76. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala
A, Yang M and Rice-Evans C: Antioxidant activity applying an
improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol
Med. 26:1231–1237. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bhutkar MA and Bhise SB: In vitro assay of
alpha amylase inhibitory activity of some indigenous plants. Int J
Chem Sci. 10:457–462. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Fouotsa HA, Lannang M, Mbazoa CD, Rasheed
S, Marasini BP, Ali Z, Devkota KP, Kengfack AE, Shaheen F,
Choudhary MI and Sewald N: Xanthones inhibitors of α-glucosidase
and glycation from Garcinia nobilis. Phytochem Lett. 5:236–239.
2012.
|
|
27
|
Balouiri M, Sadiki M and Ibnsouda SK:
Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J
Pharm Anal. 6:71–79. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Eloff JN: The antibacterial activity of 27
southern African members of the Combretaceae. S Afr J Sci.
95:148–152. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Sermakkani M and Thangapandian V: GC-MS
analysis of Cassia italica leaf methanol extract. Asian J Pharm
Clin Res. 5:90–94. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Rasouli H, Farzaei MH and Khodarahmi R:
Polyphenols and their benefits: A review. Int J Food Prop.
20:1700–1741. 2017.
|
|
31
|
Nunes XP, Silva FS, Guedes da Silva
Almeida JR, de Lima JT, Ribeiro LAA, Quintans Júnior LJ and Filho
JMB: Biological oxidations and antioxidant activity of natural
products. In: Rao V (ed). Phytochemicals as nutraceuticals-global
approaches to their role in nutrition and health. Intech, pp1-20,
2012.
|
|
32
|
Kim H, Moon JY, Kim H, Lee DS, Cho M, Choi
HK, Kim YS, Mosaddik A and Cho SK: Antioxidant and
antiproliferative activities of mango (Mangifera indica L.)
flesh and peel. Food Chem. 121:429–436. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Ribeiro SMR, Barbosa LCA, Queiroz JH,
Knödler M and Schieber A: Phenolic compounds and antioxidant
capacity of Brazilian mango (Mangifera indica L.) varieties.
Food Chem. 110:620–626. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Zhou X, Shang J, Wang J, Jiang B and Wang
Q: Antioxidant activity of extracts from the aril of Torreya
fargesii Franch. And its protection on the oxidation of DHA algal
oil. CyTA J Food. 16:381–389. 2018.
|
|
35
|
Liu S, Sun J, Yu L, Zhang C, Bi J, Zhu F,
Qu M and Yang Q: Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of
Holotrichia parallela Motschulsky extracts. Food Chem.
134:1885–1891. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Magalhães LM, Segundo MA, Reis S and Lima
JLFC: Methodological aspects about in vitro evaluation of
antioxidant properties. Anal Chim Acta. 613:1–19. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Barone E, Calabrese V and Mancuso C:
Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for
age-related diseases. Biogerontology. 10:97–108. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Aderibigbe AO, Emudianughe TS and Lawal
BA: Antihyperglycaemic effect of Mangifera indica in rat.
Phytother Res. 13:504–507. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Prakash O, Mishra A, Mishra A and Singh R:
Antimicrobial activity of Mangifera indica (mango) leaves
against bacterial and fungal pathogens. J Pharmacogn Phytochem.
3:45–49. 2011.
|
|
40
|
Meera CR, Sneha SS and Sunil CJ:
Antifungal activity of Mangifera indica leaf extracts
against Fusarium species. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 10:100–106.
2019.
|
|
41
|
Adeyinka OA, Bankole IAS and John R: GC-MS
bioprospecting of phytochemicals in the ethanolic extract of fresh
Mangifera indica leaves. J Chem Soc Nigeria.
47(798)2022.
|
|
42
|
Amaechi D, Ekpe IP, Yisa BN and Adamgbe
TF: Phytochemical profiling (GC-MS) of the leaf extract of
Mangifera indica and its hypolipidemic effect on serum lipid
profile in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Asian Sci
Bull. 2:17–23. 2024.
|
|
43
|
Sharma A, Gaur V, Sharma R and Kumar N:
Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of Mangifera
indica bark extracts. J Med Plant Res. 12:154–162. 2018.
|
|
44
|
Singh R, Gupta A and Kumar A: GC-MS
analysis of Mangifera indica bark extracts for
anti-inflammatory compounds. Phytomedicine. 21:367–374. 2017.
|
|
45
|
Vaou N, Stavropoulou E, Voidarou CC,
Tsakris Z, Rozos G, Tsigalou C and Bezirtzoglou E: Interactions
between medical plant-derived bioactive compounds: Focus on
antimicrobial combination effects. Antibiotics (Basel).
11(1014)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ngo DH, Ngo DN, Vo TTN and Vo TS:
Mechanism of action of Mangifera indica leaves for
anti-diabetic activity. Sci Pharm. 87(13)2019.
|